Fetal blood transfusions – Intrauterine blood transfusion – Intraperitoneal transfusion
Description of fetal blood transfusions
Blood transfusion is performed, when a child, which is still in the womb suffers from severe anemia. Anemia – a lack of red blood cells (erythrocyte). When blood tests show the child their number is too low, You need a blood transfusion. Transfusion is the introduction of the baby red blood cells from a donor.
There are two types of blood transfusion to the fetus:
- Intravascular transfusion (VSPK) It is through the mother's abdomen into the umbilical cord of the fetus – the most common procedure;
- Intraperitoneal transfusion (VBPK) It is through the mother's abdomen and uterus into the abdominal cavity of the fetus – usually, It is performed only if VSPK impossible to do because of the position of the baby and the umbilical cord.
Causes of fetal blood transfusions
Fetal blood transfusions are performed, if the child is in the womb suffers from severe anemia and could die without blood transfusions. Anemia can cause:
- Rh incompatibility – mother and baby have different blood type, maternal antibodies lysed (destroy) fetal blood cells;
- Parvovirus B19 – a viral infection in the mother.
Goal blood transfusion:
- Prevent or treat fetal hydrops before delivery. Dropsy causes severe anemia in the fetus, and he develops a heart failure. This leads to an accumulation of fluid in the skin, light, stomach or in the heart;
- To prevent premature births.
Possible complications of intrauterine blood transfusion
Possible complications for mother and fetus include:
- Urgently needed cesarean section after treatment;
- Premature rupture of membranes and / or premature birth
- Reaction “graft-versus-host disease” fetus (a rare disorder, wherein the red blood cells of the donor cells attack child);
- Bruises or stomach pain;
- Bleeding, spasms or fluid leakage from the vagina;
- Infection;
- Damage to the fetus;
- Introduction of too many blood;
- Fetal bleeding.
We need to discuss these risks with your doctor before the procedure.
How is intrauterine transfusion?
Preparation for the procedure
To make sure, that the fetus has severe anemia or fetal hydrops, the doctor may prescribe some tests:
- Amniocentesis – selected sample of amniotic fluid;
- Cordocentesis – selection of blood from the umbilical cord;
- Ultrasound examination – test, which uses sound waves to study the internal organs;
- If the fetus is found dropsy, Blood transfusion will be done right.
Before transfusion may be appointed:
- Introduction anesthetic;
- Intravenous injection of muscle relaxant.
Anesthesia
Local anesthesia, which numb a small area of the abdomen.
Procedure intrauterine blood transfusion
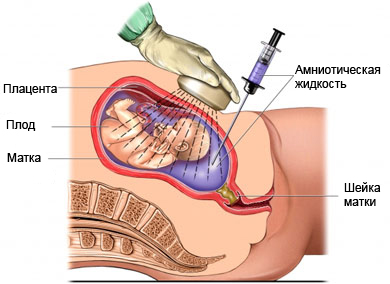
During the fruit VSPK be paralyzed for a short time. This is to ensure access to fetal blood vessels and reduce the harm to the fetus. During both VSPK and VBPK doctor will monitor the fetus by ultrasound. Ultrasound will be used to:
- Shows the position of the fetus;
- To guide the needle through the amniotic cavity to the vessel in the umbilical cord;
- Show fetal heart rate.
The doctor inserts a needle into the abdomen. Using ultrasound, make sure the doctor, The needle is inserted correctly. The needle will pass through the mother's abdomen and into the umbilical cord is inserted into the abdominal cavity or fetus. After that is done to the fetus blood transfusion.
Prior to the withdrawal of the needle the doctor will take a blood sample from the fetus. This is necessary to determine the fetal hematocrit. The doctor will find out, whether enough was one transfusion, or need to carry out the procedure again.
Transfusion, perhaps, will have to be repeated every 2-4 of the week, until the doctor decides, that the child is safe.
How long will the intrauterine transfusion?
Intravascular transfusion 10 ml of blood takes 1-2 minutes. Usually during one procedure is poured 30-200 ml of blood.
It hurt transfusion mother and child?
You will feel pain and cramping in place, where the doctor inserts a needle. If you will soon birth, or if the procedure takes a long time, the uterus will be sore.
The average hospital stay
This procedure is performed in a hospital. After the transfusion, you will be able to go home. If complications arise, perhaps, You will need to do a caesarean section.
Care after fetal blood transfusion
The doctor can provide:
- Antibiotics to prevent infection;
- Medication to prevent uterine or childbirth.
Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions.
When your baby is born, he just need to do a blood test. Your doctor will closely monitor the baby, to prevent:
- Anemia;
- Liver damage;
- Congestive heart failure;
- Respiratory failure;
- Other complications, if the child is born prematurely.
Communication with the doctor after the embryonic blood transfusion
After discharge from the hospital need to see a doctor, If the following symptoms:
- Signs of infection, including fever or chills;
- Redness, edema, increased pain, bleeding or discharge from the needle insertion site;
- You do not feel, the child moves as usual;
- The withdrawal of amniotic fluid (birth sign);
- Other signs of the onset of labor:
- Uterine contractions;
- Backache, which appears and disappears;
- Vaginal bleeding.
