Barotravma – General description
Barotrauma description
Barotravma – pain or discomfort, which occurs, When there is a difference in air pressure between the outside and inside of the body pressure Wednesday. Discomfort may occur when flying in an airplane or snorkeling lessons.
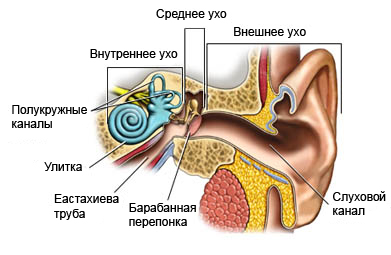
Barotrauma of the ear
- Barotrauma most commonly affects the middle ear, because there is a cavity, filled the air, which is sensitive to changes in atmospheric pressure:
- In the ear is a thin layer of skin (or membrane) at the end of the ear canal, that vibrates and transmits sound to the middle ear – the eardrum;
- Usually, the air pressure inside and outside the ear the same. Eustachian tube – cavity, that connects the middle ear and throat, balances the air pressure on both sides of the eardrum;
- Barotrauma of the ear there, When the eustachian tube is blocked, and the body cannot equalize the pressure of the air inside and outside the eardrum;
- Barotrauma of the ear, usually, is not harmful and easily treatable, but sometimes, you experience the following complications: hearing loss, ear infection, dizziness or perforating (puncture) tympanic membrane.
Sinus barotrauma (Sinus)
- Sinus – air-filled pockets in the bones around the nose.
- Sinus barotrauma occurs, When there is a difference in pressure between the air in the sinuses and external pressure:
- Pain may occur around the cheekbones or above the eye;
- You may experience headaches;
- Cold or nasal congestion, this can lead to severe sinus infection.
Pulmonary barotrauma
- Pulmonary barotrauma – trauma, which occurs, When the external pressure is different from the air pressure in the lungs:
- Divers swim with cylinders of compressed air for breathing under water. If the diver breathes compressed air too and quickly rises to the surface, light can break down;
- Another reason is “decompression illness“;
- Decompression (kesonnaâ) the disease occurs, When nitrogen, dissolved in the blood under high pressure, forms bubbles, If pressure is reduced (eg, When climbing onto the surface). These bubbles can seep into the blood, as air bubbles, called air embolism;
- Vozdšnaâ embolism can occur anywhere in the body and dangerous, When it blocks blood vessels, that nourish the blood organs, especially heart, lungs and head brain;
- Decompression sickness is classified by types – type 1 or type 2. Type 1 there, When bubbles occur in tissues around the joints, most commonly in the knees, the elbows and shoulders. Type 2 is more dangerous and involves the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) or the lungs and heart.
Barotrauma may also occur due to hardware, such as a mask or dry wetsuit, used for scuba diving. They can block and delay the air in the skin. If this air pocket there is a, When the diver dives, may appear wound. Dry suits may hurt pinch your skin. Masks can cause rupture of blood vessels in the eyes.
Cause barotrauma
Barotrauma occurs, When the air pressure inside and outside of the body are different, causing discomfort. Causes include:
- Flight;
- Scuba diving:
- His rapid rise to the surface when diving;
- Delayed breathing when lifting;
- Long scuba diving;
- Several diving 24 hours;
- Flying on an airplane after the dive;
- The presence of air tubes in the equipment (eg, masked and dry suits).
Risk factors
Factors, increase the likelihood of barotrauma:
- Nasal congestion from allergies or colds;
- Congenital blocking the eustachian tubes;
- Smoking;
- Age: children and the elderly:
- The eustachian tubes in children are smaller and more likely, will be blocked;
- Damaged eustachian tubes, caused by trauma or tumors;
- Laid ears;
- Cleft palate can affect the balance of pressure in the middle ear;
- Apnea during the dive;
- deep dive;
- Long scuba diving;
- Several diving 24 hours;
- Flying on an airplane after the dive;
- His rapid rise to the surface when diving;
- Fatigue;
- Dehydration;
- Cold water;
- Obesity;
- Incorrect hardware settings, used for scuba diving;
- Congenital narrowing or blocking sinus drainage system.
Symptoms of barotrauma
If symptoms of air embolism (air bubbles in the blood) due to pulmonary barotrauma, You should immediately seek medical assistance. Symptoms of air embolism in the brain usually, appear very quickly after the lifting on the surface of the water.
Symptoms of decompression sickness usually occurs within an hour after surfacing from the water, but can occur up to six hours after recovery. In the presence of decompression sickness, It is very important to seek medical attention immediately.
Given the symptoms can occur not only because barotrauma. They can be caused by other, less serious diseases. If any of them need to see a doctor.
Symptoms may include:
Barotrauma of the ear
- Discomfort or pain in one or both ears;
- Feeling of stuffiness in the ear;
- Feeling of pressure in the ears;
- Dizziness;
- Hearing loss (temporary);
- Bleeding from the ear (rarely);
- Tinnitus.
Sinus barotrauma
- Pressure and/or pain in the sinus area;
- Nosebleeds;
- Headache;
- Toothache.
