Gastrointestinal bleeding, blood in the gastrointestinal tract: What's it, causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
Gastrointestinal bleeding; Lower GI bleeding; GI bleeding; Upper GI bleeding; Hematochezia
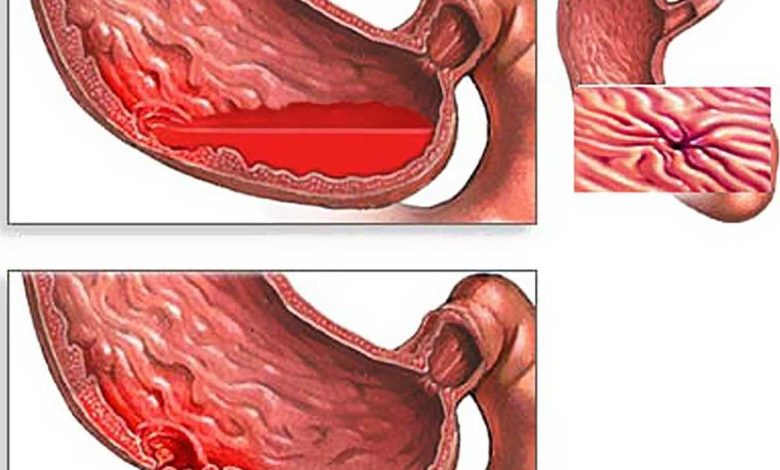
Gastrointestinal bleeding
Gastrointestinal (LCD) bleeding is a, in which bleeding occurs from any part of the gastrointestinal tract. This bleeding could be from the stomach, small intestine, colon (colon) or rectum. Gastrointestinal bleeding is a serious condition and can cause blood loss, dehydration, anemia and can even be life-threatening, if left untreated.
Gastrointestinal bleeding is usually caused by an infection, ulcer, polyp, tumor or rupture of the lining of the gastrointestinal tract. It can also be caused by certain medications., bleeding disorder or inflammatory bowel disease.
Bleeding can come from anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract, but it is often divided into:
- Bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract: the upper gastrointestinal tract includes the esophagus (tube from mouth to stomach), stomach and first part of the small intestine.
- Bleeding from the lower GI tract. The lower gastrointestinal tract includes most of the small intestine, large intestine or intestines, rectum and anus.
Causes of gastrointestinal bleeding
Gastrointestinal bleeding may be caused by non-serious conditions, including it can cause:
- Anal fissure
- Hemorrhoids
Gastrointestinal bleeding can also be a sign of more serious diseases and conditions.. These may include cancers of the gastrointestinal tract, such as:
- Colon cancer
- small intestine cancer
- Stomach cancer
- Intestinal polyps (a precancerous condition)
Other causes of gastrointestinal bleeding can be:
- Abnormal blood vessels in the intestinal mucosa (also called angiodysplasia)
- Bleeding diverticulum or diverticulosis
- Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis
- Varicose veins of the esophagus
- esophagitis
- Gastric ulcer
- Intestinal intussusception
- Mallory-Weiss syndrome
- Meckel's diverticulum
- Radiation damage to the intestines
Gastrointestinal bleeding symptoms
Symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding vary depending on the location of the bleeding.. Signs and symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding may include:
- Anemia: paleness, fatigue, breathlessness, palpitations and feeling weak or dizzy.
- Blood in the stool. Fresh and red blood indicates bleeding from the lower gastrointestinal tract (from the colon), whereas darker, tarry stools may indicate bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract (from the stomach).
- Vomiting blood: vomiting with blood, fresh (red) or dark (black).
- Abdominal pain: pain or cramps in the abdomen.
- Fever. Fever can occur with infections or inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
When to contact a healthcare professional
If you experience any symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding, it is important to seek immediate medical attention. It is also important to see a doctor, if you have previously had gastrointestinal bleeding.
Seek immediate medical attention, if:
- You have black tarry stools (it could be a sign of gastrointestinal bleeding)
- you have blood in your stool
- You vomit blood or vomit, similar to coffee grounds
Questions, that your doctor may ask
Your doctor may ask you a number of questions, to better understand your condition, eg:
- How long do symptoms last?
- Do you have other diseases?
- Are you taking any medication?
- Have you had a history of bleeding disorders or inflammatory bowel disease?
- Are you experiencing any abdominal pain?
- Do you have a family history of gastrointestinal bleeding?
Diagnosis of gastrointestinal bleeding
To diagnose gastrointestinal bleeding, your doctor may perform a physical examination, and then order tests, such as:
- Blood test: to check for anemia and other signs of infection or bleeding.
- Endoscopy: a flexible tube with a light and a camera at the end is used to view the entire gastrointestinal tract, which can reveal the cause of bleeding.
- CT scan. CT scans can be used to look for tumors or other blockages in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Colonoscopy. The camera is used to view the entire colon for polyps., tumors and other abnormalities, which can cause bleeding.
- Fecal studies. Stool samples are checked for blood or parasites in the stool.
Gastrointestinal bleeding treatment
Treatment for gastrointestinal bleeding depends on the cause and severity of the bleeding.. Treatment options may include:
- Medicines. Some forms of gastrointestinal bleeding can be treated with medication, such as antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Operation. In some cases, surgery may be required to remove a tumor or repair damage to the gastrointestinal tract..
- Angiography. Angiography is a procedure, which uses a special dye and x-rays to pinpoint the source of bleeding.
- Endoscopic treatment. Endoscopic procedures are used to block or stop bleeding, closure of bleeding vessels or removal of tumors or polyps.
- Blood transfusion. If the bleeding is heavy, blood transfusion may be required.
- Dialysis. In some cases, with significant bleeding, It may require dialysis.
Home treatment for gastrointestinal bleeding
In case of gastrointestinal bleeding, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. But there are some procedures, which you can make at home, to manage and relieve symptoms:
- Drink plenty of fluids, to prevent dehydration.
- Avoid taking any medication, which can cause irritation of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Avoid spicy or acidic foods, which can cause irritation of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Limit your activity and get as much rest as possible.
- Eat soft, tasteless food, like mashed potatoes, applesauce and boiled cereal.
Prevention of gastrointestinal bleeding
In addition to seeking medical attention for gastrointestinal bleeding, you can make some lifestyle changes, to reduce the risk of developing this condition:
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Eat a balanced diet, including plenty of fresh fruit, vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Manage stress and get regular physical activity.
- Take steps to prevent gastrointestinal infections, eg, wash your hands and avoid contaminated food and water.
- If you are taking medicines, talk to your doctor about the risks, associated with specific drugs.
Gastrointestinal bleeding can be a life-threatening condition, and it is important to seek immediate medical attention, if you are experiencing any symptoms. Making lifestyle changes, to reduce the risk, and telling your doctor about your medical history, you can reduce your risk of developing this condition.
Used sources and literature
Kovacs TO, Jensen DM. Gastrointestinal hemorrhage. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 126.
MeguedDician by, Goranick e. Gastrointestinal bleeding. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen’s Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 27.
Savides TJ, Jensen DM. Gastrointestinal bleeding. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 20.
