Bedsores
Description of bedsores
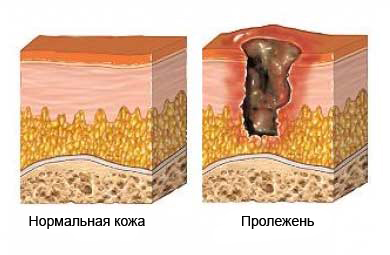
Bedsores – defeat, that develops on the skin and surrounding tissues due to the strong pressure is usually in the region of bone. The skin and tissues needed blood supply, oxygen and nourishing substances. When tissues are compressed for an extended period – from several hours to several days, blood supply may stop, which leads to the development of an ulcer.
Causes of bedsores
Pressure ulcers result from prolonged lying or sitting. Prolonged pressure stops blood flow to tissues, which are compressed between the bony areas and the mattress, chair, or other object. Without oxygen and nutrients, tissue begins to die off.
Several factors contribute to the development of pressure ulcers:
- Pressure – under pressure, ulcers can result from the inability to change position. People with normal mobility can change position automatically, without hesitation.
- Rubbing against bedding can damage small blood vessels, which supply skin tissues;
- Poor diet;
- Moisture – bedsores can occur due to perspiration, temperature increase (fever) or discharge of urine or feces;
- Obesity – being overweight increases pressure on the skin around bones and joints.
Risk factors
Factors, increasing the likelihood of pressure ulcers:
- Stillness, being in a bed or chair;
- Loss of sensation;
- Poor diet;
- Urinary incontinence or the flow of urine or feces;
- Advanced age;
- Chronic or complex medical problems, such as:
- Anemia;
- Infection;
- Poor blood circulation;
- Neuropathy;
- Imbecility;
- Cancer;
- Diabetes;
- Stroke;
- Spinal cord injury or paralysis;
- Bone fracture;
- Swelling or fluid retention;
- Dry skin;
- Fever.
Symptoms of bedsores
Pressure ulcers symptoms may include:
- Feeling of numbness or skin tissue;
- Local redness, heat, tenderness or swelling;
- Reddish or purplish skin color, often in the bone area;
- Pain or itching of the skin;
- Blisters, skin ulcers.
If redness remains after half an hour after, how the pressure was stopped, skin, likely to die off. Blisters and small ulcers may develop on the reddened area., sludge which can ooze liquid. The wound may deepen and spread through fat and muscle to the bone. The pressure sore area can hurt a lot. The wound can become infected, blush, swell, have an unpleasant odor, suppuration. If left untreated, pressure ulcer infection can progress to gangrene., blood poisoning, or infection of the bone underneath.
Diagnosis of pressure ulcers
The doctor asks about the symptoms and medical history, and performs a physical exam. He also examines the ulcer, paying attention to the location, form, size, depth, and any depressions or cavities.
Tests may include:
- Wound culture – taking a sample of material from a sore spot, to check for bacteria;
- Blood tests, to check for infection and nutritional status;
- X-rays or bone scans, if a bone infection is suspected.
Treatment of pressure ulcers
Treatment aimed at, to relieve pressure on the area, heal the wound, avoid complications and prevent future bedsores. In many cases, proper care will ensure that pressure sores disappear..
Treatment includes:
Correct body position
- Pressure on the wound should be avoided;
- Change of position at least every two hours, around the clock;
- Be sure to, that the bedding is clean and wrinkle-free;
- If necessary, you need to use a special mattress.
Hygiene
Cleanse contaminated skin after each bowel movement and urination, wash with soap and warm water. You also need to apply a special lotion in accordance with the doctor's recommendations..
Wound care
The nurse or doctor will teach the patient, how to properly care for wounds. Some measures include:
- Cleaning the wound, removal of dead tissue, as well as the use of a bandage;
- Can't put anything on the ulcer;
- Hands should be washed before and after treating wounds;
- It is necessary to clean the wound every time after changing the dressing.;
- Maybe, you need to take painkillers half an hour or an hour before dressing.
Proper nutrition
You need to eat a balanced diet. Your doctor may recommend vitamins, minerals, or supplements.
Surgery and other procedures
The doctor can surgically remove the dead tissue and do a skin graft., if necessary. In some situations, electrotherapy can be used, to stimulate blood flow and promote healing.
Prevention of pressure sores
Most pressure sores can be prevented. Techniques include:
- When changing position, the following must be done:
- Change your position in bed at least every two hours, or, in a wheelchair, at least every hour. If the patient is able to move independently, you need to change the position every 15 minutes;
- To prevent friction, the headboard cannot be raised anymore 30 °. You need to discuss the position of the bed with your doctor, when, if contraindicated due to the risk of breathing difficulties, suffocation, or aspiration;
- When in a supine position, it is not recommended to lie on the hip for a long time;
- Place a pillow between your knees;
- You need to talk to your doctor about using a special mattress, designed to reduce the risk of pressure ulcers;
- You need to use a special pillow when in a wheelchair;
- You need to wear special pads to protect the skin;
- When moving the patient, you need to lift, but pull it;
- You can try placing a soft pad under your body to reduce friction.;
- Keep your skin clean and dry;
- If there is incontinence, you need to use a protective skin cream, which will protect her from contact with urine or stool. The patient needs to be checked frequently, and not allowing feces or urine to remain for an extended period of time;
- Check your skin daily for pressure problems;
- Maintain good nutrition.
