Chronic Bronchitis
Description of chronic bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis – long-term illness in the airways of the lung. Injury or irritation causes swelling of the airways and increases the production of mucus, making it difficult to the entry of air into the lungs and makes breathing difficult.
Chronic bronchitis is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
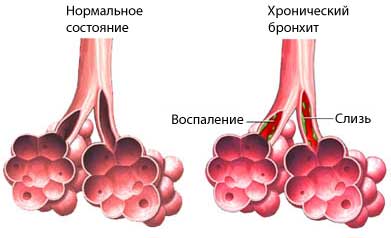
Causes of chronic bronchitis
The cause of chronic bronchitis is airway injury. The main causes of damage are:
- Cigarette smoking;
- Inhalation of toxins and other irritants;
- Genetic predisposition – It can make a person's lungs more susceptible to the effects of smoke or pollutants (including alpha-1-antitrypsin).
Risk factors for chronic bronchitis
Smoking is a major risk factor for chronic bronchitis. The more you smoke, and the longer you smoke, the greater the likelihood of chronic bronchitis. Frequent and long-term smoking also increases the likelihood of severe chronic bronchitis.
Factors, which can increase the likelihood of chronic bronchitis:
- Long-term exposure to chemicals, respirable dust and other substances;
- Long-term cigar smoking or smoking marijuana;
- Exposure to tobacco smoke;
- I have a family member with COPD;
- History of frequent childhood lung infections;
- Age: 40 and older;
- Prolonged asthma.
Symptoms of chronic bronchitis
Symptoms include:
- Cough;
- Increased mucus production;
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, especially after some physical exertion;
- Recurrent respiratory infections, which cause worsening of symptoms;
- Wheezing when breathing;
- Fatigue.
Diagnosis of chronic bronchitis
To diagnose chronic bronchitis, symptoms of cough with phlegm must be present for three or more months, at least two consecutive years, and they must not be caused by another disease. The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, a physical exam. Tests may include the following:
- Breathing tests, to check lung function;
- Test the number of arterial blood gases;
- Blood tests, to determine the composition of the blood and blood oxygen saturation;
- Chest X-ray – test, which uses X-rays, to take a picture of inside the chest;
- Chest CT – type of X-ray, which uses computer, to make pictures of organs inside the chest.
Treatment of chronic bronchitis
There are no drugs to treat chronic bronchitis, but there are treatments, which can reduce symptoms and improve lung function. The best way to reduce symptoms – smoking cessation.
Treatment of chronic bronchitis include:
Medication
Medications may include bronchodilators or steroids. They reduce the symptoms of chronic bronchitis, allowing:
- Open airway;
- Reduce inflammation;
- Cure lung infection (antibiotics).
Some drugs can be taken in the form of tablets or liquids. Other applicable inhalation, acting directly into the lungs.
Antibiotics are rarely prescribed to treat bronchitis. They may be needed to treat pulmonary infection, which developed because of bronchitis.
Vaccines
Influenza and pneumonia may worsen symptoms. Make pneumonia vaccine and Flu Shot. Influenza vaccine may also reduce the severity of the disease.
Oxygen
Oxygen therapy may be helpful, if the oxygen level in blood is too low. The procedure will help alleviate shortness of breath and feel better. Oxygen may only be needed for a while, or by means of a special device supplied permanently.
Exercises
Special exercises can strengthen chest muscles. This will help ease breathing.
Regular physical activity can reduce the load on the lungs. Follow your doctor's recommendations to maintain the level of activity and its limitations.
Methods of breath and cough
Special breathing techniques can help the lungs to breathe in more air. Effective methods of cough can also help remove mucus from the lungs. Ask the doctor, whether these techniques help you.
Lifestyle changes
The following steps can help manage symptoms and prevent exacerbations of chronic bronchitis:
- Monitor your physical activity;
- Learn relaxation techniques and other methods,, that will cope with stress;
- Seek emotional support from professionals, family and friends. Anxiety may increase the respiratory rate, making it more intense.
Prevention of chronic bronchitis
Methods, that reduce the likelihood of developing chronic bronchitis:
- If you smoke, try to quit;
- Avoid second-hand smoke;
- Avoid inhalation of contaminated air or irritants;
- Wear protective clothing when exposed to irritants or toxins at work.
