medical erosion: What's it, causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
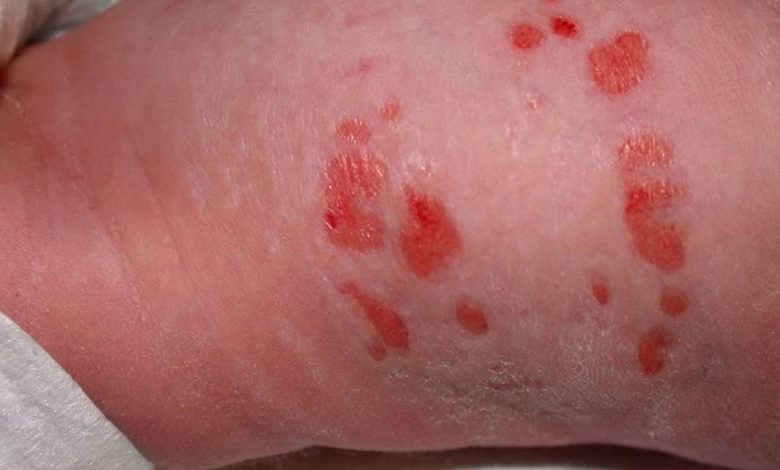
Erosion
What is erosion?
Erosion is damage to the outer layers of the skin. Medical erosion is a type of tissue damage, caused by an external factor, like pressure, friction or misalignment. It is usually associated with a lesion or ulceration of the skin., but can also refer to destruction of other tissues, e.g. organs or bones.
Medically, erosion is a physical process, which includes not only the loss of physical material, but also tissue and cellular architecture. It's more extensive, than just a superficial injury, such as a scratch or cut.
Causes of erosion
There are many different types of erosion. Some of the most common reasons include:
- Pressure. Denture pressure, eg, orthopedic or wheelchair, can cause erosion due to friction. Clothing can be other sources of pressure, seams of clothes and decorations.
- Friction. Erosion may occur, when two surfaces rub against each other due to constant or intense movement. This is seen in athletes and those, who perform repetitive movements in their daily activities.
- Wrong position. Sitting and lying in uncomfortable positions or positions, applying pressure or friction to a specific area, can lead to erosion.
- Poor mobility. People with limited mobility are at risk of developing pressure, friction and malpositioning in certain areas of the body, which can lead to erosion.
erosion symptoms
The signs and symptoms of erosion will depend on the type of tissue and the severity of the damage.. Some common signs and symptoms of tissue erosion include:
- Redness and inflammation. Usually it is swelling and pain.
- Skin ulcers are open sores, which may be painful or itchy.
- Changing the color of the fabric - the color can vary from white to yellow or black.
- Defeats. These are red raised spots, which may be a sign of a more serious underlying condition.
- Fluid-filled blisters - usually seen in cases of erosion, caused by friction.
When to see a doctor
If you begin to notice any signs and symptoms of erosion, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible. Your doctor will be able to diagnose the condition and suggest an appropriate treatment or management plan.
Questions, that your doctor may ask
When you visit your doctor, he may ask you some questions, to better understand your condition. These may include:
- How long do these symptoms last?
- Where on your body does erosion occur??
- Are there any activities or tasks, that, in your opinion, can cause erosion?
- Are there any other diseases, for which you are currently being treated?
- Have you been treated for this disease before??
Diagnostics
Your doctor diagnoses erosion through a physical examination and review of symptoms. He may also order additional tests., to confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of damage. These tests may include:
- X-ray - to detect and diagnose areas of tissue erosion.
- CT – To prevent the spread of infection.
- Ultrasound - to create a tissue map and determine the area of erosion.
- Biopsy - to determine, whether there are any cancer cells in the tissue.
Treatment
Erosion treatment will depend on the type of tissue affected and the extent of the damage.. Some common treatments include:
- Topical medications or ointments – these can reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Surgery. In rare cases, surgery may be required to repair destroyed tissue..
- Wound care. The wound may require frequent cleaning, dressing changes and topical medications.
- Physiotherapy - to improve the flexibility and mobility of the affected areas.
- Medicines. In more severe cases, pain medication may be prescribed..
home treatment
Along with traditional treatments, there are also a number of home remedies., which can help with erosion symptoms. These include:
- Avoid tissue irritants. Wear loose clothing and avoid harsh soaps or detergents, to reduce irritation and inflammation.
- Use heat therapy. Applying a hot compress to the affected area can help reduce pain and swelling..
- Eat a balanced diet. Eating a well-balanced diet will help provide your body with nutrients., necessary for proper self-healing.
- Get plenty of rest. Adequate rest will give your body time, necessary for the restoration and healing of damaged tissues.
Prevention
Prevention is the best treatment for erosion. There are a number of steps, you can take, to reduce the risk of erosion:
- Wear appropriate protection. Wear protective gear, when you are doing activities, which can lead to friction or pressure on the skin.
- Avoid tight clothing - this can cause friction when moving and make it difficult for your skin to breathe.
- Use Lubricants. The use of lubricants in the classroom, causing friction, may help reduce the risk of tissue damage.
- Keep skin clean. Keeping the skin clean and dry will help prevent infection and irritation..
- Avoid smoking. Smoking linked to tissue damage and slower healing time.
Conclusion
Erosion is a type of tissue damage, pressure-induced, friction or misalignment. It can happen on any part of the body, including skin, organs or bones. Although erosion can occur due to daily activities, it is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms and seek medical attention, if you start experiencing any of them. Various treatment options available, ranging from topical medicines to surgery and wound care. Besides, it is important to take preventive measures, e.g. wear protective clothing and avoid activities, which can cause tissue damage.
Used sources and literature
Gawkrodger DJ, Ardern-Jones MR. Terminology of skin lesions. In: Gawkrodger DJ, Ardern-Jones MR, eds. Dermatology: An Illustrated Colour Text. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 7.
James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA, Neuhaus IM. Cutaneous signs and diagnosis. In: James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA, Neuhaus IM, eds. Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 2.
