Removal of acoustic neuroma – Nevrilemmoma – The vestibular schwannoma
Description removal of acoustic neuroma
Nevrilemmoma auditory nerve is a benign (noncancerous) tumor. It grows on the auditory nerve, which extends from the brain to the ear. This type of tumor grows rather slow. However, this may lead to hearing loss, problems with balance, cause numbness of the face, and headaches.
There are three main options for the treatment of auditory nerve neuroma:
- Careful monitoring of tumor growth;
- Radiation (Radiation) therapy;
- Microsurgical removal of neuroma.
The most effective treatment is a microsurgical removal.
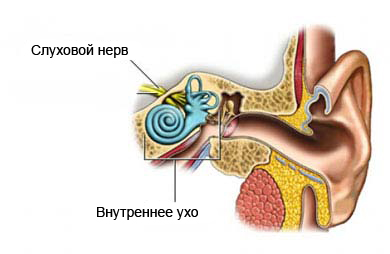
Indications for removal of acoustic neuroma
- Tumor growth;
- The size of the tumor may be life-threatening;
- The tumor is the cause of hearing loss.
The operation is performed quite well with minimal hearing loss.
Possible complications in removing acoustic neuromas
If you plan to have surgery, you need to know about possible complications, which may include:
- Hearing loss;
- Excessive dryness of the eyes;
- Problems with balance;
- Tinnitus;
- Numbness of the face on the side of the tumor;
- Headache;
- Infection;
- Bleeding;
- Leakage of cerebrospinal fluid (TsSJ).
Some factors, that may increase the likelihood of complications include:
- Age of the operated;
- Tumor Size.
How to conduct the removal of neuroma?
Before surgery
Before the operation is carried out following the reception of drugs:
- Steroids – Usually introduced by 48 hours before surgery;
- Antibiotics – administered intravenously preoperatively.
Perhaps it will be necessary to stop taking certain medicines a week before surgery, eg:
- Aspirin or other anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Blood thinners, such as warfarin, Clopidogrel.
Anesthesia
The operation is performed under general anesthesia, during the operation the patient is asleep.
Activity description
Type of surgery depends on the individual case. It takes into account such factors, the degree of hearing loss, location of the tumor. The operation is performed by one of the following surgical methods:
Translabirintoobrazny (Translabyrinthine) method
This method is mainly used, when there is a significant loss of hearing. Mastoid (part of the temporal bone of the skull) and bone in the inner ear are removed. This allows access to the external auditory canal and tumors.
Retrosigmovidny / Sub-occipital (Retrosigmoid/Sub-occipital) method
The skull behind the ear is a hole, for access to the neuroma. This method is used for large, or so for small tumors. This method allows you to see the nerves during surgery and to act cautious.
Operation via the middle cranial fossa
The tumor is removed through the top surface of the external auditory meatus. This method is used, when there is a high shansya on plnoe Hearing Conservation.
After operation
The patient must spend at least one night in the intensive care unit for observation.
How long does the surgery?
The operation takes about 6-12 hours. The time depends on the size and location of the tumor.
Will it hurt?
Anesthesia will prevent pain during the procedure. For pain relief after surgery appoint appropriate painkillers.
The time spent in hospital
Usually stay is 4-7 days. The stay may be longer, If there are complications.
Postoperative care
In the hospital
Immediately after the operation may cause some unpleasant symptoms:
- Discomfort in the head (because of the cut and the holes in the skull);
- Fatigue and sleepiness;
- Emotional decline;
- Headache;
- Dizziness;
- Nausea.
It is necessary to report these symptoms staff, for appropriate action.
Houses
To speed up recovery, you need to follow your doctor's instructions. They may include:
- Maintaining the incision clean and dry;
- Drive the car only after doctor's permission;
- It is necessary to take medication as instructed.
Complete recovery usually takes 4-6 weeks. You will need to do to make regular MRI within the next few years. Scanning will allow time to see the tumor, if it starts to grow again.
It is necessary to go to the hospital in cases
- There were signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Krasnoja, swelling, strong pain, bleeding, or any selection from the incision site;
- Inability to relieve pain using painkillers;
- Cough, breathlessness, or chest pain;
- Nausea or vomiting;
- Rigidity (tension) neck;
- Cold.
