Hemorrhages on the skin, purpura: what is this, causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
Purpura; Blood spots; Skin hemorrhages
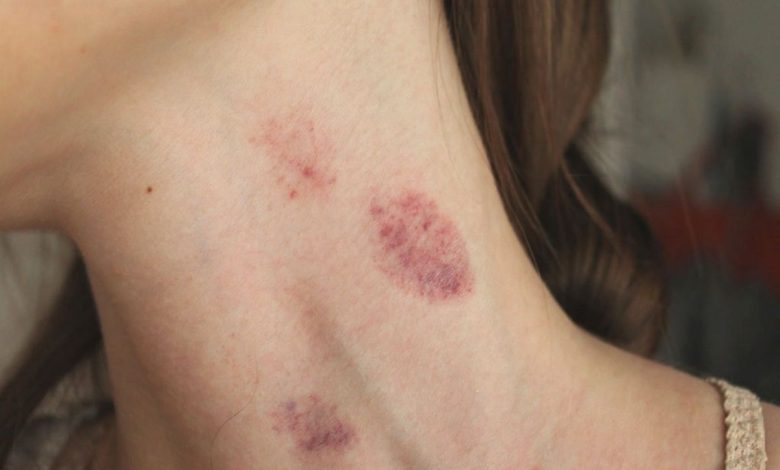
What is purpura?
Purpura is a skin condition, characterized by the presence of purple or red patches or patches on the skin. The spots may be irregular or round in shape and usually range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter.. The patches may be raised or flat and may sometimes be slightly warm or prickly to the touch.. Purpura is a form of petechiae, which is the medical term for a group of small reddish-purple spots on the skin, caused by bleeding under its surface. Petechiae look like purple, but usually less, less 3 millimeters in diameter.
Causes of purpura
Purpura can be caused by a wide range of conditions., including, among other things, injury, inflammation, injury, disease, Disorder, taking drugs and toxins.
- Trauma is one of the most common causes of purpura. Skin lesions may include cuts, scratch, stab wounds, burns and bruises. Injury to the skin can cause blood to leak from blood vessels, what causes purpura.
- Inflammation is another common cause of purpura.. Inflammation of the skin can be caused by various factors., including allergies, infections and irritation from irritants.
- Certain diseases and disorders can also cause purpura, including autoimmune diseases, blood disease, chronic granulomatous disease and cancer.
- Medicines, including aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can also cause purpura.
- Toxins can also cause purpura. This includes drugs, alcohol, pesticides and other environmental toxins.
Symptoms of purpura
The main symptom of purpura is the presence of purple or red patches or patches on the skin.. The spots may be irregular or round in shape and usually range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter.. The patches may be raised or flat and may sometimes be slightly warm or prickly to the touch.. The spots may be accompanied by pain., bruised, edema, redness, soreness or itching.
When to contact a healthcare professional
You should see a doctor, if you develop any symptoms of purpura, as this may be a sign of a more serious underlying condition. You should also see a doctor, if you develop any other symptoms, such as fever, chills, fatigue or joint pain.
Diagnosis of purpura
The doctor will diagnose purpura, by conducting a physical examination and taking a detailed medical history. Your doctor may also order laboratory tests, such as complete blood count, to check for an underlying disease.
Treatment of purpura
Treatment for purpura depends on the underlying cause. If the cause is an infection, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics. If the cause is an underlying disease, such as a blood disorder, your doctor will treat the underlying condition.
If the cause is unknown, a doctor may recommend corticosteroids or other medications to reduce inflammation and reduce purpura patches.
home treatment for purpura
There are a number of home treatments, which may help reduce the symptoms of purpura.
- Applying cold compresses to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and itching..
- Applying aloe vera gel or hydrocortisone cream can also help reduce itching and inflammation..
- Using a moisturizer can help keep skin hydrated and reduce dryness..
- Taking antihistamines may help relieve itching.
Prevention of purpura
There are a number of steps, you can take, to prevent purpura.
- The importance of avoiding, which can lead to skin injury, such as contact sports or rough play.
- If you have an underlying condition, such as a blood disorder or an autoimmune disease, be sure to follow your doctor's instructions for treating this condition.
- If you are taking any medications, which can cause purpura, it is important to follow your doctor's instructions for taking your medications.
- Wearing protective clothing and using insect repellants can help protect against insect bites., which can lead to purpura.
- It is also important to avoid exposure to environmental toxins., such as pesticides.
- Finally, it is important to take good care of your skin, keeping it hydrated and avoiding irritants, such as harsh soaps and cleaning products.
Used sources and literature
Dinulos JGH. Principles of diagnosis and anatomy. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif’s Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 1.
Kitchens CS. Purpura and other hematovascular disorders. In: Kitchens CS, Kessler CM, Konkle BA, Streiff MB, Garcia DA, eds. Consultative Hemostasis and Thrombosis. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 10.
