Malignant breast tumors
Sarcoma of the breast
In addition grandular proliferous cyst in the breast may be other types of sarcomas: angiosarkoma, stromal sarcoma, liposarcoma, lymphosarcoma, etc..
Neinfiltriruyuschy lobular (alveolar, acinar, carcinoma in situ) mammary cancer
When cytology punctate or fingerprint removal of benign tumor found large atypical cells with large round-shaped light or moderately hyperchromatic nucleus and cytoplasm general. Cells are arranged separately and in small groups.
Neinfiltriruyuschy intraduct breast cancer
Neinfilytriruyushtiy vnutriprotokovыy cancer It is characterized by moderately polymorphic cells of average size with a large hyperchromatic nucleus. Cells are located separately, clusters in the form of papillary formations in violation of cell polarity.
Infiltrating breast cancer
Histologically, there are three grade infiltrating cancer.
Infiltrating cancer, grade I
Infiltrating cancer grade I in most cases is adenocarcinoma.
Microscopically punctate tumor characterized by a relatively similar round cells predominantly mid-sized to large, eccentrically located hyperchromatic nuclei. The cytoplasm of cells with a fine-grained or large granules, resemble those in the apocrine cells. Cells are located separately, large clusters, as well as groups in a zhelezistopodobnyh and papillary structures.
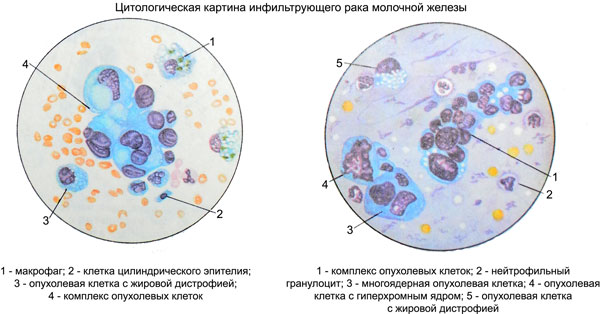
Infiltrating cancer, grade II
The cells in cytological preparations vary in size, polymorphic, with large hyperchromatic, often vesicular nuclei, containing large nucleoli. The cytoplasm of the cells is relatively wide, inhomogeneous, often with signs of secretory activity, not always clearly contoured edges.
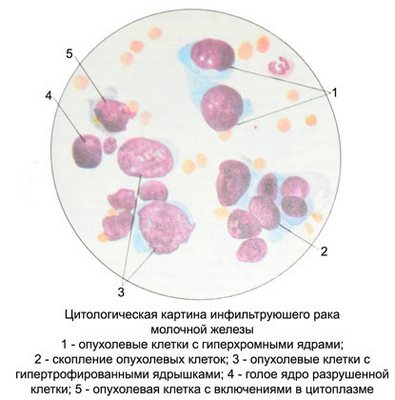
When fibrous cancer (scirrhoma) in cytological preparations are detected small tumor cells with large hyperchromatic nucleus without nucleoli and a narrow rim of basophilic cytoplasm. Signs absent secretion. Cells are located separately, in the form of small groups, and tissue scraps.
Infiltrating cancer grade III
In cytological preparations are found cells with distinct signs of malignancy. The size and shape of the cells are different, often there are large and even giant cells with large hyperchromatic light or, irregularly shaped nuclei, containing a significant number of large nucleoli. There may be two- and multi-cell. Many cells in the pathological state of mitosis. The cytoplasm of cells of different widths, often abundant, homogeneous or fine-grained.
Cells are located separately, clusters, groups, sometimes in the form syncytia and symplast.
In cases of infiltrating breast cancer all grade marked lymphoid- tion and plasma cell infiltration, most pronounced in cancer III grade.
Special histological types of breast cancer
Medullary breast cancer
Scraping punctate and abundant, prints tumor juicy. Cytological picture monomorphic. Dominated polymorphic atypical epithelial cells of round shape with a round nucleus, located centrally or eccentrically. Chromatin kernels or fine tyazhisty, uniform.
