Gallstones – Cholelithiasis
Description of gallstones
Cholelithiasis – formation of gallstones. The gallbladder is located near the liver and the stomach. Most gallstones are composed of cholesterol. The rest are made up of bilirubin – disintegrated pigment hemoglobin.
Zhelchnыe colic – pain, arising after getting stuck in the bile duct stone – tube, at which bile enters the small intestine. Sometimes a stone in the bile duct causes cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) or cholangitis – inflammation of the bile ducts, caused by a gallstone or a bacterial infection.
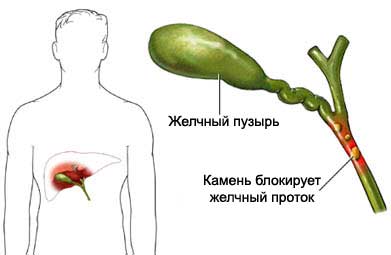
Causes of gallstones
The gallbladder bile This fluid is produced in the liver and used for fat digestion to the small intestine. Bile contains cholesterol, water, bilirubin and bile salts.
Gallstones can form under the following disorders:
- Excessive absorption of bile salts into the bile;
- Too much water absorption of bile;
- Too much cholesterol in the bile;
- Mucositis gallbladder.
Risk factors for gallstone disease
Factors, which increase the likelihood of gallstones:
- Age: senior 60 years;
- Paul:
- Females from 20-60 years;
- Women with high estrogen levels associated with pregnancy, use of oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy using;
- Obesity;
- Using drugs to lower cholesterol;
- Diabetes;
- A diet rapid weight loss;
- The presence of stones in the gallbladder before;
- Diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts;
- Blood diseases, including serpovidnokletochnaya anemia.
Symptoms of gallstones
For many people, the symptoms of gallstones does not appear.
In other cases, gallstones can cause pain in the upper abdomen. The pain starts suddenly, often after a fatty meal. The pain is very strong and can last for 30 minutes or a few hours.
Other symptoms include:
- Recurring pain on the right, below the ribcage;
- Abdominal distention, nausea and vomiting;
- Belching, gas and indigestion.
Consult your doctor, If the following symptoms, :
- Abdominal pain;
- Sweating;
- Chills;
- Low-grade fever;
- Jaundice (yellowish color of the skin and whites of the eyes);
- Clay-colored stool.
Diagnosis of gallstones
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical examination.
Tests may include:
- X-ray of the abdomen – analysis, which uses X-rays, to take a picture of structures in the body. About 15% gallstones can be detected with a simple X-ray;
- Ultrasound – analysis, which uses sound waves, to find gallstones;
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRHP) – accurate and non-invasive method of examination of the pancreas and gall bladder;
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERKhP) – analysis, which uses a combination of endoscopy (Use of a flexible tube with a camera, to examine the digestive system) and X-ray;
- Holestsintigrafiya – X-ray, which shows the movement of the gallbladder and any blockage of the cystic duct, through which bile flows to the bile duct;
- Blood tests – may be used, to detect infection, jaundice, pancreatitis or obstruction (obstruction).
Treatment of gallstones
The doctor will determine the best method of treatment, which may include:
Surgical treatment of gallstones
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy – removal of the gallbladder through several small incisions in the abdomen. To control the operation to remove gall bladder, in one of the sections is administered thin tube with a camera and light source. To remove the gall bladder through the other incisions used miniature surgical instruments;
- Open cholecystectomy – removal of the gallbladder through a large incision in the abdomen. It's necessary, if there is an infection of the abdominal cavity, and formed a lot of scar tissue.
Medications in cholelithiasis
Your doctor may prescribe medication, allowing to dissolve small stones. Maybe, I will have to take medication for a few months or even years.
Other treatments for gallstones
Procedure, which can be used to treat gallstones called endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERKhPG). ERCP uses a combination of endoscopy and x-rays to detect and remove the stones before or during gallbladder surgery.
Prevention of gallstones
To reduce the probability of formation of gallstones:
- Maintain a healthy weight;
- Avoid diets rapid weight loss;
- Exercise regularly;
- Eat foods low in saturated fat;
- Eat plenty of fruits, vegetables and whole grain foods (Cereals).
