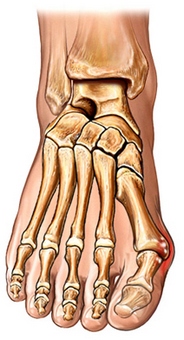
Bursectomy – Removal of bunions
What bursectomy?
Removal of bunions – operation, performed, to get rid of the deformation in the joint, that connects the big toe to the foot. This is done by removing excessive bone in the joint.
Reasons for bursectomy
Bunion – inflammation and increase joint of the big toe and the tissue around. In some cases, deformation is so hard, that the big toe begins to bend beyond the legs. The decision about the operation is taken in the following cases:
- Other attempts at therapy, such as anti-inflammatory agents, Physiotherapy, specially shaped shoes, or inserts, to reduce the pressure failed;
- The pain of a bunion interferes with walking;
- Deformation of feet walking difficult.
Possible complications of bursectomy
If you plan to carry out the removal of bunions, the doctor will consider the risk of possible complications, which may include:
- Tumor;
- Infection;
- Bleeding;
- Toe can be displaced or become too short;
- Bunion may recur.
Factors, that may increase the risk of complications include:
- Smoking and alcohol abuse;
- Diabetes;
- Poor diet;
- Poor health.
How is the removal of bunions?
Preparing for the removal of bunions
Doctor, probably, perform some or all of the following::
- Physical examination, especially the legs;
- X-ray foot;
- Check the blood flow in the leg.
Before the surgery, you may need:
- The patient may be asked to stop taking certain medicines a week before the procedure,:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (eg, aspirin);
- Blood thinners, such as clopidogrel (Plaviks) or warfarin (Coumadin);
- Organize a trip to the hospital and back after surgery;
- To organize home care after the procedure;
- On the eve of the evening before surgery you can have a light meal, You can not eat or drink anything after midnight;
- The patient may be asked to shower the morning before the procedure with a special antibacterial soap.
Anesthesia
Depending on the complexity of the operation, may be used:
- Local anesthesia – It will anesthetize the area of surgery;
- General anesthesia – during the operation, the patient will sleep.
Procedure remove bunions
There are several types of procedures for the removal of bunions.
Usually, Dr. cuts up about bunions. Excess amount of bone is removed medical saws. Depending on the degree of deformation of the doctor, perhaps, is to remove part of the bone toe. Bone thus formed, to toe is no longer bent to the outside.
To support formed bones and recovery may require a metal pin, screw or rod. These funds will help to keep the bones in place.
The incisions will be sewn stitches. In the area of operations bandage.
How long will the removal of bunions?
The duration of the operation of 30 minutes so 2 hours.
Will it hurt during bursectomy?
Anesthesia will prevent pain during the procedure. The pain may be felt during recovery. The doctor will give pain medicine, to reduce pain.
Average time spent in the hospital after bursectomy
0-1 day
Postoperative care
- The leg is bandaged. The patient, perhaps, it will be necessary to wear a special postoperative shoe for several weeks;
- Sometimes after surgery in the recovery period you need to use crutches or a walker;
- To reduce the swelling of the legs, it is necessary to apply ice. The ice should be wrapped, for example in towel, but not applied directly to the skin;
- After, as the leg has healed enough, perhaps, to do special exercises. They will help restore power, flexibility and endurance in the legs;
- It is necessary to discuss with your doctor the kind of shoe, which it is desired to use;
- If the pins were used, their, perhaps, You have to remove a few weeks after surgery;
- We need to ask your doctor about, when it is safe to shower, bathe, or taking a bath;
- Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions.
Removal of bunions may ultimately lead to an improvement of mobility and reduce pain finger. This can take up to eight weeks after surgery.
Contact your doctor after bursectomy
After discharge from the hospital need to see a doctor, If the following symptoms:
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Redness, edema, increased pain, bleeding, or any discharge from the incision;
- Cough, shortness of breath or chest pain;
- Pain, which does not pass after taking painkillers appointed;
- Nausea and / or vomiting, which do not disappear after taking the prescribed medicines, and persist for more than two days after discharge from the hospital;
- Swelling and pain in the calf or leg.
In the case of a serious and rapidly deteriorating health should immediately call an ambulance.