Hyperchromia cores is not expressed, small nucleoli, single or multiple. The cytoplasm of epithelial cells has the form of a narrow rim with irregular contours. Arranged in isolation cells, but densely, multicellular structures do not form. There are clusters of cells piled haphazardly, Numerous cells in mitosis, isolated macrophages, fibroblasts, fibrocytes, lymphocytes.
A large number of lymphocytes is observed in tumors with lymphoid stroma, characterized by a more favorable prognosis. However, when the puncture needle can get to the lymph node, in which case the lymphocytes in the preparation are not related to tumor.
Papillary breast cancer
Punctate tumor sanioserous, with small patches of grayish. Against the background of structureless mass, fragments of the nuclei and cytoplasm of cells destroyed, including macrophages, gistiocitov, neutrophils and lymphocytes revealed monomorphic abnormal cells (slight, average, occasionally large) with intensely colored polymorphic nuclei, having irregular contours. The nucleoli are not visible. The cytoplasm bazofylna. Cells are located mainly in the form of papillary complexes, often with a bizarre shape, and piecemeal. The cells, located separately and on the periphery of the complexes, pronounced fatty degeneration and vacuolization.
Slime breast cancer
Aspiration tumor material and scraping the mucous nature. Microscopic examination against the background of blednookrashennyh (by Pappenheim) in blue-gray color of the mucous masses detected homogeneous structure, atypical small, medium and large epithelial cells with eccentrically located, mostly bean and crescent-shaped, nucleus and abundant cytoplasm. These cells resemble proliferating epithelia.
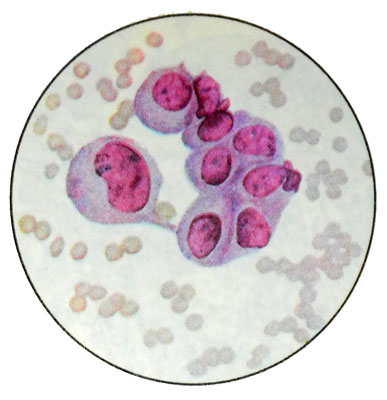
They are intensely colored, the boundary between the nucleus and the cytoplasm, they often lubricated. Fuzzy boundaries between cells. Abnormal cells are arranged in isolation, in small clusters and groups zhelezistopodobnyh. In a small number of low-grade abnormal cells are found, lymphocytes, sometimes snatches of capillaries.
Slime breast cancer from signet ring cell
Scraping and punctate, usually, mucous character. Microscopic examination against the background of the mucous masses (Sometimes there is no mucus) abnormal cells are detected homogeneous large and medium-sized, round shape. Eccentric nucleus bean, oval or circular shapes are sometimes concavity, painted hyperchromic.
The cytoplasm is extensive, Pale, basophilic, painted unevenly, its boundaries are often fuzzy. The outer layer of cytoplasm lighter, imperceptibly merges with the background of the drug. Dominated atypical signet ring cells with a nucleus, shifted to the periphery, and extensive colorless cytoplasm, filled vacuole. The signet ring cells, mucus, sometimes you can find the rejection of the cytoplasm. Signet ring cells are arranged separately and clusters, often in the form of strands.
Cancer Paget
Research exposed scrapings, Taken from the surface of the skin ekzemopodobnoizmenennoy breast nipple, representing a flake or plate dryish fabric scraps. Sometimes investigated punctate of compacted areas of the nipple or areola, prints eroded or ulcer surface of the nipple and nipple discharge, which appear at a significant distribution of tumor deep into the prostate.
Punctate, usually, bloody nature, grayish fabric scraps, and highlight the various: serous, spotting, purulent.
Microscopic examination against the background of neutrophilic granulocytes, lymphocytes, plasma cells, gistiocitov, macrophages, polyblasts, fibroblasts, fibrocytes and fine detritus (with concomitant inflammation), as well as the cells of stratified squamous epithelium with enlarged nuclei detected light of the same type of large and giant atypical squamous cells irregularly rounded, oval, polygonal shape with clear margins.
