Zhelezodefitsitnaya anemia
Anemia, associated with iron deficiency - One of the most common diseases. Most often it occurs in women.
When this type of anemia reduced iron content in blood serum, bone brain and blood pool. As a result, the formation of hemoglobin is broken, and further - erythrocytes, there is hypochromic anemia, developing trophic disorders in the tissues. Prior to the development of anemia in patients showing signs of tissue iron deficiency - latent iron deficiency.
Exchange iron
Iron - one of the most important basic constituents of the organism, despite the fact that its mass is normally only 0,0065 % body weight. According to reports, in an adult weighing 70 kg contains 4,5 g of iron.
Almost all of the iron, which is part of the body, It is part of various proteins. The most important of them - hemoglobin, whose function - to transport oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. In the molecule heme iron is associated with protoporphyrin. In addition to heme in hemoglobin is part of myoglobin, cytochromes, catalase, lactoperoxidase.
The main protein, containing iron and having no heme group, It is ferritin. Iron is a part derived ferritin - hemosiderin. Protein transferrin, transporting iron, It contains a heme group. Nonheme iron is part of a series of enzymes - aconitase, ksantinoksidazы, NAD-N-degidrogenazy.
The main part of the body's iron (57,6 %) a part of the hemoglobin contained in red blood cells.
A considerable amount of iron contained in the muscles (27,9%), and most of it is iron, included in ferritin (69,1 %), and the rest is included in the myoglobin (21,9 %). In the liver delayed 7,8 % iron the body, mainly consisting of ferritin and hemosiderin.
Protein plasma - transferrin - Binds iron in serum and transfers it to the bone marrow and other tissues. Transferrin refers to the β-globulins. Its molecular weight of about 80000. This protein consists of a single polypeptide chain, having two active sites, each of which can bind one atom of iron in the trivalent form. A transferrin molecule contains four groups of sialic acids.
Iron absorption
The basic amount of iron absorbed in the duodenum, and in the initial part of the jejunum. It is now known, that iron absorption is determined by the levels of it in the body. The greater the iron deficiency, the farther the small intestine extends iron absorption zone and the greater its absorbed.
The mechanism of iron absorption so far can not be considered solved. There are a number of hypotheses, explain the mechanism of regulation of iron absorption, but none of them fully explain all the known facts.
- The process of iron absorption in the human body includes the three components:
- and) penetration of iron into the mucosa of the intestinal lumen;
- to) penetration of iron from the intestinal mucosa into the blood plasma;
- in) replenishment of iron stores in the mucosa and their influence on the absorption.
Permeation iron mucosally from the lumen of the intestine is always great, than the speed of supply of iron from the intestinal mucosa into the blood plasma. Although both values depend on the needs of the organism in iron, penetration of iron into the intestinal mucosa is less dependent on the content of it in the body, iron than the penetration of the mucosa to the blood plasma.
With increased demand for iron speed it enters the blood plasma of the mucosa close to the speed of penetration into intestinal mucosa. Iron with virtually no delayed mucosa. Time of passage through the iron intestinal mucosa It is a few hours. During this period she refractory to further absorption of iron. After some time, the suction process is resumed with the same intensity.
By reducing the body's need for iron in the penetration rate of its intestinal mucosa is reduced, even more reduced intake of iron from the mucosa into blood plasma. A large part of the non-absorbable iron is deposited in the form of ferritin.
Now it is proved, that the absorption of iron, a member of the heme, very different from the absorption of ionized iron. Heme molecule decomposes not in the intestinal lumen, and its heme absorption mucosa occurs much more intensively, than inorganic iron absorption food.
At normal body iron only a certain part of it passes through the intestinal mucosa into the blood stream, and the rest is retained in the mucosa. With a lack of iron in the body mucosa is delayed significantly smaller part, main falls into the blood plasma. With an excess of iron in the body of the main part, penetrated into the mucosa, delayed it. In the future, the epithelial cells of the mucous membrane, filled with iron, exfoliated and excreted in the feces with iron nevsosavsheysya.
