Cyst: what is this, causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
Cyst
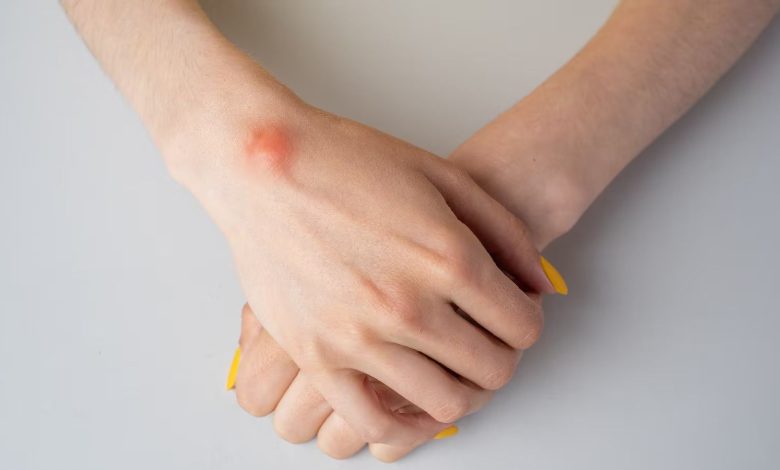
The cyst is a sac-like structure, which can form in various parts of the body, including skin, ovary, kidneys and other organs. Cysts are usually filled with fluid, air or semi-solid materials and can range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters. Although most cysts are benign and cause no symptoms, some of them may become painful or cause complications, if they get too big or break.
Causes of cysts
Cysts can have different causes depending on their location and type.. Some of the common causes of cysts include:
- Hormonal Imbalance. Hormonal changes can cause cysts to form in women's ovaries, known as ovarian cysts.
- Trauma: cysts can also form as a result of injury or damage to the affected area.
- Blocked ducts: cysts may form, when the ducts in the body are blocked, obstructing the normal outflow of fluid.
- Genetic factors. Some cysts, eg, found in the liver or kidneys, may be caused by genetic factors.
Cyst symptoms
Not all cysts cause symptoms, and some of them can be discovered by chance during imaging studies. But, when do cysts actually cause symptoms, They may include:
- Pain: Depending on the location of the cyst, it may cause pain or discomfort.. For Example, ovarian cysts can cause pelvic pain, and skin cysts can be painful, if they become infected or inflamed.
- Edema: cysts can cause swelling in the affected area, like chest, ovaries or skin.
- Redness: If the cyst becomes infected, it can cause redness, fever and pain in the affected area.
- Changes in bowel or bladder function: in some cases, cysts in the pelvis can cause changes in bowel or bladder function.
When to contact a healthcare professional
If you have symptoms of a cyst, you should see a doctor for evaluation. Besides, if you notice any change in the size or appearance of the cyst, you should see a doctor. Some signs of that, that you should seek immediate medical attention, include:
- Strong pain: if you experience severe pain or sudden onset of pain, you should seek emergency medical attention.
- Signs of infection: if you notice redness, warmth or pus, coming from the cyst, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible.
- fast growing cyst: If the cyst is growing rapidly, it could be a sign of a more serious condition, and you should see a doctor.
Questions, that your doctor may ask
When you see a doctor about a cyst, he will ask you questions about your symptoms and medical history. Some questions, that your doctor may ask, include:
- When did you first notice the cyst??
- Have you had any symptoms, such as pain or swelling?
- Have you noticed any changes in the size or appearance of the cyst?
- Have you had a history of cysts or other diseases?
- Are you taking any medications or supplements?
Diagnosis of cysts
To diagnose a cyst, the doctor will perform a physical examination and may order imaging tests, such as ultrasound or MRI. In some cases, the doctor may also perform a biopsy, to determine, is the cyst malignant. During a biopsy, a small sample of tissue is taken from the cyst and examined under a microscope..
Treatment of cysts
Treatment for a cyst depends on its location., size and underlying cause. In most cases, small cysts, causing no symptoms, do not require treatment. But, if the cyst is causing symptoms or is growing in size, may need treatment. Some of the cyst treatment options include:
- Vыzhidatelynaya tactics: if the cyst is small and causes no symptoms, your doctor may recommend expectant management. This means watching the cyst over time, to see, whether it is growing or causing any symptoms.
- Medicines: in some cases, the doctor may prescribe medication, such as birth control pills, to help reduce or prevent cyst formation. Pain medications may also be prescribed to relieve pain., cyst related.
- Drainage: if the cyst is large or causing symptoms, the doctor may drain it with a needle or catheter. This is usually done under local anesthesia., and the cyst can be aspirated or completely drained.
- Surgery: in some cases, surgery may be required to remove the cyst. This is usually reserved for large cysts or those, that cause severe symptoms or complications.
Home treatment for cysts
In addition to medical treatment, there are some home remedies, that can relieve symptoms, associated with cysts. These include:
- Applying warm compresses. Applying a warm compress to the affected area can relieve pain and reduce swelling.
- Taking over-the-counter painkillers: over-the-counter painkillers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can relieve pain, cyst related.
- Compliance with hygiene rules. If the cyst is located on the skin, it is important to keep this area clean and dry, to prevent infection.
Prevention of cysts
Although it is not possible to prevent all types of cysts, there are some steps, you can take, to reduce the risk of their development. These include:
- Compliance with hygiene rules. Keeping your skin clean and dry can help prevent cysts from forming..
- Injury Prevention. Taking steps to prevent injury, e.g. wearing protective equipment while playing sports, may help prevent cyst formation.
- Treatment of major diseases. If you have an underlying condition, which increases the risk of developing cysts, e.g. polycystic ovary syndrome, it is important to control this condition as directed by the doctor.
Conclusion
Cysts are a common disorder, which can form in various parts of the body. Although most cysts are benign and cause no symptoms, some of them may become painful or cause complications, if they get too big or break.
If you have symptoms of a cyst, it is important to see a doctor, to determine the cause and prescribe appropriate treatment. In some cases, home remedies and lifestyle changes can also help relieve symptoms and prevent cysts from forming..
Used sources and literature
Dinulos JGH. Principles of diagnosis and anatomy. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif’s Clinical Dermatology: A Color Guide in Diagnosis and Therapy. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 1.
Fairley JK, King CH. Tapeworms (cestodes). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 289.
James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA, Neuhaus IM. Epidermal nevi, neoplasms, and cysts. In: James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach, MA, Neuhaus IM, eds. Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 29.