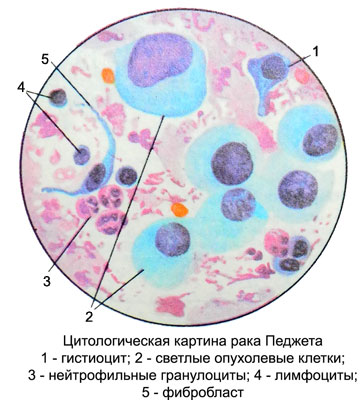
Kernels large, bright, round or oval, located in cells of the central or eccentric. Chromatin Punctate, evenly distributed. In most of the available cores 2-3 hypertrophied nucleolus. The cytoplasm is moderately expressed or abundant, light, Pale, basophilic, fine-grained. Often around the nucleus it is painted more intensively, than cells at the periphery. Cytoplasm wavy contours, often unclear. Sometimes, there are observed effects dystrophy (adipose, vacuolar). Cells are arranged separately and small beds.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the breast
The discharge from the nipple and breast tumor punctates, often bloody nature with tiny fabric scraps, They can be identified elements of squamous cell carcinoma of the three degrees of maturity (highly differentiated, moderately differentiated and poorly differentiated). Atypical squamous cells of breast cancer did not differ from those of squamous cell cancers of other sites.
For the detection of squamous cell carcinoma and determine the extent of its differentiation is essential to start with native microscopy preparations, which is easy to diagnose abnormal cells in actinic opacity dense cytoplasm pearlescent (in preparations stained by Pappenheim stratum cytoplasm intensely- of blue color). A high degree of differentiation of squamous cell carcinoma show actinic atypical cells and the presence of specific groups of cells in the form of rods, cancer "pearls" (bulbs). In moderately differentiated cancer pronounced polymorphism of cells, actinic not observed in all atypical cells, they are often placed in a heap of scraps of fabric separate tumor cells. When poorly differentiated cancer actinic missing.
For squamous cell carcinoma is often characterized by marked degenerative changes (vacuolation, fatty degeneration, disintegration of cells). Often the background of the preparation of the constituent elements of blood (erythrocytes, neutrophilic granulocytes, lymphocytes), and stromal cells (gistiocitы, fibrocytes, fibroblasts etc.), fine detritus.
Apocrine breast cancer
Apocrine carcinoma relates to highly malignant tumors with low differentiation of parenchyma cells, retain the ability to apokrinizatsii, at which it is relatively easy to recognize. The secretions or breast punctates on the background of grainy structureless mass of decaying atypical cells are found, bright, large round epithelial cells, prismatic or cubic form.
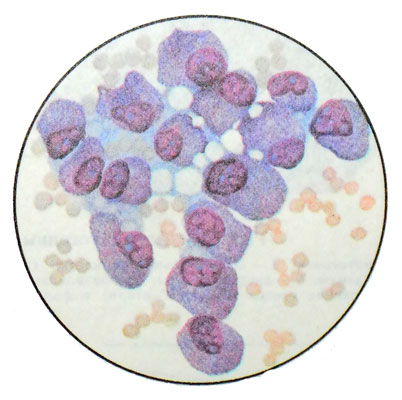
The nuclei of different sizes, mostly round or polymorphic, with rough chromatin glybchatym, eccentrically located in the cell, and occupy a large part of it. They contain polymorphic hypertrophied nucleoli. Cytoplasm abundant, light, anisochromatic, with light blue, sirenevato gray and pink areas, It contains azurophilic granules, are unevenly distributed in the cytoplasm, or collected in the apical part. May be cells without granules. The boundaries of cells fuzzy, often merge with the background of the drug. There are cells of the apical part of cytoplasm rejects.
Metastatic breast tumor
The mammary gland is often a wide variety of tumors metastasize, cytogram which differ little from cytograms primary breast tumors. The origin of the metastases can be set in cases, When metastatic disease (pigmentnaya melanoma, primary liver cancer, kidney cancer, seminoma, well-differentiated thyroid cancer and others.) maintains secretory activity or other signs, allowing it to differentiate.
If metastatic tumors accompanied by inflammatory processes or hyperplastic mammary gland, the cytologic diagnosis is much more complicated, since there is a large number of formulations elements inflammation and abnormal cells mammary epithelial cell proliferation in a state, metaplasia and dystrophy, which is not always easy to differentiate cancer cells.
