Debridement, infection, and scalding
Description treatment of wounds
Debridement is the removal of unhealthy tissue from a wound to promote healing. This can be done by surgical, chemical, mechanical or autolytic (using their own processes in the body of the patient) methods for removing tissue.
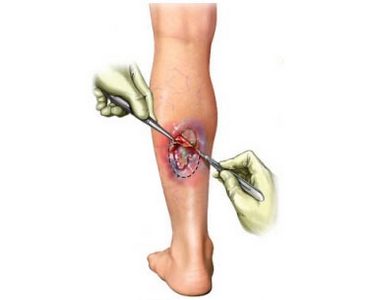
The reasons for the treatment of wounds
Surgical wound treatment is used to remove dead and contaminated material from a wound, to aid in recovery. This procedure is most often done for the following reasons:
- To remove tissue, infected with bacteria, foreign bodies, dead cells;
- To create a neat wound edge to decrease scarring;
- To help in the healing of very severe burns or pressure sores;
- To get a sample of tissue for testing and diagnosis.
Possible complications of surgical treatment of wounds
Complications are rare, but that does not mean the absolute absence of risk. If you plan to perform a debridement, the doctor will review the possible complications, which may include:
- Pain
- Bleeding;
- Infection;
- Delayed healing;
- Removal of healthy tissue during mechanical debridement;
Factors, that may increase the risk of complications include:
- Infection;
- Pre-existing diseases;
- Smoking;
- Diabetes;
- Use of steroids or other immunosuppressive drugs;
- Poor diet;
- Poor blood circulation;
- Immune disorders.
How is the surgical treatment of wounds
Preparation for the procedure
Doctor, probably, perform these steps::
- A physical exam;
- It measures the size of the wound;
- Anesthetize the wound before dressing changes (for non-surgical procedures);
- It will be necessary to organize a trip to the procedure and return to the hospital.
If the procedure is performed under general anesthesia, there is nothing to eat or drink in the evening and the day of the procedure.
Anesthesia
Anesthesia can be used at strong bedsores or other serious injuries.
Local anesthesia numb the treatment area. General anesthesia is able to support the patient during the entire procedure.
Procedure surgical treatment of wounds
The following four methods are often used in combination:
Surgical treatment of wounds
Surgical treatment is made with a scalpel, tweezers, scissors and other tools. It is used, if the wound is large, It has deep tissue damage, or if the wound is especially painful.
It can also be used, If cleaning the wound is urgent. The skin around the wound is cleaned and disinfected. Rana will be investigated, to determine its depth and find foreign objects.
The doctor cuts off the dead tissue. The wound will be washed, to remove dirt. In some cases, it may be carried out extra skin grafts. Sometimes, removal of all contaminated and damaged tissue can be the most effective treatment.
Chemical debridement
The wounds are treated with a special compound (It depends on the nature of the wound). Enzymes dissolve the dead tissue in the wound.
Mechanical debridement
Mechanical debridement could include various methods for the removal of dead or infected tissue. This method can include the use of whirlpool, syringes and catheters, or wet or dry dressings. When applying bandages some of the dead tissue sticks to it, and is removed after the removal of.
Autolytic debridement
In applying this method is used debridement using bandages, treated with the composition, which helps the body naturally clean the wound. This type of treatment is often used to treat pressure sores.
Autolytic method takes more time, than other methods. It is not used for the treatment of infected wounds, or wounds, requiring emergency intervention. This method is good, If the body can not tolerate other, more stringent treatments.
Immediately after treatment
Samples of the removed tissue may be sent to a lab for examination.
How long will debridement?
The duration of treatment depends on the type of debridement. Surgical treatment is the fastest way. Nonsurgical debridement may take 2-6 weeks or longer.
Debridement – Will it hurt?
During debridement, general anesthesia prevents pain during the procedure. When local anesthetic or sedative reception, Some patients feel uncomfortable.
Often the wound hurts the patient in the recovery period after the procedure. They can be given painkillers, to ease the pain.
Machining and chemical sanitation often hurt. Analgesics in this case can be used prior to treatment, to help ease the pain.
The average hospital stay
Depending on the cause debridement, You can go home the day of the procedure. If the patient is already in the hospital,, this procedure must not extend the stay.
Postoperative care
It may take many weeks, the wound healed. Proper wound care can help speed up recovery.
- Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions. If there is uncertainty about the correct treatment, you need to discuss this with the doctor;
- It is necessary to contain the wound clean and dry;
- We need to ask your doctor about, when it is safe to shower, bathe, or taking a bath;
- It is necessary to regularly take prescribed medication, without stopping reception, even if the wound starts to look better.
