Caries – Tooth Decay
Description caries
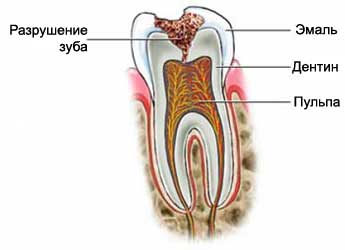
Tooth decay is the destruction of tooth material, which comprises:
- Enamel – solid outer surface of the tooth;
- Dentin – soft layer under the enamel;
- Pulp – the interior of the tooth, contains nerves and blood vessels;
- Root – mounting area of the tooth to the bone.
Causes of dental caries
Every person has the bacteria in the mouth. The bacteria feed on sugar, which remains on teeth, and then produce acid. Acids and bacteria form plaque on the teeth, which adversely affects the teeth. Eventually acid can lead to tooth decay.
Risk factors for caries
Each person can develop tooth decay. Factors, that may increase the risk of caries include:
- Frequent snacking;
- Poor oral hygiene;
- The large number of bacteria in the oral cavity;
- Inadequate intake of fluoride;
- Medication, which contain sugar or cause xerostomia;
- A diet high in sugar;
- The lack of vitamins and minerals in the diet;
- Disease, which reduce the secretion of saliva in the mouth (eg, Sjogren's syndrome or heartburn);
- For children: the presence of brothers and sisters with severe tooth decay.
Children are also at risk of dental caries. The risk of its occurrence increases frequent irregular feeding.
Symptoms of caries
Symptoms include caries:
- Tooth sensitivity to hot or cold food;
- Discomfort in the teeth after eating;
- Darkening of the tooth surface;
- Bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth;
- Throbbing, zatâžnaâ pain in the teeth.
Diagnosis of dental caries
Caries is diagnosed by clinical examination, as well as an X-ray of the tooth.
The dentist checks for tooth decay with the following symptoms:
- The presence of pain in the teeth;
- Visual inspection of the surface of the tooth;
- Check teeth dental tool to check:
- Sensitivity;
- Pain;
- Surface defects.
In addition, X-rays of the teeth is performed.
Caries treatment
Sometimes, initially, caries can pass by itself.
Treatment for more severe cases of dental caries includes:
Filling in cavities
If tooth decay reaches the dentin, doctor:
- Numb the tooth and the surrounding tissue;
- Remove loose tooth portion;
- Fill the hole is sealed up with a solution.
Cleaning the root canal caries
Caries, which reaches the pulp and / or the tooth root requires cleaning of the root canal:
- Tooth anesthetized and its upper part is drilled;
- Pus and dead tissue are removed tooth;
- Channels inside the tooth and the root will be cleaned and filled with a permanent special filler;
- The root canal is closed;
- To protect the tooth, the Crown is placed on it.
Removal of a tooth
Removal of a tooth necessary, if:
- Tooth decay and / or tooth infection is too extensive and allows you to set the seal or to purge the root canal;
- Zub schism, which does not allow it to cure;
- Between the tooth and gum infection there is an extensive.
If the tooth is removed, its location can be set:
- Bridge;
- Prosthesis;
- The implant tooth.
If the diagnosis of caries, Follow your doctor's instructions.
Prevention of tooth decay
Measures, that help prevent and stop tooth decay:
- Proper oral hygiene, including:
- Brushing teeth with fluoride toothpaste after meals or, at least, twice a day;
- Daily flossing – bacteria, living between the teeth can only be removed by a thread or special cleaners;
- Regular dental checkups and teeth cleaning;
- Limiting the amount of sugar and carbohydrates in the diet, including the following products:
- Honey;
- Carbonated drinks;
- Candy;
- Cakes;
- Cookies;
- Other sweets;
- Rinse mouth with water after eating;
- Substitution toothbrush every 3-4 of the month;
- Avoid consumption of sugary drinks (including fruit juices);
- The use of chewing gum with xylitol or sorbitol (may reduce the risk of tooth decay).
Caries prevention is especially important for children. A sufficient amount of fluorine, ingested in childhood can prevent early caries.
