Cystocele and rectocele
Description cystocele and rectocele
Connective tissue separates the pelvic organs. Cloth, called fascia, is attached to nearby muscles. In a healthy state of the fascia and muscles support the urinary bubble, vagina and rectum. Defects in the fascia can lead to cystocele or rectocele.
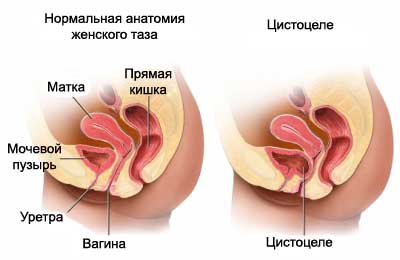
Cistocele – a defect in the fascia between the bladder and vagina. A portion of the bladder wall bulges into the vagina. There are three types of cystocele:
- View 1: mild form, bladder gets into the vagina only partially;
- View 2: moderate form, in which the bladder is lowered far enough, and may reach the vagina;
- View 3: most severe form, in which the bladder sags through the opening of the vagina.
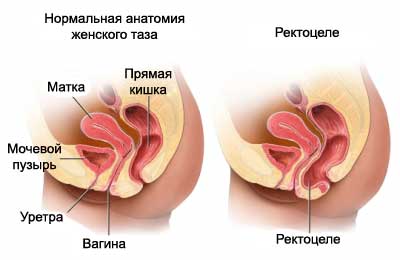
Rectocele – defect in the fascia between the rectum and vagina. In this part of the wall of the rectum bulges into the vagina.
The sooner treatment begins cystocele or rectocele, the better the result. If you suspect, that you have this disease, consult a doctor.
Causes of cystocele and rectocele
The wall between the vagina and bladder or rectum can be damaged if one or more of the following factors:
- Complex vaginal birth:
- Multiple births;
- Using forceps at birth;
- Perineal tears during childbirth;
- Episiotomy childbirth.
- The strain of lifting heavy objects;
- Chronic cough;
- Chronic constipation;
- The weakening of the muscles of the vagina, due to lack of estrogen after menopause.
Risk Factors cystocele and rectocele
If you have any of the risk factors, tell your doctor:
- Age: postmenopause;
- The presence of difficult vaginal births;
- Tension during defecation;
- Obesity;
- Smoking.
Symptoms of cystocele and rectocele
Many cases are mild and do not have symptoms.
In more serious cases, the symptoms of cystocele include:
- Leakage of urine when you laugh, cixanii, cough;
- Incomplete emptying of the bladder during urination;
- Pain or pressure in the pelvic region;
- Frequent bladder infections;
- Pain during sexual intercourse;
- Feeling of tissue, protruding from the vagina.
Symptoms of rectocele include:
- Pain or pressure in the vagina;
- Pain during sexual intercourse;
- Pain or pressure in the rectum;
- The complexity of the passage of stool;
- The need to put pressure on the vagina, to assist passage of stool;
- Feeling of incomplete stool passage;
- Feeling of tissue, protruding from the vagina.
These symptoms are not always associated with cystocele or rectocele. These symptoms may be caused by other, less or more serious diseases. If you have one of the symptoms, consult a doctor.
Diagnosis of cystocele and rectocele
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical examination. Tests for cystocele may include the following:
- Gynecological examination;
- Voiding cystourethrography – X-ray, performed during urination;
- Urine, to seek to find infection.
Tests for rectocele may include:
- Examination of the vagina and rectum;
- Roentgen, performed during a bowel movement.
Treatment of cystocele and rectocele
In mild cases of cystocele and rectocele requires no treatment. In more serious cases, treatment options include the following:
Changes in physical activity
- Your doctor may suggest that you avoid heavy lifting;
- Kegel exercises (contraction of the pelvic floor) can help strengthen the muscles around the vagina and bladder;
- For rectocele – diet, which improves the passage of stool, with the addition of liquids, and a stool softener if necessary.
Pessary
Pessary – device, which is inserted into the vagina and can provide support to the bladder and / or rectum in situ.
Zamestitelynaya therapy эstrogenami
Adding estrogen may help strengthen the walls of the vagina after menopause. It can be provided in the form of tablets, creams, or patch.
Surgery
For severe cases may be necessary surgery for cystocele or rectocele, for the return of the bladder or rectum in place.
Prevention cystocele and rectocele
To reduce the likelihood of cystocele and rectocele, proceed as follows:
- Avoid heavy work;
- Perform regular Kegel exercises;
- Treat constipation;
- Quit smoking;
- Maintain a healthy weight.
