Cesarean section
Description of Cesarean section
When a child is born through caesarean section incision in the abdomen of the mother. About 15%-40% all births in developed countries occur by caesarean section.
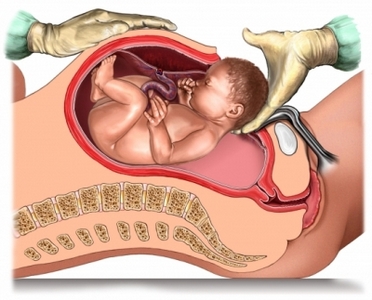
When Caesarean section is performed?
Cesarean section may be necessary in the following situations:
- Big kid;
- The child's head is incorrect;
- Mother disease (eg, diabetes, high blood pressure, Active herpes infection, HIV);
- The placenta blocks the birth canal;
- The lack of progression of parturition – childbirth slows or stops before, a child is born;
- Health problems the child during childbirth;
- If a previous child was born by caesarean section, It is best to, that subsequent children born by caesarean section;
- Abnormalities and fetal problems, who were diagnosed during pregnancy.
Possible complications during caesarean section
Cesarean section is a surgical operation, Therefore, it has risks. The estimated risk of death of a woman after caesarean section is less than one in 2500. The risk of death after vaginal births is less than one in 10000. Other risks include:
- Infection of the uterus or nearby organs of small pelvis, such as bladder and kidney;
- Bleeding, Sometimes the average loss is about twice as much for caesarean section, than that associated with vaginal delivery;
- Reduced bowel function. Sometimes the bowel slows down for several days after surgery, resulting in bloating and discomfort;
- Damage to organs in the abdominal cavity;
- A longer hospital stay and recovery time, that generally is 4-5 days in the hospital after cesarean section, and 1-3 days for vaginal births;
- Reaction to anesthesia. Maternal health can be endangered by the unexpected reaction to anesthesia or other medicines;
- The need for additional operations, These may include hysterectomies, bladder or repeated Caesarean section for future pregnancy.
Factors, that may increase the risk of complications:
- Smoking.
Cesarean section also carries risks for children, especially those, who were born prematurely. Death risk for premature babies, born by caesarean section is 54 from 10000, While the risk of death for infants, born vaginally – 14 from 10000.
How does caesarean section?
Preparation for the procedure
Caesarean section is often unplanned operation. If a c-section is planned in advance, It is recommended that you do not eat or drink anything after midnight before the procedure.
Anesthesia
At birth by caesarean section uses the following types of anesthesia:
- General anesthesia – during labor patient will sleep;
- Regional anesthesia (eg, epidural or spinal) – some areas of the body will obezboleny, but the patient will be awake.
Many women prefer regional anesthesia, so that they can stay awake, and see your child.
Description of the cesarean section procedure
The doctor makes an incision in the skin of the abdomen and uterus. There are two types of abdominal incisions: vertical (up and down) or horizontal (from side to side). There are also three different types of incisions in the uterus:
- A low transverse incision – the most common type, usually bleeds less, builds stronger scars and represents the lowest risk of bursting during future childbirth;
- Classic cut (high vertical incision), associated with a high risk of bleeding and future uterine rupture, is only used in emergency situations;
- Low vertical incision – used, If the child is in an unnatural situation, or if the need arises to perform classic cut.
After, like a baby and the placenta will be extracted, the uterus will be sewn stitches, which subsequently dissolved by themselves. To close the stomach will be used or parentheses.
Immediately after cesarean section
The child will be examined. Depending on the status of women in childbirth and the child is decided, can I immediately leave a newborn near mother.
How long does it take for cesarean section?
Duration of treatment 45-60 minutes.
Cesarean section – Will it hurt?
Anesthesia prevents pain during surgery. The mother may feel some pressure and twitching, When the uterus is opened and the baby and the placenta is removed. During recovery, the patient is given a pain reliever.
The average time of stay in the hospital after a caesarean
3-5 days.
Patient care after cesarean section
Care in a hospital
- Very soon after birth, the child may be placed on the mother's breast, for skin-to-skin contact;
- The mother may need help breastfeeding training. The correct position will protect the patient from a strong pressure on the incision;
- Maybe, you need to take medicine, that helps relieve nausea and pain;
- The mother may experience some cramping and pain of uterus;
- The intestines will be slower, than usual. Maybe, some time will need to have a light meal. Chewing gum can help speed up the process of normalization of the intestine;
- Sometimes you need to wear special compression stockings. They will help reduce the likelihood of blood clots in the legs;
- A woman may be asked to use an incentive spirometer and often cough. These steps will help normalize the patient breathing;
- You cannot lift anything heavier than a child;
- After the caesarean section will be moderate and severe vaginal bleeding. The patient will need to use absorbent pads.
Home care after cesarean section
Upon returning home, must adhere to the following rules, to ensure the normal recovery:
- Do not lift anything heavier than a child in the first weeks after surgery;
- You can't sit behind the wheel without the permission of the physician;
- We need to ask your doctor about, when it is safe to shower, bathe, or to expose the surgical site to water;
- For six weeks to stop having sex or any objects into the vagina, to validate a gynecological;
- It is recommended that breastfeeding;
- Need to consider joining a support group for young moms. There you can get support and explore new methods of education;
- Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions.
Usually after cesarean stitches heal quickly and completely. Cut type, used for caesarean section may play a role in decision-making about future births.
Communication with a physician after cesarean section
Upon returning home, you need to see a doctor, If the following symptoms:
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Excessive bleeding, redness, swelling, increased pain, or discharge from the incision;
- Nausea and / or vomiting, which do not disappear after taking the prescribed medicines, and persist for more than two days after discharge from the hospital;
- Pain, which does not pass after taking pain medication appointed;
- Swelling and/or pain in one or both legs;
- Cough, shortness of breath or chest pain;
- Joint pain, fatigue, constraint, rash or other symptoms;
- Dizziness and fainting;
- Heavy vaginal bleeding;
- Foul-smelling vaginal discharge.
