Acute erythromyelosis – Di Guglielmo's disease
Leukemia was first described in 1917 g.
It occurs in adults around 5 % nelimfoblastnyh cases of all forms of acute leukemia, have children - 0,6 % cases. In the history of patients with acute erythromyelosis uncommon data received radiation or chemotherapy: This acute leukemia is most often induced, rather than spontaneous, it occurs in persons, lechivshihsya of limfogranulematoza, multiple myeloma, eritremii.
The clinical picture of acute erythremic myelosis
In most cases, the onset of acute anemic syndrome is characterized erythremic myelosis, which slowly increases and is accompanied by mild ikterichnost. Anemia is usually moderately hyperchromic character, Blood found erythrokaryocytes, of reticulocytes usually does not exceed 1-3 %.
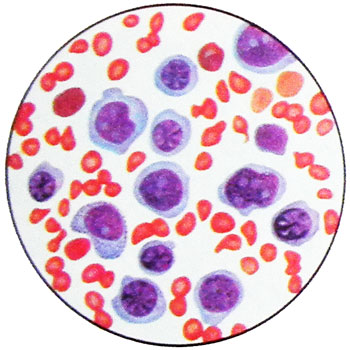
Blood picture of acute erythremic myelosis
Blood picture may be aleukemic, but as the disease occurs leukemization: go into the blood or erythrokaryocytes, or blasts, or both cells simultaneously. Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia is often observed from the very beginning, sometimes they appear later. Bilirubin is usually slightly increased due to the indirect fraction.
Cytochemical characterization of cells in acute erythromyelosis
Unlike other forms of acute leukemia, in which the diagnosis is based on detection of In bone marrow blast cells and atypical, Consequently, It is not difficult, in acute erythromyelosis any characteristic changes in the disease is not detected punctate.
This disease is characterized by a sharp increase in the number of red cells in the bone marrow. This pattern occurs in hemolytic, IN12-deficiency anemiyah and ineffective erythropoiesis any nature (hemolysis erythrokaryocytes).
Unlike other forms of acute leukemia differentiation of tumor cells in acute red number erythromyelosis it happens often to the stage and polychromatic oxyphilic erythrokaryocytes or to red blood cells.
But along with the number of red cells, sometimes different atypia, of cores, bone marrow, and later in the blood appear blast items, and that allow a diagnosis.
Blast cell morphology erythroleukemia divided into two variants:
- actually erythromyelosis, wherein the substrate is represented by the tumor and non-differentiable erythrokaryocytes blasts;
- erythroleukemia, in which along with erythrokaryocytes there are many myeloblasts.
In the dynamics of the first version marked the gradual transition to the predominance of undifferentiated blasts, the second - to myeloblastosis. Clinical differences between these options indistinct.
Where, If there is a pronounced inhibition of normal hematopoiesis germs (leiko-, thrombocytopenia, anemia, high content of reticulocytes - no more than 2 3%), and in the bone marrow - the abundance of ugly erythrokaryocytes and many atypical undifferentiated blasts or myeloblasts, diagnosis of acute erythremic myelosis becomes apparent. If the number of red cells are morphologically different from normal, number of small undifferentiated blast cells (to 10%), and in the peripheral blood is no distinct signs of depression of normal hematopoiesis germs, diagnosis of acute erythremic myelosis definitely can not deliver. In this case, the discovery in trepanate proliferative undifferentiated cells favors acute leukemia.
In acute erythromyelosis (as well as any other acute leukemia) must increase the percentage of blast cells in the bone marrow in the dynamics.
Before the establishment of an accurate diagnosis any cytostatic treatment, including prednisolone, can not be carried; however, symptomatic therapy (blood transfusion in severe anemia and so on.) not further complicate diagnosis.
A study of the chromosome apparatus of bone marrow cells could provide substantial assistance in the diagnosis erythremic myelosis: finds in the number of red cells aneuploid clone diagnosis can be considered proven.
Aneuploidija (often hypodiploid sets of chromosomes) in this disease occurs in about 40 % cases. The presence of a red germ disorderly (without the formation of clones) aneuploidy is not a sign of tumor growth, since this phenomenon occurs in hemolytic anemia, pernicious anemia. In acute erythromyelosis often, than with other forms of leukemia, there are a variety of structural changes in chromosomes (ring dicentric chromosome).
Cytochemical erythremic myelosis feature is the presence of PAS-positive substance in cytoplasm of nucleated red cell number, in particular erythrocytes, Although this feature is not specific for leukemic process. In erythrokaryocytes it can be detected and α-naftilesteraza, common to the cells of monocytic series.
The morphology of erythrocytes in erythromyelosis It may be different. Usually, As with other forms of acute leukemia, despite anemia, no anisocytosis and poikilocytosis. In the presence of anisocytosis it reaches such a degree of sharp, In both at12-deficiency anemia, It is not marked as its characteristic polisegmentatsii neutrophilic granulocytes, but gigantism and ugly elements of granulocytic series can take place. Often there is a fair hyperchromia erythrocytes with increasing color index to 1.2-1.3.
When a complication of acute erythremic myelosis increased hemolysis establish exactly this form of acute leukemia is possible only if in the number of red cells aneuploid clone (or clones). In the absence of this trait is difficult diagnosis of acute erythremic myelosis.
The occurrence of acute erythremic myelosis
A characteristic pathology of the internal organs in acute erythroleukemia is not observed. Lymph nodes are usually not enlarged, liver and spleen, As with other forms of acute leukemia, may increase, but most remain in the normal.
Dynamics of hematological indices can have two directions:
- in one case increases the number of blast cells in the bone marrow, and peripheral blood, until almost complete displacement of pathological red sprout,
- in others - in the bone marrow to the end retained a high content of the red series elements with a moderate build-up percent blast cells.
However, in this and in another case, naturally growing granulozitopenia, thrombocytopenia and anemia. As with other forms of acute leukemia, cause of death of patients is the failure of hematopoiesis.
Remission in Acute erythromyelosis
Despite the relative rarity of complete remission, Acute erythromyelosis no different rapid progression. The life expectancy of most patients is about 6 months, to 20 % patients live about 18 months. Reach slowing the progression of the process, get a clear improvement in the blood on the background of cytostatic therapy and red blood cell transfusions are usually not possible.
