Жгутиконосцы – Morphology and development cycle of pathogenic protozoa
Of the numerous species of this class are most important Leishmania (transmitted by blood-sucking vectors) and trypanosomes, and Giardia (live in. kişkax) and various Trichomonas, that They are intestine, oral (opportunistic), urinary and genital organs.
There are three species of Leishmania (Leischmania), parasites in humans: L. tropica, L. braziliense, L. donovani
The main difference between Leishmania - presence in one of the stages of development of flagella (one or more). In the development of these parasites are two stages: bezzhgutikovuyu and flagellates, altering the shape.
Bezzhgutikovaya form of Leishmania Oval, size of 2-6 microns, kernel round, It takes up 1/3 cell, Next to it is a short kinetoplasts sticks. When stained with Romanovsky cytoplasm blue, the core of the red-violet, kinetoplasts intensely colored, than the core.
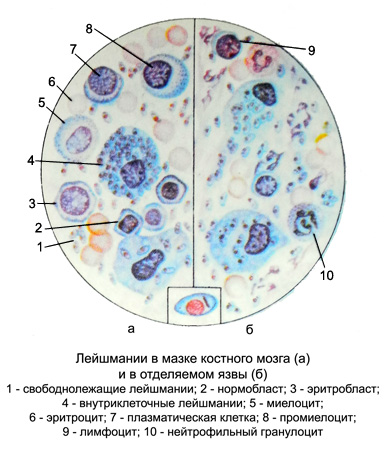
At this stage still Leishmania, flagella are absent. Bezzhgutikovaya form of Leishmania found in humans, dogs, rodents, parasitizing intracellularly in macrophages, bone marrow cells, spleen, liver (in a single cell to a few tens Leishmania). Leishmania multiply by simple division.
Flagellated form Leishmania - Extended, fusiform, a length of 10-25 mm and a width of 5-6 m. The core is in the midsection, kinetoplasts located at the forward end of the cell, It departs from the free flagellum (15-20 M). This form of mobile, It develops in the body of the invertebrate host transporter (Moschino) or in culture.
A mosquito becomes infected when hit in his stomach Leishmania (in the form bezzhgutikovoy) together with blood or tissue fluid. In the first day ingested parasites transform into mobile form, They multiply in the gut of mosquito and accumulate in his throat.
When an infected mosquito bites a person Leishmania penetrate the wound and introduced into the cells of the skin or internal organs (depending upon the species of parasite). L. tropica causes of human cutaneous leishmaniasis, L. braziliensis - mucocutaneous (American) и L. donovani - vistseralynыy leishmaniasis Mediterranean-sredneaziatskogo and indiyskogo (kala azar) types.
The final diagnosis is established on the basis of the detection of pathogens in blood smears (practically unsuitable for research), bone marrow, in the preparations of the infiltration of the skin, scraping the affected skin. In some cases, the method of sowing on the special environment.
Trypanosomes
For human pathogens are three types of trypanosomes, causing African (sleeping sickness) and the US (Chagas disease) Trypanosomiasis. In Europe, the only possible imported cases of the disease. The body is elongated trypanosomes, length 17 28 m, bottleneck, has flagella and undulating membrane. Inside it is located in the center of the core, closer to the rear end - kinetoplasts, from which extends a thread, running along the edge of the undulating membrane. Propagate by dividing the longitudinal trypanosomes.
In the initial period African trypanosomiasis parasites can be detected in the peripheral blood, in the later - in a punctate lymph nodes, and in the stage of central nervous system is the most informative study of the cerebrospinal fluid.
In the acute phase American trypanosomiasis parasites can be detected as a flagellate stage, in the later period, they are in bezzhgutikovoy step in myocardial cells, and other muscle, as well as in cells of the central nervous system. The intracellular form of the parasite rapidly multiply, forming clusters, they can be detected only during the opening.
