Auricular flutter
Description of atrial flutter
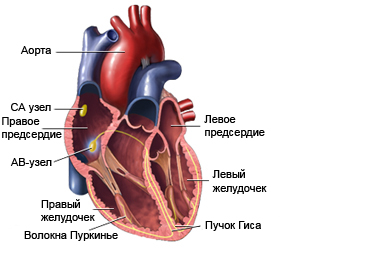
The heart has four chambers: two upper (predserdiya) and the two lower chambers (želudočki). Electrical signals regulate the heart beat, and help the atria and ventricles work together in the same rhythm. Blood from the Atria to the ventricles is pushed, and then from the heart spreads through the rest of the body.
Atrial fibrillation is a type of abnormally fast heartbeat (Arrhythmia) in the upper Chambers (predserdiyah) hearts. These quick hitting impede blood from the Atria to the ventricles. As a result, the ventricles serves less blood to organs of the body.
Atrial flutter can be acute or chronic. With proper treatment of atrial flutter is usually not life-threatening. Nonetheless, This may increase the risk of developing blood clots and stroke.
Causes of atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation may be caused by the following::
- Heart disease;
- Heart surgery – atrial fibrillation is the most common in the first few weeks after open-heart surgery;
- Hospitals in other parts of the body, especially in light, that affects the heart;
- Consumption of such substances, as caffeine, alcohol, diet pills or certain medicines, that affect the electrical impulses of the heart;
- Stress and anxiety.
Risk factors for atrial fibrillation
Factors, that increase the likelihood of atrial fibrillation:
- Heart disease;
- Heart surgery;
- History of high blood pressure (hypertension);
- Abnormalities of the heart or heart valves (eg, hypertrophy, mitral valve prolapse);
- Overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism);
- The history of the development of chronic lung disease (eg, эmfizema, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease);
- High levels of stress or worries;
- Caffeine, alcohol, diet pills, some medicines (eg, medicines for colds).
Older people are more prone to trepetaniû flutter.
Symptoms of atrial fibrillation
These symptoms may be caused by other serious diseases. When they occur, seek medical advice.
Atrial flutter is not always leads to symptoms. Nonetheless, symptoms, If they are present, They include:
- “Atrial” or tremoropodobnye feeling in the chest;
- Heartbeat (heart palpitations or chest knocking feeling);
- Pressure or discomfort in the chest;
- Breathlessness;
- Alarm;
- Dizziness or fainting.
Diagnosis of atrial fibrillation
The doctor asks about the symptoms, and medical history, and performs a physical exam. Depending on the condition of the patient, the doctor may also recommend a visit to the cardiologist. Tests may include the following:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) – test, that records heart activity by measuring electrical current through the heart muscle;
- Holter – wearing a portable heart monitor, which records heart rhythms during 24-72 hours;
- Echocardiogram – test, which uses high frequency sounds waves (ultrasound), to examine the size, shape and motion of the heart;
- Electrophysiological study – test, in which catheters threaded through a vein in the groin or neck to the heart and detect the activity of certain parts of the. This test can determine the exact source of an abnormal heart rhythm. The area of the heart, responsible for the abnormal rhythm can also be examined.
Treatment of atrial fibrillation
The goal of treatment of atrial flutter is slowing down electrical impulses, that are sent from the Atria (the top of the heart), in ventricles (the bottom of the heart), restore normal rhythm, and prevent future episodes of the disorder. Treatment options include the following:
Medication
Medications can be taken, to slow down heart palpitations and reduced atrial flutter. These drugs may include:
- Beta Blockers (eg, metoprolol);
- Digoxin;
- Adenosine;
- Blockers calcium channel blockers (eg, diltiazem, verapamil).
Antiarrhythmic funds may be used to bring the rhythm back to normal, and help maintain a normal heart rhythm. Some drugs in this group include:
- Sotalol;
- Propafenone;
- Flekainid;
- Amiodarone;
- Ibutilide;
- Ibutilid.
Kardioversija (defibrillation)
External Defibrillator connects to chest, and uses shock electric impulse to normalize the heart rhythm.
Ablation
For patients with recurrent atrial fibrillation, that cannot be controlled with medication, ablation can be performed. Using a catheter, the area of the heart, of which are generated by abnormal electrical rhythms, can be destroyed. This could lead to cure atrial fibrillation.
Blood thinners
When atrial flutter is irregular, blood thinners (warfarin) are used to prevent blood clots, that can cause atrial or other serious complications.
Prevention of atrial fibrillation
To reduce the risk of atrial fibrillation, you must perform the following actions:
- To reduce or stop drinking caffeine, stimulants, alcohol, Nicotine, certain medications;
- Heal the heart or lung disease, causing atrial flutter;
- Reduce the level of stress and anxiety;
- Consult with your doctor, before taking any new medicines.
