Hematuria in adults – Blood in the urine
Description hematuria
Blood in the urine is called hematuria. Usually, Urine contains blood.
There are two kinds of hematuria:
- Microscopic hematuria – Urine contains a very small amount blood. It can not be seen with the naked eye;
- Makrogematuriâ – urine is red or the color of tea.
Causes of hematuria
In some cases, the cause of hematuria can not be found. Some of the most common causes include:
- Injuries to the abdomen, clean, internal organs and urinary tract;
- Vigorous movement;
- Urinary tract infection or kidney problems;
- Prostate Cancer, renal or Bladder;
- Kidney disease;
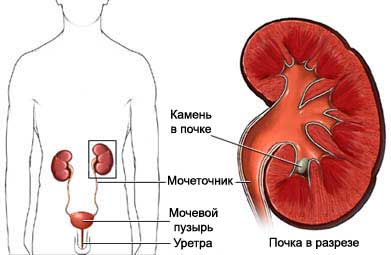
- Stones in the kidneys;
- Blood clotting (eg, hemophilia);
- Certain congenital diseases (eg, multicystic kidney disease);
- Radiation therapy pelvic area (for treating cancer);
- Some medications.
Risk Factors hematuria
Risk factors include:
- Smoking;
- Medication (eg, some antibiotics or painkillers);
- Recent upper respiratory tract infection;
- A family history of kidney disease.
The symptoms of hematuria
In some cases, but blood, may not be additional symptoms.
But, If you have an underlying condition, you may also have other symptoms. For Example, Kidney stones may lead to the presence of blood in urine, as well as the pain in his side, abdomen or groin.
When to see a doctor?
If you see blood in the urine, you need to see a doctor.
Diagnosis of haematuria
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical examination. You can be a doctor napravlenyk, who specializes in kidney disease (nephrologist) or urinary system (urologist).
Tests may include:
- Analysis of urine, to confirm the presence of blood and protein found, bacteria, or cancer cells in urine;
- Blood tests, to check kidney function and to identify disorders, causing hematuria;
- Roentgen – test, which uses X-rays, to take pictures of structures inside the body;
- US – examination, which uses sound waves to create an image on the monitor of the kidneys and urinary tract;
- CT scan – type of X-ray, and that uses a computer to produce images of the kidneys and urinary tract;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRT) – test, which uses powerful magnets and radio waves to take pictures of the kidneys and urinary tract;
- Cystoscopy – through the urethra into the bladder inserted a thin tube, allowing you to view it from the inside.
Treatment for hematuria
Treatment will depend on the causes of hematuria. Some cases do not require treatment (eg, hematuria, caused by exercise), either tested alone (eg, the passage of kidney stones). More needs to be treated with medication (in the treatment of urinary tract infections used antibiotics) or surgery (removal of the bladder or treatment for prostate cancer).
Preventing the child hematuria
Treatment of the underlying disease, which causes hematuria, can help prevent it from occurring.