This physiological mechanism of the suction effect in those cases, when in the lumen of the intestine are edible mass with the usual, normal iron concentration. If the concentration of iron in the diet exceeds physiological tens and hundreds of times, absorption of ferrous ion is many times increases. This should be taken into account when treating patients with salts of bivalent iron. Trivalent iron is virtually not absorbed almost any physiological concentrations, even more so in excess.
Iron absorption, contained in the food, is strictly limited. During the day, virtually not absorbed more 2 mg.
Iron is found in many foods like vegetable, and animal. The high concentration in meat, liver, kidney, and from plant products - in soybeans, Petrushka, peas, spinel, Dried apricots, prunes, raisins. Significant to the amount of iron contained in rice, bread.
However, the iron content of the product does not determine the possibilities of its absorption. It is not the amount of iron in the product, and its absorption of this product. So, of products of plant origin iron is absorbed very limited, and animal products, especially beef and veal, a much larger quantity of. Iron, included in the composition of proteins, containing heme, It absorbed much better, than iron, ferritin and hemosiderin. Therefore, absorption of iron from the liver and significantly less fish, than meat.
On the absorption of iron is influenced by several factors. Some of them attached great importance, than they deserve, some - less. So, a lot of research devoted to studying the effect on iron absorption of gastric secretion.
Hydrochloric acid It has an undeniable influence on the absorption of iron, is in a trivalent form. This applies to both salt glands, and to iron, incorporated in a food. However, the absorption of radioactive iron into bivalent form, that has been added to bread, independent of gastric secretion. It also has no effect on iron absorption, a member of the heme.
Doubtless effect on iron absorption has a number of substances. So, oxalates, phosphates form a complex with iron, which reduces its absorption.
Substances, enhancing iron absorption – ascorbic, succinic acid and pyruvic, fructose, sorʙit.
Iron absorption is also enhanced under the influence of alcohol.
Transporting iron to blood cells
Proceeding in blood, Iron binds to transferrin, which transfers it to the bone marrow erythrokaryocytes. One molecule transferrin adds two atoms of iron. Besides, Transferrin transports iron from cells, where his stocks, to the red bone marrow nucleated cells, as well as the phagocytic macrophages, where iron breaks, bone marrow cells and sites, where stored iron stores. One molecule transferrin adds two atoms of iron.
On membranes erythrokaryocytes and reticulocytes are specific sites for reversible attachment of transferrin.
After transferrin delivers iron to the surface erythrokaryocytes, It penetrates the cell. In most cases returned to the plasma transferrin, but some of its molecule erythrokaryocytes penetrate and bind to the carrier molecule - protein with a molecular weight 20000. Described protein sideroxilin, that binds iron in the cell and transfers it for hemoglobin synthesis and ferritin.
Iron, optionally in a complex with transferrin or siderohilinom, It penetrates into mitochondria, where there is a synthesis of heme and iron protoporphyrin. Further changes transferrin unknown. Education takes place in ferritin from apoferritin eritrokariotsite, synthesized within the cell, and Fe, penetrated into a cell.
Most likely, what eritrokariotsite ferritin synthesis is required to remove excess iron from the cell, not logged in hemoglobin. This is going to ferritin in the lysosomes, and then removed from the cells in the bone marrow, and peripheral blood. During removal of the iron nuggets from the circulating cells, apparently, participates spleen, since human erythrocytes, from which it was removed on the injury in the absence of diseases of the blood, found iron nuggets, whereas normally determine their mature erythrocytes fail.
Iron reserves
The main protein, used to store excess iron in the body, It is ferritin. It is a water soluble complex of ferric hydroxide and protein apoferritin. Iron hydroxide attached to the rest of phosphoric acid.
The shape of a walnut ferritin: walnut shells - a protein apoferritin, inside which are various amounts of iron atoms, almost flat against one another. Ferritin can accommodate up 4500 iron atoms, substantially one molecule contains about 3000 atoms. The molecular weight depends on the number of ferritin iron atoms, and this figure may vary. The average molecular weight is close to ferritin 460 000. Normally, plasma ferritin and there is practically almost all cells of the organism, but the basic fabric, in which it is incorporated - is the liver and muscles.
