Hearing loss: what is this, causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
Hearing loss; Decreased hearing; Deafness; Loss of hearing; Conductive hearing loss; Sensorineural hearing loss; Presbycusis
Hearing loss is a common problem, that affects millions of people around the world. The disorder causes a decrease in the ability to hear sounds and can range from mild to severe.. Hearing loss can happen gradually over time or suddenly, and may affect one or both ears.
What is hearing loss?
Hearing loss, also known as hearing loss, represents a state, in which it is difficult for a person to hear sounds and understand speech. The disorder can range from mild to severe and may affect one or both ears.. Hearing loss can be caused by various factors., including aging, noise exposure, disease, genetics and trauma.
Causes of Hearing Loss
There are many causes of hearing loss, including:
- Age-related loss of hearing (presbyacusis): it is the most common cause of hearing loss in the elderly, usually caused by changes in the inner ear.
- Hearing loss, caused by noise. Prolonged exposure to loud sounds, such as music concerts, construction noise and sounds of firearms, can damage the hair cells of the inner ear and cause hearing loss.
- Disease: some diseases, such as meningitis, mumps and rubella, can cause hearing loss.
- Genetics: some types of hearing loss are inherited and run in families.
- Trauma: Head or ear injury can lead to hearing loss.
Hearing Loss Symptoms
Hearing loss symptoms can vary depending on the severity and type of hearing loss.. Common symptoms include:
- Difficulty hearing speech, especially in noisy environments
- The need to listen to sounds, conversation
- Turn up the volume on the TV or radio
- Ringing or buzzing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Difficulty hearing high pitched sounds
When to contact a healthcare professional
If any of the above symptoms appear, it is important to seek medical attention. Hearing tests can help determine the cause and severity of hearing loss.
Questions, that your doctor may ask
During the appointment, the doctor will ask questions, to help diagnose the cause of hearing loss, including:
- When did your hearing loss start??
- You have hearing loss in one or both ears?
- What specific sounds are you hard of hearing??
- Have you been exposed to loud noises recently??
- Do you have other symptoms, such as ringing in the ears or dizziness?
Diagnosis of hearing loss
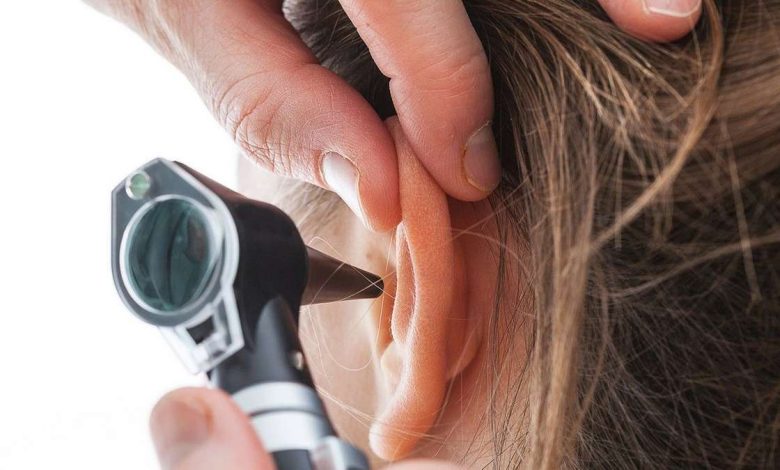
To diagnose hearing loss, the doctor will conduct a physical examination and use a series of tests. This may include an otoscopic examination, in which the ear is examined with an instrument, called an otoscope. It is used to look for signs of infection or structural damage..
Besides, the doctor may use audiometry, test, which measures the human hearing threshold in the frequency range. This test is used to measure the degree of hearing loss..
Hearing Loss Treatment
Hearing loss treatment varies depending on the cause and severity. In some cases, hearing loss is temporary and can be treated with antibiotics or other medications.. In other cases, the hearing loss is permanent and may require the use of hearing aids., cochlear implants or other devices.
- Hearing aids. Hearing aids amplify sound and can help people with mild to severe hearing loss. There are many different types of hearing aids, including behind the ear, intra-ear and intracanal. Your doctor can help determine, what type of hearing aid is best for you.
- cochlear implants. Cochlear implants are electronic devices, that help people with severe hearing loss. The implant consists of a microphone, speech processor and electrodes, which are surgically implanted into the cochlea. The device stimulates the auditory nerve and sends sound signals to the brain.
- Other devices. There are other devices, that can help with hearing loss, including personal amplifiers, public address devices and FM systems.
home treatment for hearing loss
In addition to medical treatment, there are several steps, things you can do at home, to improve hearing, including:
- Ear protection from loud sounds: Avoid exposure to loud sounds, such as concerts and gun shooting. If you need to be in a noisy environment, use earplugs or noise canceling headphones.
- Keep your ears clean: clean your ears regularly, to prevent the accumulation of earwax, which can lead to hearing loss.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: healthy eating, regular exercise and avoiding smoking and excessive drinking can help improve hearing.
- Use of assistive devices. Auxiliary devices, such as telephones with an amplifier, can help improve communication and make daily activities easier.
Hearing Loss Prevention
Hearing loss prevention is important to maintain good hearing. Here are some tips, how to prevent hearing loss:
- Limit exposure to loud sounds: avoid exposure to loud sounds, such as concerts and gun shooting. If you need to be in a noisy environment, use earplugs or noise canceling headphones.
- Wear protective gear: if you work in a noisy environment, wear protective gear, eg, earplugs or headphones.
- Get your hearing checked regularly: regular hearing tests can help detect hearing loss early and prevent it from getting worse.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: healthy eating, regular exercise and avoiding smoking and excessive drinking can help improve your hearing and prevent hearing loss.
Conclusion
Hearing loss is a common problem, that affects millions of people around the world. Understanding the reasons, symptoms and treatment options important for maintaining good hearing.
If you are experiencing hearing loss, it is important to seek medical attention and follow the recommended treatment plan.
Taking steps to prevent hearing loss, such as limiting exposure to loud noises and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, can help maintain good hearing health for life.
Used sources and literature
Arts HA, Adams ME. Sensorineural hearing loss in adults. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 152.
Eggermont JJ. Types of hearing loss. In: Eggermont JJ, ed. Hearing Loss. Cambridge, MA: Elsevier Academic Press; 2017:chap 5.
Kerber KA, Block RW. Neuro-otology: diagnosis and management of neuro-otological disorders. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff’s Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 22.
Le Prell CG. Noise-induced hearing loss. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 154.
Shearer AE, Shibata SB, Smith RJH. Genetic sensorineural hearing loss. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 150.
Weinstein B. Disorders of hearing. In: HM starts, Rockwood K, Young J, eds. Brocklehurst’s Textbook of Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier, 2017:chap 96.
