Barotrauma of the ear – Dysfunction of Eustachian tube
Description of Eustachian tube dysfunction
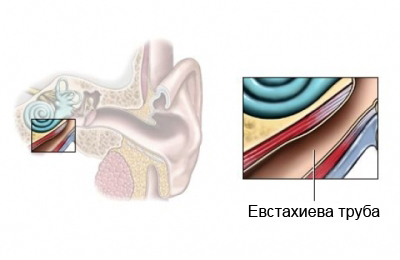
Eustachian tube – a small channel, that connects the middle ear to the back of the nose and the upper part of the throat (the nasopharynx). Its task is to align the pressure air in the middle ear with outside pressure.
Eustachian tube dysfunction occurs, When the channel does not open when swallowing or zevanii. As a result, there is a difference between the air pressure inside and outside the middle ear. It causes discomfort in the ear and temporary hearing problems.
Causes of dysfunction of Eustachian tube
Lock in your ear can occur, If the pressure outside the ear varies, but the pressure inside the ear does not change. When this happens, eardrum cannot vibrate in normal mode. This often happens when you are changing the height, during the flight the plane, driving on steep hills, or when diving lessons. With time, when swallowing, zevanii, or chewing, these symptoms disappear.
Eustachian tube dysfunction occurs, If the channel is locked or swells, or in the middle ear gets liquid. Symptoms can last up to several hours. Sometimes barotrauma can cause damage to your auditory function.
Causes of Eustachian tube dysfunction include:
- Nasal congestion from allergies;
- Colds and other upper respiratory tract infection;
- Ear infection or sinus infections;
- Narrow Eustachian tube;
- The presence of lymphoid tissue, blocking of the auditory canal (children);
- Tumors (adult).
Risk factors
Factors, increase the likelihood of Eustachian tube dysfunction:
- Actions, associated with large, fast high-altitude changes, such as flying in an airplane or scuba diving;
- Allergy, cold, or other upper respiratory infection;
- Ear infection or sinus infections;
- Narrow auditory tube;
- The presence of sdavlivajushhih tumours in the nasopharynx;
- Kids with big adenoidami;
- Age: children (their auditory tubes are narrower).
- Allergy.
The symptoms of Eustachian tube dysfunction
Symptoms may include:
- Feeling of stuffiness or blockage in the ear;
- Discomfort or pain in the ear;
- Hearing loss;
- Tinnitus;
- Dizziness;
- Symptoms of stuffiness if swallowed., zevanii or chewing;
- Pain, If the blockade leads to infection.
Diagnosis of Eustachian tube dysfunction
The doctor asks about the symptoms and medical history, and performs a physical exam. Tool, called an Otoscope, used, to look inside the ear. The doctor checks the ear on a small bulge around the eardrum, the presence of fluid and swelling. If the case is severe, You may want to inspect Otolaryngologist, doctor, specializing in hearing disorder.
Other possible tests include:
- Tympanograms – for measuring pressure in the ear canal and tympanic membrane traffic research;
- Audiogram – for the measurement of hearing;
- Inspection of the nose and nasal.
Treatment of dysfunction of Eustachian tube
To fix a stuffiness in the ear, discomfort, or pain, You can try:
- Swallow, yawn, or chew gum, to normalize the pressure;
- Clean the ears, inhaling, and then gently exhaling air, While holding the nostrils and mouth closed.
If symptoms don't go away within a few hours or amplified, the doctor may recommend the following medications:
- Protivozastojnye remedies for nose;
- Antihistamines;
- Nasal steroids, to relieve nasal congestion and allow auditory tube open;
- Painkillers (eg, acetoaminofen or ibuprofen).
In rare cases, it may be necessary to miringotomija. The doctor makes an incision in the eardrum, to equalize pressure and drain the fluid.
Prevention of Eustachian tube dysfunction
To reduce the risk of barotrauma, it is recommended to perform the following actions:
- Avoid flying in a plane or scuba diving in the presence of allergies or colds;
- In flight:
- If you have any allergies or the common cold, need to use decongestants or antihistamines;
- You can yawn or chew gum. It is also recommended that you swallow, suck lollipops or drink water;
- During takeoff and landing need to clean ears, inhaling, and then gently exhaling, While holding the nostrils and mouth closed;
- You can use special earplugs, that slowly equalizes pressure in the ear. You can find them in pharmacies and airports.