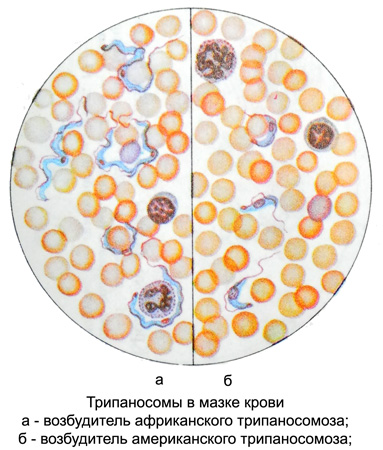
In the study of fresh drop of blood products, mixed with sodium citrate, либо пунктат лимфатического узла, или спинномозговую жидкость помещают на предметное стекло, накрывают покровным и исследуют под микроскопом. Подвижные паразиты заметны даже при малом увеличении. Мазки и толстую каплю красят по Романовскому: тело паразита окрашивается в голубоватый, ядро и жгутики — в красный цвет. Если в препаратах возбудитель не обнаруживается, прибегают к заражению лабораторных животных: на второй-третий день после подкожного или внутримышечного введения белым мышам исследуемого материала в их крови появляются паразиты. При затруднениях в диагностике проводятся посевы на питательные среды, а также используются специальные серологические реакции.
Лямблии
Практический интерес представляет Intestinal inflammation — кишечная, паразитирующая в двенадцатиперстной и тонкой кишках и вызывающая лямблиоз. Цикл развития лямблий включает вегетативную стадию и стадию цисты.
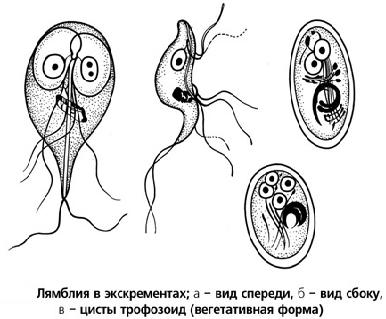
(cm. incl., rice. 104)
В вегетативной стадии лямблия активная, moving, грушевидной формы, длиной 9—18 мкм, шириной 7—10 мкм. Передний конец тела лямблии закруглен, задний заострен. Тело лямблии состоит из двух симметричных половин, разграниченных аксостилем, от каждой половины отходят по четыре жгута, каждая половина имеет ядро. В переднем отделе тела лямблии имеется присасывательный аппарат. Движение лямблий поступательное, иногда вращательное (паразит все время как бы переворачивается боком). В цитоплазме включений нет.
Размножаются лямблии делением. В препаратах при комнатной температуре быстро погибают. Лямблий в вегетативной стадии легко обнаружить в содержимом двенадцатиперстной кишки. С испражнениями они обычно не выделяются, но при поносе их можно найти в жидком свежевыделенном кале. В желчном пузыре лямблии не обитают, так как протеолитические ферменты желчи действуют на них губительно. При зондировании лямблии обнаруживаются в желчи при попадании их со стенок двенадцатиперстной кишки.
В нижних отделах кишок условия для жизни паразитов неблагоприятные и они превращаются в цисты (обычно встречаются в оформленном кале) -- неподвижные, oval, размером 8—14 мкм. Оболочка цист толстая, double-circuit, четкая. Раствором Люголя жизнеспособные цисты окрашиваются в коричневато-желтоватый цвет, погибшие — в голубоватый: видны два или четыре ядра, аксостиль, жгуты. Цисты хорошо сохраняются во внешней среде, getting. в полость рта, а затем в кишки, они превращаются в вегетативные формы.
Диагностическое значение обнаружения лямблий и вопрос об их патогенности до сих пор являются спорными. Ряд ученых считают лямбдой непатогенными. По мнению других, они могут вызывать механическое раздражение слизистой оболочки кишок, затруднять всасывание жиров и жирорастворимых витаминов, ухудшать течение других заболеваний пищеварительного канала и желчных путей.
Трихомонады
В организме человека паразитируют три вида трихомонад:
- кишечная — обитает в толстой кишке, грушевидной формы, diameter 10 m, имеет в переднем отделе пять жгутиков; движение беспорядочное суетливое; цист не образует, непатогенна;
- ротовая — по строению похожа на кишечную, непатогенна;
- влагалищная — вызывает мочеполовой трихомоноз (trichomoniasis).
