Operation during abdominal aortic aneurysm – Operation ABA
Description of operations for abdominal aortic aneurysm
The aorta is the largest artery in the body. The abdominal aorta carries blood to the abdomen, pelvis and legs. Sometimes the walls of the aorta weaken and become raised in any field. This is called abdominal aortic aneurysm (ABA). An aneurysm is most often caused by atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) and high blood pressure.
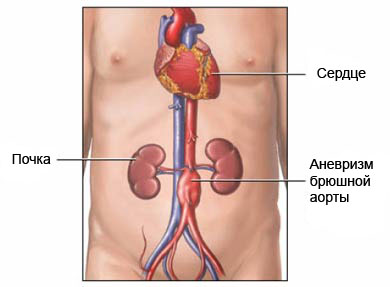
The need for surgery
Surgical treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysm is shown in the following cases:
- Physical discomfort (eg, abdominal pain);
- Aneurysm reaches a size of five centimeters or too fast increases in size. Smaller aneurysms require constant monitoring and the need for surgery is rare;
- Aortoclasia – the operation should be done immediately.
Preventive surgery in General provides good results for people, that are relatively healthy. Emergency surgery for aortic rupture is not much chance of survival, due to loss of blood.
Possible complications
Complications, that may arise during the operation abdominal aortic aneurysm:
- The negative reaction to a general anesthetic (eg, dizziness, low pressure, labored breathing);
- Infection;
- Bleeding;
- Damage to internal organs;
- Death.
The risk of complications increases as a result of:
- Emergency surgery due to aortic rupture;
- Heart trouble;
- Transient ischemic attack or stroke;
- Lung diseases;
- Weakening of the body due to cancer;
- Having diabetes;
- Obesity.
When it is necessary to do the operation?
The operation is performed in two cases. This can be done before (prevention) after a break or rupture of the aorta (serious condition). Prophylactic operation outline is described below.
Before the operation it is necessary to pass the following examination:
- Make x-rays of structures inside the abdomen;
- MRT – examination, which uses magnetic waves, to make pictures of structures inside the abdomen;
- Abdominal ultrasound – otsledovanie, that uses sound waves to study organs in the abdominal cavity;
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) – record heart activity by measuring electrical current, passing through the heart muscle;
- Go fluorography.
Probably also need to be examined by a cardiologist.
Before surgery
Maybe, I have to stop taking certain medications one week before surgery, in particular:
- Aspirin or other anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Blood-thinning medicines (eg, klopidogrela (Plaviks), varfarina, or ticlopidine).
On the day of the procedure, It will make the angle of the antibiotic. You can also take a laxative or enema, to cleanse the bowel.
Anesthesia
The operation is performed under general anesthesia.
Activity description
In most cases the incision from the sternum to below the navel. The doctor puts on clamps the aorta slightly above and below the aneurysm. Any blood clots (blood clots) on the inner side of the aorta are removed. In order to strengthen the area of the aneurysm wall using artificial dacron. This is called a graft. The graft is sutured to the healthy part of the aorta from both sides. Then the clamps are removed. The incisions are closed with stitches.
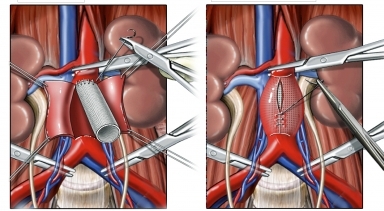
How long does the surgery?
The average time a single operation 4 – 6 hours.
Will it hurt during surgery?
Anesthesia prevents pain during the procedure. Most people experience an increase in body temperature after surgery, and little discomfort at the site of incision. The residence time in the hospital depends on the condition of the patient.
Nursing care after surgery
In the hospital
While in the hospital can be applied following the procedure:
The room in the intensive care unit for monitoring the state of the body.
- For the normal functioning of the body can be used additional funds:
- Urinary catheter - monitors urine output;
- The arterial catheter - blood pressure monitors;
- Central venous catheter - monitors the pressure in the heart;
- Epidural Catheter – It provides an introduction to pain medication;
- Levin tube – is inserted through the nose into the stomach to remove secretions and provide nutrition to restore normal bowel function.
Houses
You must perform the following actions, to ensure the normal recovery of the body:
- Follow the instructions for the care of postoperative suture;
- Gradually return to normal activities;
- To prevent further problems, Maintain a healthy lifestyle, Avoid high blood pressure. If you smoke, you must get rid of this bad habit.
You should immediately go to the hospital in cases:
- Redness, edema, strong pain, excessive bleeding, or discharge at the surgical site;
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills;
- Stomach ache;
- Backache;
- Any change of color or sensation in your legs;
- Burning, pain, or problems with urination;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Abdominal cramps or diarrhea;
- Unusual fatigue or depression;
- Disorientation or confusion;
- Numbness or tingling in the legs;
- Cough, breathlessness, chest pain.
