Treatment of cuts and lacerations – The healing of lacerations
Description laceration
Laceration – early, which occurs, when the skin, cloth, and / or muscle torn or cut. The wounds can be deep or superficial, long or short, wide or narrow. Treatment lacerations – cleaning, preparation and wound closure.
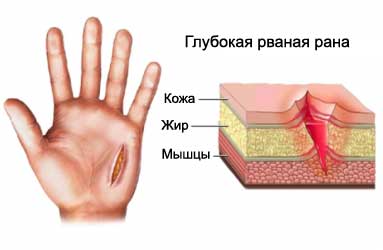
The reasons for the treatment of a laceration
Minor wounds and cuts (fine, Small, not bleeding, and clean) do not require medical attention. It is enough to handle the wound with antibiotic and bandage. Some need to see a doctor. The reasons are:
- Muscle injury, tendons, bones;
- The wound is visible dirt and foreign objects, remaining after washing and processing;
- Foreign body sensation in the back, even if the examination can not see anything;
- The risk of developing tetanus (eg, deep, laceration, burn, entering the wound faeces, dirt or saliva);
- Develop symptoms of tetanus symptoms through 3-21 days after injury: spasm or stiffness of the jaw muscles, Neck, life, or in an area near the wound;
- Bleeding, continued after pressing the wound within 10-15 minutes;
- The edges of the wound torn or uneven;
- Ran over 2 cm, It is located in the joint and / or around (knee, wrist, ankle);
- The edges of the wound broke and can not be pushed together;
- The wound is located in the region of application of high load (joints, hands, legs, breast);
- To reduce the risk of scarring.
Possible complications of treatment laceration
If you plan to treatment laceration, the doctor will review a list of possible complications, which may include:
- Infection;
- Bleeding;
- Noticeable scars;
- Poor wound healing;
- An allergic reaction to the anesthesia.
Anesthesia
The type of anesthetic depends on the type of wound, eg:
- Local anesthesia – Only certain anaesthetises, usually a small area. It is used as an injection, used for small lacerations;
- General anesthesia – blocks pain and plunges the patient in a State of sleep. It is used for severe lacerations.
In some cases, treatment of wounds and treatment is carried out without anesthesia.
Description of the procedure for treating a laceration
Preparations wounds:
- Cleaning:
- Hair, that will prevent access and wound healing are removed;
- The wound was washed with sterile water, which will wash away dirt and debris;
- They may also be used or antiseptic soap, if the wound is deep and dirty;
- Preparing wounds:
- Ragged edges can be cut. This will reduce the likelihood of scarring;
- Damaged or dead tissue will be removed, to prevent infection;
- Closing wounds:
- The procedure is performed after the cleaning and disinfection of wounds;
- The doctor selects one of several methods of wound closure:
- Skin glue Dermabond;
- Special plaster, eg Steristrips;
- Seam;
- Surgical staples.
Dermabond – Derma Bond
Dermabond – special glue, that allows the wound edges together. Dermabond is used for treatment of wounds on the face, hands, legs and trunk. It can also be used for smaller lacerations, than 1-3 cm.
Dermabond does not apply to lips, lacerations around joints, deep lacerations, and lacerations to the hands and feet. The doctor brings together the wound edges. He then applied a thin layer of glue. When applying the adhesive can feel the heat. Dermabond applied in three layers. The wound is fixed in a stationary position within 60 seconds. The doctor may put a bandage on the wound. In some cases, require additional suturing.
Note: glue acts as a protective coating. It is not applied directly to the wound or between its edges. Never attempt to apply the Dermabond home. Contact glue into wounds may prevent proper healing.
Plaster Steristrips
This adhesive tape used for small lacerations, that:
- Clean;
- Have relatively straight edges;
- The edges can be easily closed;
The doctor brings together the wound edges, then superimposed over the strip of adhesive.
Stitches
Sutures are used to treat deep, bleeding wounds, that have jagged edges, or damage to muscle or adipose tissue. The wound area treated with iodine, then can be applied surgical protective film. This will maintain the sterility.
If the wound is deep and there is muscle injury, It may be needed for their operation crosslinking. This will restore the muscles and tissues. Stitches, used under the skin, absorbed by the body. They do not need to be removed.
If the wound is not deep, or the suturing under the skin is finished, edges of the wound sutured. How tolyko wound sutured, area operation were treated with brine. It can be used as antiseptic ointment. The seam can be bandage or elastic bandage.
Staples
Staples are best suited for the scalp, Neck, hands, Foot, torso and buttocks. The skin around wounds treated with iodine. The edges of the wound are connected together and aligned. Along wounds placed staples.
The doctor uses a saline solution, to clear the area around the wound, and then treats it with an antibiotic ointment. It is recommended to apply on top of the treated wound transparent film dressing, eg Tegaderm, or ordinary gauze bandage. The bandage will be used to protect wounds.
How long will the treatment of the wound?
It depends on the type of laceration. The procedure can take anywhere from 15 minutes to an hour or more.
Will it hurt?
Soreness is also dependent on the type of wound. Severe lacerations will be very painful. The decision to accept the application of anesthesia doctor.
Wound care
In the hospital
After the procedure, the staff may provide the following assistance:
- Provides painkillers and antibiotics;
- The analysis of blood. This is done mostly after a sting or dirt in the wound;
- We introduce the vaccine against tetanus.
Home Care
When you return home, follow these steps:, to ensure the normal recovery:
- Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions, such as:
- Avoid strenuous activity;
- Take antibiotics and pain relievers to destination;
- We need to ask your doctor about, when it is safe to shower, bathe, or to expose the surgical site to water:
- If you want to keep the wound dry, wrap it with a plastic bag, taking a shower;
- After a shower or bath, Wipe dry with a wound, not rubbing it. Besides, not necessary to use hydrogen peroxide or iodine. This will lead to tissue damage and slow healing.
Removing material, closing a wound depends on the type of:
- Dermabond behind himself through 5-10 days;
- Steristrips usually,removed by 5-10 days;
- The stitches will be removed through 5-14 days;
- Staples are removed through 5-10 days.
Note: Do not attempt to remove material, wound closure. Removing it yourself can lead to infection, Scarring, or open wounds.
After healing of lacerations may remain scars. The degree of scarring depends on the following:
- Predisposition to scarring (keloids);
- Location, the type and size of the wound;
- Skill doctor.
Poor treatment of wounds, scratch, infection can lead to poor wound. If there is a noticeable scar, to reduce the appearance of scars can be used plastic surgery.
Contact your doctor after treatment laceration
After returning home, you need to see a doctor, If the following symptoms:
- Wound reopens;
- Redness, heat, edema, separation or excessive bleeding at the wound site;
- Signs of infection, including fever, chills, or red stripes, appeared on the hands or feet;
- Any other business.
