Muscular atrophy: what is this, causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
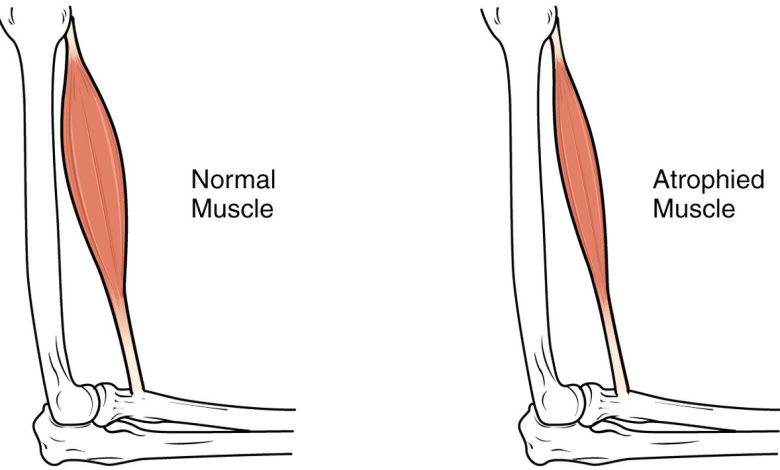
Muscle atrophy; Muscle wasting; Wasting; Atrophy of the muscles
What is Muscular Atrophy?
Muscular atrophy is a condition, in which the muscles of the body shrink or weaken over time. It can happen as a result of aging, inactivity or injury and can have a significant impact on a person's ability to perform activities of daily living and maintain mobility. In severe cases, this condition can lead to disability and reduced quality of life..
Causes of Muscular Atrophy
Muscle atrophy can be caused by various factors., including aging, inaction or injury.
For Example, aging can cause a decline in muscle mass and strength due to the body's natural decline in the ability to regenerate muscle fibers. Inactivity is another common cause of muscle atrophy, because, when muscles are not used, they can become weak and shrink over time.
Dysfunctional atrophy can be caused by a sedentary lifestyle, prolonged bed rest or simply lack of regular exercise.
Injury can also cause muscle atrophy, because when damaged, the muscle can no longer contract and, Consequently, unable to perform their normal functions.
Symptoms of Muscular Atrophy
Muscle atrophy symptoms may vary depending on the cause of the condition.. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Reduced muscle strength
- Reduced muscle mass
- Joint pain
- Difficulty performing daily activities
- Fatigue
- Joint stiffness
Diagnosis of muscular atrophy
Muscular atrophy is usually diagnosed on physical examination., during which the doctor assesses muscle strength, weight and flexibility of the patient. The doctor may also order tests, such as a blood test, to check for any underlying diseases. In some cases, imaging studies may be ordered to assess the degree of muscle loss..
Treatment of muscular atrophy
Treatment for muscle atrophy depends on the underlying cause. Treatment may include physical therapy, pain medication and lifestyle changes to improve strength and flexibility. In cases of severe muscle loss, surgery may be required to restore muscle function..
Treatment may also include physical therapy., ultrasound therapy and, in some cases, contracture repair surgery .
Home Treatment for Muscular Atrophy
Home Treatments for Muscle Atrophy Can Help Improve Strength and Flexibility, and prevent further loss of muscle mass. Some home treatments include:
- Exercises. Exercise helps strengthen muscles and improve flexibility. Before starting any exercise program, it's important to talk to your doctor or physical therapist..
- Diet: Healthy, a balanced diet can help provide the body with nutrients, essential for muscle growth and repair.
- Bracing: stretching can help improve flexibility and prevent further muscle loss.
- Heat and cold therapy: applying heat or cold to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Prevention of muscular atrophy
The best way to prevent muscle wasting is to stay active. Exercise regularly, eat a balanced diet and stretch regularly, to keep muscles strong and flexible. Besides, it is important to be aware of any injuries or illnesses, which can lead to loss of muscle mass, and seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Used sources and literature
Ball JW, Dains I, Flynn YES, Solomon BS, Stewart RW. Musculoskeletal system. In: Ball JW, Dains I, Flynn YES, Solomon BS, Stewart RW, eds. Seidel’s Guide to Physical Examination. 10th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2023:chap 22.
Selcen D. Muscle diseases. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 393.