Hemosiderin - Protein, ferriferous, detected in phagocytic macrophages and their derivatives, bone marrow macrophages, spleen and liver stellate retikuloendoteliotsitah.
Hemosiderin - Is partially denatured and deproteinized ferritin. Immunologically it is completely identical to the ferritin. Ferritin molecule contains 20 % gland, hemosiderin in the contents of his higher - 25 30 %. Unlike ferritin, hemosiderin insoluble in water.
As hemosiderin, and ferritin proteins used as stock, However, ferritin is consumed much faster, than hemosiderin.
Normally, the bulk of the iron, bound to transferrin, the body uses for erythropoiesis. Fagotsitiruyushtie macrophages, received iron in the destruction of red blood cells in them, basically pass it on iron-transferrin, which uses it again for erythropoiesis.
Parenchymal cells also contain iron, but preferably in the form of stock, only a small part of it is transferred to transferrin, and is used for erythropoiesis. Parenchymal cells, in turn, obtain iron from transferrin, but, Unlike iron macrophages, it is consumed slowly.
Vitamin C increases the release of iron sludge macrophages, but it does not affect osvobo. Suppress it from the parenchymal cells. When bleeding the release of iron from parenchymal cells increases, and when massive transfusion is reduced. However, if bleeding is reduced capture erythrocytes and macrophages, Consequently, iron release by macrophages in this situation is less important.
Loss of body iron
In males, within days of iron loss in the urine, faeces, then, exfoliated epithelium of the skin up 0.6-1 mg. Non-menstruating women have the same performance, and that in men. Iron loss in menstruating women is much higher due to menstrual bleeding, consumption of iron during pregnancy, delivery, Lactation. According to various researchers, they range from 2 to 79 mg during one menstrual, averaging 15 mg. In calculating the one day of the month under normal menstrual loss of iron from the body, women make up 0,5 to 1,2 mg.
During pregnancy iron loss reach 700-800 mg, with a higher demand for it - 800 1200 mg. For the compensation of losses of iron by the body of women during pregnancy requires 3-3.5 years.
The etiology and pathogenesis of iron deficiency anemia
The most common cause of iron deficiency anemia are blood loss, especially long-term permanent, although minor. Thus the amount of iron, lost by the body, exceeds the amount, that a person can get from food.
The possibilities of physiological absorption of iron from food is limited. The iron content in the normal daily diet of an average of 15-18 mg, of them can be absorbed 1-1.5 mg, and for an increased need for iron - 2 mg. Hence, Iron deficiency develops in conditions, accompanied by a loss of more than one day 2 Iron mg.
Men physiological iron loss urine, faeces, then, sluschivayushimsya epithelium of the skin does not exceed 1 mg, Therefore, when a sufficient amount of iron in the diet, normal intestinal absorption and no blood loss (from the stomach and intestines, urinary organs, and others.) iron deficiency have not developed.
Women Physiological iron loss the body more, than men due to the loss of iron during menstruation, pregnancies, childbirth and lactation. In connection with this female iron requirements often exceed the capacity of his food intake, which is the most common cause of iron deficiency anemia have.
The daily iron requirement in women, lost during menstruation 30-40 ml of blood, 1,5-1.7 Mg. If heavy and prolonged menstrual iron requirement in women increases to 2.5-3 mg per day, however, this amount of iron can not be absorbed even with a significant content in the food. In fact, this amount is compensated for only 1.8-2 mg per day and per month, thus, a deficiency of iron in the body is 15-20 mg. During the year, the deficit increased to 180- 240 mg, and for 10 years - up to 1,8 2,4 g. Even with less blood loss can occur an imbalance between iron requirements and it enters the body. This is the main cause of iron deficiency in women.
Of great importance in the pathogenesis of iron deficiency anemia in pregnant women has. Usually, pregnancy and lactation without previous iron deficiency does not lead to a significant reduction of body iron stores Women. However, when the second pregnancy, came in a short time after the first, or during the first pregnancy, emerged on the background of the previous latent iron deficiency, there is a significant shortage of iron in the body. With each pregnancy, childbirth, lactating woman loses not less than 700-800 mg of iron.
