Protrusion of the fontanel in a child: what is this, causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
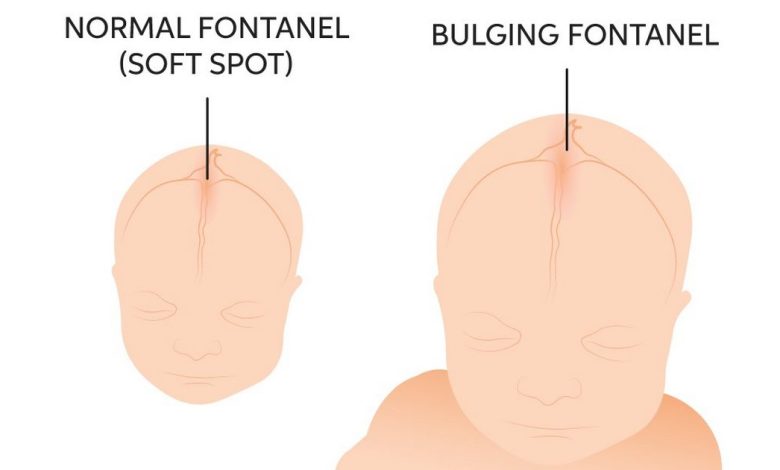
Fontanelles – bulging; Soft spot – bulging; Bulging fontanelles
Protrusion of the fontanel in a child: what you need to know
The fontanel is the soft spot on the baby's head., where the bones of the skull have not yet fused. In most cases, fontanelles are normal and harmless., but a bulging fontanel can be a sign of a serious health problem. In this article, we will discuss, what is bulging fontanelles, their reasons, symptoms, when to contact a healthcare professional, questions, that your doctor may ask, diagnostics, treatment, home treatment and prevention.
What is a convex fontanel?
A bulging fontanel is a condition, in which a soft spot on the child's head, also known as spring, protrudes abnormally. This can happen as a result of increased pressure inside the skull., because of what the fontanel protrudes outward.
Causes of bulging fontanelles
There are several reasons for bulging fontanelles, including:
- Increased intracranial pressure: it can be caused by various conditions, including cerebral edema, hydrocephalus and meningitis.
- Dehydration: if the child is dehydrated, his fontanel may bulge, because there is not enough fluid in his body to maintain normal pressure in the skull.
- Anemia: anemia can cause a protrusion of the fontanel in a child, because there is not enough oxygen in their blood to feed the brain.
- Overfeeding: overfeeding can lead to protrusion of the fontanel of the child, because his stomach is too full and puts pressure on his diaphragm, what, in turn, increases pressure inside the skull.
Symptoms of bulging fontanelles
The most common symptom of a bulging fontanel is a noticeable bulge in the soft spot on the baby's head.. Other symptoms may include:
- Irritability or fussiness. A child with a bulging fontanel may become more irritable or fussy due to increased intracranial pressure..
- Loss of appetite: a child with a bulging fontanel may lose their appetite due to discomfort or pain.
- Sleeping problems: a child with a bulging fontanel may have trouble sleeping due to increased pressure inside the skull.
- Vomiting: a child with a bulging fontanel may vomit due to increased pressure inside the skull.
When to contact a healthcare professional
If you suspect, that your child's fontanel bulges, you should contact your doctor immediately. In some cases, a bulging fontanel can be a sign of a serious health problem., therefore prompt medical attention is needed..
Questions, that your doctor may ask
When you take your child to the doctor with a suspected fontanel bulge, you may be asked the following questions:
- When did you first notice the bulging fontanel?
- Did your child have any other symptoms, such as nervousness or vomiting?
- Your child is drinking and urinating normally?
- Your baby is eating normally?
- Have you noticed any changes in fontanel size over time??
Diagnosis of bulging fontanelles
To diagnose a protrusion of the fontanel, the doctor will perform a physical examination of your child's head. He may also order imaging tests, such as ultrasound or computed tomography, to get a better view of the inside of your baby's head.
Treatment of protrusion of the fontanel
Treatment for a bulging fontanel will depend on the underlying cause..
- If the cause is increased intracranial pressure, your doctor may recommend medication to lower your blood pressure.
- If the cause is dehydration, your doctor may recommend increasing your child's fluid intake.
- If the cause is an increase in the size of the child's head, your doctor may recommend surgery to correct the problem.
Home treatment for protrusion of the fontanel
If your child has a bulging fontanel, important to keep a close eye on it.. Be sure to monitor his behavior for any changes. If you notice any changes in your child's behavior, such as increased irritability or lethargy, consult a physician immediately.
Prevention of protrusion of the fontanel
The best way to prevent a fontanel bulge is to provide your child with enough fluids.. Be sure to give your child plenty of fluids., such as breast milk or formula, during the day. It is also important to monitor your child's behavior for any changes.. If you notice any changes in your child's behavior, such as increased irritability or lethargy, consult a physician immediately.
Conclusion
The protrusion of the fontanel is a condition, in which the soft spots on the baby's head enlarge and bulge outward. This can be caused by various factors, such as increased intracranial pressure, dehydration or enlargement of the baby's head.
The most common symptom of a fontanelle protrusion is an enlarged and protruding soft spot on a child's head.. If you notice any symptoms of fontanelle protrusion, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Treatment for a bulging fontanel will depend on the underlying cause..
The best way to prevent a fontanel bulge is to make sure, that your child drinks water well, and monitor its behavior for any changes.
Used sources and literature
Goyal NK. The newborn infant. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Bloom NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 113.
Rosenberg GA. Brain edema and disorders of cerebrospinal fluid circulation. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff’s Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 88.
Somand DM, Meurer WJ. Central nervous system infections. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen’s Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 99.
