Elimination of atrial septal defect in children – open heart surgery
Description of the operation to eliminate atrial septal defect in children
Atrial septal defect – opening in the wall between the two upper chambers (right and left atrium) hearts. Operation open heart surgery can eliminate the hole by sewing or install the patch (salary) on him.
Reasons for the operation to eliminate atrial septal defect in children
If a child is born with a hole between the upper chambers of the heart, blood can flow back, the right side of the heart and the lungs. It causes the heart to work harder. Over time, this can cause damage to the blood vessels in the lungs and congestive heart failure. The operation is performed, to close the opening.
For most children, this gives good results opertsii.
Possible complications in eliminating atrial septal defect in children
Complications are rare, but no operation ensures no risk. Before, how to perform the operation, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Bleeding;
- Damage to the heart or lungs;
- Reaction to anesthesia (eg, dizziness, lowering blood pressure, breathlessness);
- Infection, including endocarditis (inflammation of the lining of the heart muscle);
- Heart attack;
- The formation of a blood clot – thrombus;
- Arrhythmia (abnormal heart rhythm);
Some factors, that may increase the risk of complications:
- Existing diseases (eg, poor kidney function);
- Low birth weight;
- Recent infection.
How is the elimination of atrial septal defect in children?
Preparing for Surgery
A doctor examines a child and can assign the following tests:
- Blood and urine tests;
- Echocardiogram – test, which uses sound waves to visualize functioning of the heart;
- Electrocardiogram (ECG ) – test, that records heart activity by measuring electrical current, passing through the heart muscle;
- Chest X-ray – test, which uses X-rays, to take a picture of structures inside the chest;
- Heart catheterization – of the heart through an artery using special equipment.
If a child needs to stop taking certain medications, the doctor will tell about it.
Anesthesia
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. During the operation, the patient is asleep.
Description surgery to remove atrial septal defect in a child
The doctor cuts the skin and chest. Chest cavity is opened. Then the heart connects to the machine extracorporeal circulation (AIK). He will take over the functions of the heart and lungs. The doctor stops the heart, to make the operation.
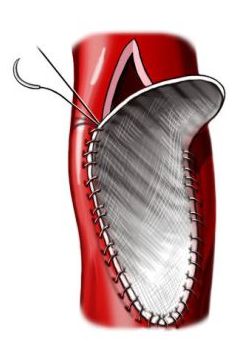
Pericardial sac around the heart will be open. A doctor may remove a small part of the bag and use it to close the opening. The right atrium will make the cut. If the hole is small, it will be closed by sutures. A large hole is closed patch, which is made from a portion of the pericardial sac or other material. As soon as the defect is eliminated, doctor sews up the incision. The heart is then started to work. Once it will function normally, AIC will be disabled. The doctor closes the chest cavity and sews the skin incision.
Immediately after surgery
A child is placed for the monitoring in the NICU (OBE) and is connected to the following systems:
- Heart Monitor;
- Breathing apparatus (until, until the baby is able to breathe on their own);
- Chest tube – for draining liquids, which accumulate in the breast;
- To measure blood pressure in the arm or leg is connected tonometer;
- Tube through the nose into the stomach – to drain the liquid and gas, which is collected in the stomach;
- Bladder catheter.
How long will the surgery?
2-4 o'clock
Will it hurt?
If pain or soreness during recovery will be appointed painkillers.
The average hospital stay
Typically, the duration of stay of 5-7 days. If complications arise, the doctor can extend the term of at the hospital.
Postoperative care
In the hospital
The hospital staff does the following:
- Carry out an analysis (blood, Urine, ECG, etc.);
- It gives painkillers;
- Gradually transfer the child to a normal diet.
Nursing homes
When the child returns home, you need to do the following:
- If prescribed by a doctor, the child is given antibiotics. This will help prevent endocarditis. Besides, as required are appointed painkillers;
- We need to keep the incision clean and dry;
- Gradually, the need to transfer the baby to the daily diet;
- We need to ask the doctor about, when you can take a shower, bathe, or to expose the surgical site to water. Typically, these procedures can be performed after ten days after the operation;
- A child needs a rest for a few days after the operation. It is not recommended at this time to play energetic games;
- We need to dress the baby in the free, comfortable clothes;
- If a child had surgery, to keep it, supporting his back and buttocks. Do not pull the child's hands or underarms;
After about six months, heart tissue grows completely.
It is necessary to go to the hospital in the following cases
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Increased perspiration;
- Redness, edema, strong pain, bleeding or discharge from the incision;
- Gapping;
- Nausea and / or vomiting;
- Increased pain;
- Problems with urination (eg, pain, burning, frequent urination, blood in urine) or inability to urinate;
- Cough, shortness of breath or chest pain;
- Rattling in the chest;
- Fatigue;
- Rash;
- Reluctance to eat and drink;
- Noisy breathing.
It is necessary to call an ambulance in the following cases
- Fast breathing or trouble breathing;
- Blue or gray skin color;
- The child does not wake up or does not respond to treatment.