Pulmonary barotrauma
Symptoms of air embolism
Symptoms may include:
- A reaction similar to stroke:
- Headache;
- Excitation;
- Confusion;
- Other symptoms:
- Partial paralysis;
- Sudden loss of consciousness;
- Convulsions;
- Coughing up blood;
- Foaming at the mouth, blood;
- Chest pain;
- Breathlessness;
- Hoarseness;
- Pneumothorax – state, where the air goes out of the lung into the chest cavity and compresses the lungs as a result of the collapse of the lung.
Decompression symptoms
Symptoms may include decompression:
- Swelling;
- Myalgia, joints, tendons;
- The problem of spinal cord, paralysis;
- The problem of sensor system;
- Lung problems, chest pain, cough, breathlessness;
- Rash or itching skin;
- Bubbles beneath the skin.
Diagnosis of barotrauma
The doctor asks about the symptoms and medical history, and performs a physical exam.
For suspected pulmonary barotravmu or decompression disease should immediately seek medical assistance.
Barotrauma of the ear
The doctor examines the special ear flashlight – otoskopom. An Otoscope allows the doctor to see the eardrum. In the presence of barotrauma the doctor may see a bulge eardrum due to the difference in pressure between the inner and outer part of the. If the patient's condition is serious, behind the eardrum may even be blood.
Sine barotrauma
There are no tests to diagnose sinus barotrauma. Diagnosis depends on the history of sinus disease, and then conduct due diligence.
Pulmonary barotrauma
To instantly check availability for all air embolism and possible lung damage, your doctor may prescribe the following tests:
- Chest X-ray, which will show the changes in the structure of blood vessels;
- CT scan – retrieving images, where you can find small strokes in the brain, that can be caused by air emboli;
- Pulmonary test – test, which indicates, What is the amount of air can be inhaled into the lungs and how fast the air you can breathe out;
- Perfusion lung scan – tests for detection of pulmonary embolism. A small amount of a radioactive substance is injected into the vein and it enters the lungs. Scanning allows the doctor to examine the blood supply to the lungs;
- Magnetic resonance imaging – allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the body, that allows the doctor to look for violations of the brain or spinal cord;
- Pulse oximetry – to measure the level of oxygen in the blood. This simple device, that is worn on a finger to measure oxygen levels.
In recent sessions, diving and the occurrence of symptoms of decompression sickness, the doctor can begin treatment immediately, without any tests or waiting for test results.
Treatment of barotrauma
After examination and diagnosis of doctor prescribes a treatment plan. Treatment options include the following:
The collapse of the
To relieve the pressure in the eustachian tube, It is possible to:
- Sucking candy;
- Chew gum;
- Yawn;
- Need to breathe and gently breathe out through the nose, clamping the nostrils, forcing the air to pass through a blocked Eustachian tube and, perhaps, open it.
Medication
To relieve nasal congestion and open eustachian tubes, especially if you have allergies or colds. Your doctor may recommend taking some medications, including:
- Decongestant nasal sprays;
- Decongestants;
- Antihistamines;
- Painkillers.
Antibiotics
Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to prevent infection of the ear, If barotrauma is severe.
Operation
Operation, usually, conducted in a pinch. If the eustachian tube is not open other treatments, surgery may be needed to relieve pressure. The doctor makes a small incision in the eardrum to equalize air pressure, as well as remove any liquid, which can block pipes.
Treatment with oxygen
Oxygen should be immediately, If there is a pulmonary barotrauma. Oxygen is served either through a mask on the face or the tube next to the nose.
Rekompressionnaâ therapy
In the presence of decompression sickness, need to be in high pressure Wednesday, to air bubbles, formed decreased and decayed in the blood. Some medical centers have hyperbaric chamber (also known as a pressure Chamber) to ensure high environmental pressure Wednesday.
Prevention of barotrauma
To reduce the likelihood of obtaining barotrauma, do the following:
Flights
- You need to postpone your flight, When you have a cold or runny nose;
- When flying in an airplane, especially during take-off and landing, need to do something, that will help keep the eustachian tube open, to reduce the pressure. Actions include:
- Sucking candies;
- Chewing gum;
- Oh I see;
- Breath with your mouth open;
- When flying to avoid sleeping during the decline;
- You need to use special earplugs for slow leveling air pressure in the eardrum;
- Children on flights we recommend sucking on a bottle or pacifier; You must not allow the child to sleep during descent;
- You can take protivozastojnye tablets or nasal spray before the flight. It helps Unclog ears;
- If there is a tendency to barotrauma, the doctor may surgically placed in the ears special rolls, to help balance the pressure and prevent the condition.
Scuba diving
- Need to be properly trained;
- You need to be healthy before immersing;
- Be sure to, that all the equipment is working properly;
- Need to take protivozastojnye tablets or nasal spray before you dive, to unlock the auditory tubes, the nose or sinuses;
- To prevent pulmonary barotrauma, you do not need to hold your breath while lifting;
- We need to quit smoking;
- You need to exhale while lifting to the surface, even in shallow basins;
- You do not need to dive to a depth of;
- You cannot long be under water at great depths;
- Be careful not to fly or climb to greater heights during the 24 hours after diving;
- It is recommended that you know the location of the nearest recompression chamber;
- You need to check the dry suit and face mask, To make sure, that the equipment is working properly;
- Never need to hold your breath when breathing compressed gas when lifting to the surface;
- You cannot dive alone.
