Pyeritonyealinyi dialysis – AP
Description peritoneal dyalyza
Dialysis – procedure, which replaces the kidney function, if they do not fulfill their functions. The kidneys have many functions, that help the body stay healthy. They help to remove toxins from the blood and maintain the body's electrolyte balance level. Most patients begin dialysis kidney, when they lose 85% -90% its capabilities. Dialysis may be needed for a short time, or, perhaps, It needs to pass the rest of his life (or until a kidney transplant), depending on the cause of kidney failure.
If the kidneys can not be restored, this is called end-stage renal failure (WBC). ESRD is caused by certain diseases, such as diabetes, kidney cancer, drug use, high blood pressure, or other kidney problems. Dialysis is not a cure for ESRD, but it helps the patient feel better and live longer.
There are two types of dialysis: hemodialysis E pyeritonyealinyi dialysis. This paper describes peritoneal dialysis.
Causes of Peritoneal Dialysis
The main objectives of peritoneal dialysis are:
- Removing waste and excess fluid from the blood;
- Control blood pressure;
- Support at a safe level of salts in the body (potassium, sodium and chlorine).
Possible complications of peritoneal dialysis
Complications are rare, but no procedure does not guarantee the absence of risk. Before, how to perform peritoneal dialysis, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Lowering the number of erythrocytes, causing anemia, especially in chronic renal failure;
- Muscle cramps;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Headache;
- Feeling the heat, Sweating, weakness and / or dizziness;
- Abdominal infections;
- Inflammation of the heart sac (perikardit);
- Neurological problems;
- An imbalance of calcium and phosphorus, which leads to weakening of the bones.
Factors, that may increase the risk of complications:
- Adhesions or significant amount of scar tissue in the abdominal cavity;
- Infection of the peritoneum (cover the abdomen);
- Abdominal hernia;
- Diverticulitis – sac infection, which is formed in the wall of the colon;
- Defects of the abdominal cavity.
How is peritoneal dialysis?
Preparation for the procedure
Peritoneal dialysis is often possible to perform a home-.
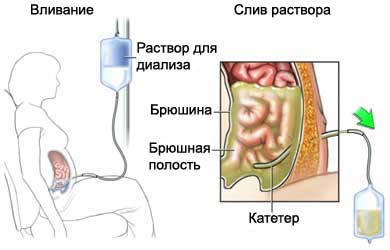
Cover the abdomen is called the peritoneal membrane. It is used to filter the blood. Cleaning solution, called dialysate, injected into the abdominal cavity through the tube. Liquids, waste and chemicals pass from the tiny blood vessels of the peritoneal membrane into the dialysate. The dialysate is drained a few hours. It can be added to a new batch of dialysate, to repeat the process.
There are three types of peritoneal dialysis:
Postoyannyi ambulatornyi pyeritonyealinyi dialysis (CAPD) – the most common type of peritoneal dialysis. The dialysate is injected into the abdominal cavity through the tube, called a catheter. He remains there for 3-6 hours, then drained. The abdomen is filled with new solution. Thus, blood is always cleared.
Continuous Cycling Peritoneal Dialysis (CCPD) – infusion and refilling abdominal dialysate is performed using a special machine. Held night, during sleep.
Pryeryvistyi pyeritonyealinyi dialysis (EDP) – using the same apparatus, and that CCPD. It, usually, It performed in hospital and often take longer, than CCPD.
How long will peritoneal dialysis?
Time, required for peritoneal dialysis depends on several factors:
- The current function of the kidneys;
- Increasing the amount of liquid after last treatment;
- The amount of waste in the body;
- Body Weight;
- The level of certain salts in the body, such as sodium, potassium chloride;
- Type yspolzuemoho peritoneal dyalyza.
The approximate time and frequency of each type of dialysis:
| Type | Duration | Procedure frequency |
| CAPD | 3-6 hours, plus 30 minutes overflow | 4 once a day |
| CAPD | 9-12 hours | Every night |
| EDP | 12 hours and more | 36-42 hours per week |
Pyeritonyealinyi dialysis – Will it hurt?
In peritoneal dialysis generally causes no pain.
After leaving peritoneal dyalyza
Home Care
Be sure to follow your doctor's instructions. There are some features of care after the peritoneal dialysis:
Recommendations on food intake
You must be complied with some dietary advice. This will help to maintain overall health and increase the effectiveness of treatment.
Medications
Your doctor may prescribe different medications. They include, but are not limited:
- Medications to control blood pressure;
- Calcium supplements or multivitamins;
- Phosphorus binding drugs – to reduce phosphorus levels in the blood;
- Diuretics, to remove excess fluid;
- A stool softener or laxative – for preventing or treating constipation, which may be caused by a decrease in fluid intake;
- Iron preparations – you need to increase your intake of iron, which is very important for the development of red blood cells;
- Drugs, stimulate the production of red blood cells.
Communication with the doctor after the procedure of peritoneal dialysis
We need to see a doctor, If the following symptoms:
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Redness, edema, fever, strong pain, bleeding, or discharge at the site of the catheter or tube;
- Blood or cloudiness in the peritoneal dialysis fluid;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Abdominal pain;
- Dizziness and weakness.
