Shoulder tendinopathy, biceps tendon injury: What's it, treatment, symptoms, diagnostics, prevention
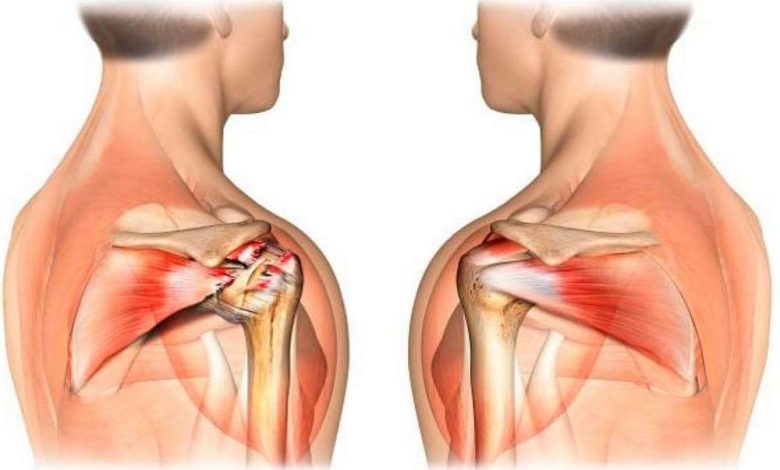
Description shoulder tendinopathy
Tendinopathy is called tendon injury. It can cause pain, swelling and limited range of motion. The types of tendinopathy may include:
- Tendinitis is an inflammation of the tendon. (Although the term is used quite often, in most cases it tendinopathy not associated with a significant inflammatory);
- Tendinosis is tiny tears in tendon tissue without significant inflammation..
The shoulder is a few tendons, including the tendons of the rotator cuff and biceps. They support the head of the humerus (upper arm bone) in the glenoid cavity of the blade. Treatment of tendinopathy and associated pain may take months.
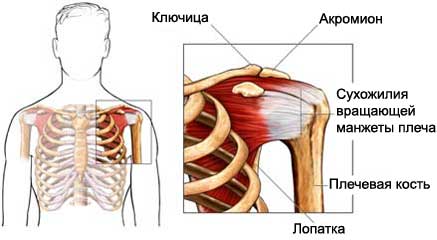
Causes of shoulder tendinopathy
Tendopatiya, usually, caused by excessive strain on the muscles and tendons. Over time, the load on the tendon causes structural changes in it.
The load on the shoulder tendons often arises:
- Repeated strong flick of the wrist;
- Repetitive throwing motion.
Tendinitis of the biceps tendon is associated with damage to the rotator cuff. Tendinopathy cuffs may also occur with age, due to wear.
Risk factors for shoulder tendinopathy
Factors, which increase the risk of shoulder tendinopathy:
- Age: 30 and older;
- Keeping your hands up position or performance of the throwing motion:
- Playing tennis or other sports Racket;
- Swimming;
- Baseball;
- Job (eg, erection work, cutting or working on the compression machine).
Symptoms of shoulder tendinopathy
Symptoms develop gradually, time, and pain slowly increases with the progression of the disorder.
These symptoms, except for shoulder tendinopathy can be caused by other diseases. Tell your doctor, if you have:
- Pain (Blunt pain) in the shoulder and upper arm;
- Pain at night, especially while sleeping on the affected side of the body;
- Pain when trying fastening zipper behind, or using back pocket;
- Pain when lifting arms up;
- Weakness in the shoulder, usually, because of the pain;
- Stiff shoulder with some loss of range of motion.
Diagnosis of shoulder tendinopathy
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical examination. He will check the sensitivity of the problem areas, range of motion and muscle strength.
If you have severe symptoms or to rule out other problems, your doctor may prescribe:
- Roentgen – examination, which uses X-rays, to make pictures of structures inside the body;
- MRT – examination, which uses magnetic waves, to make pictures of internal structures of the body;
- CT arthrography – such as X-rays, which uses computer, to take pictures of the joint after injection of radiopaque dye into a;
- The injection of local anesthetic into the bursa in rotator cuff;
- This may confirm the diagnosis, if the pain after the injection is reduced;
- Arthroscopy– after applying anesthesia longest, thin, fiber optic tube at the light source end is inserted through a small incision in the shoulder, to examine its structure;
- The procedure is typically used for suspected rupture in the rotator cuff.
Treatment of shoulder tendinopathy
Treatment includes:
Peace
Avoid actions, that cause shoulder pain.
Ice
To control pain and swelling:
- Apply ice for 20 minutes at a time.
- Use ice during the first 24-48 hours after injury or after exercise;
- Protect your skin by placing a towel between the ice and skin.
Heat
Heat may relieve pain and is often used before exercise:
- Do not use heat in acute pain or after serious injury;
- Consult a physician before using a heat source for the first time;
- Use within 15-20 minutes at a time;
- Protect your skin by placing a towel between the heat source and the skin.
Medication
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain (eg, aspirin or ibuprofen);
- Local anesthetics (crme, Patch), are applied to the skin;
- Steroid injections into the bursa of the rotator cuff to decrease inflammation;
- Injections of botulinum toxin.
Rehabilitation
- Physical therapy to strengthen muscles, which control the movement of the shoulder;
- Exercises to maintain normal range of motion;
- Exercises for specific muscles, which are used in sports or at work;
- Education preventing re-injury.
Operation
Depending on the injury may be subjected to various surgery on the rotator cuff:
- Artroskopicheskaya surgery;
- The open shoulder surgery.
Preventing shoulder tendinopathy
To protect against a shoulder injury:
- Do exercises to strengthen the muscles of the shoulder joint;
- Do not increase the duration and intensity of exercise more than 10% in Week;
- Avoid excessive voltage hands in a raised position;
- Do not ignore or try to work in the presence of severe pain in his shoulder.