An important role in the etiology of iron deficiency anemia as a result of blood loss plays bleeding from the stomach and intestines. They are the most common cause of iron deficiency in men and the second leading cause among women. Such bleeding may be due to gastric ulcer or duodenal ulcer, tumors of the stomach or intestines, diverticular disease of different localization, invasions worms, erosions of the gastric mucosa in the presence of hiatal hernia. From helminthisms, cause blood loss from the stomach or intestines, should first be noted hookworms and doses.
Blood loss from the urinary tract rarely cause iron deficiency anemia, but sustained release of red blood cells in the urine can lead to iron deficiency. Equally it relates to the loss of iron in the urine is not composed corpuscular hemoglobin, and when hemoglobinuria, and especially in patients gemosiderinurii paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (disease Marchiafava Michele) or hemolysin form of autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
In these cases, iron deficiency anemia, chronic hemorrhagic blood loss due to the outer.
Much less Iron deficiency anemia is found, due to blood loss in a closed cavity with a subsequent breach of iron reutilization. Such forms include iron deficiency anemia in isolated pulmonary siderosis. In this disease, there are constant bleeding in lung tissue. Red blood cells per diapedesin penetrate into the space between the basement membrane of the epithelium of the alveoli and pulmonary capillary endothelium. As a result of the collapse of red blood cells and hemoglobin iron in macrophages released, which lay there in the form of hemosiderin, since normally no mechanism reuse iron, contained in lung macrophages. Closely related to this mechanism in the pathogenesis of iron deficiency glomus tumors, into which is poured out blood without subsequent recycling of iron.
The same mechanism of iron deficiency can be observed in endometriosis, not connected with the cavity of the uterus. In these cases bleeding during menstruation occurs in women in the closed cavity, most often located ectopically. When you break a cyst blood pours into the uterus, in the gut, Airways, t. it is. blood loss occurs outside. If such a cavity is closed, iron is accumulated therein and not used for further erythropoiesis.
Earlier important in the pathogenesis of iron deficiency anemia was attached to a breach of gastric secretion, thought, that atrophic gastritis with Achille is the most common cause of iron deficiency anemia. However, further studies have shown, Akhil that can only contribute to the development of iron deficiency anemia in the presence of significant needs of iron in the body. This in itself is not a violation of gastric secretion leads to the development of iron deficiency anemia. As already indicated, hydrochloric acid significantly increases the absorption of ferric, slightly increases the absorption of ferrous and virtually no effect on the absorption of iron, a member of the heme.
Food, consisting of products of animal and vegetable origin, It contains iron in the form of heme, and in the form of Fe2+ and Fe3+, thus absorbed mainly iron, which is part of heme and is present as Fe2+.
The amount of iron, which can be absorbed lie normal secretion and ahilii, It is sufficient, to cover its normal expenses. With increased costs of iron absorption from food it increases significantly. This increase is more pronounced at normal secretion, than when ahilii. Thus, reduced gastric secretion may be an additional factor, contributing to the development of iron deficiency at elevated the body needs it.
Iron deficiency in adults can be linked to a violation of intestinal absorption in chronic enteritis, and after extensive small bowel resections.
Iron deficiency anemia is common in children, especially at an early age. It can develop as a result of inadequate intake of iron in the body of the child from the mother of prematurity, multiple pregnancy, refusal of the child from eating. Probably, in the pathogenesis of iron deficiency in a child, in some cases matters pronounced iron deficiency in the mother. A newborn iron deficiency anemia can be caused by the penetration of the blood of the fetus in the mother's bloodstream and into the bloodstream of another fetus (in multiple pregnancies). Anemia may occur in children, born by Caesarean section, as in this case, the child is often a part of the placenta and its blood at the time of dressing the umbilical cord remains in the placenta.
Children 2-3 years old comes relative compensation, hemoglobin often increases to normal, although latent iron deficiency may still be. At puberty, the newly created conditions for the development of iron deficiency, especially among girls. Increased growth during this period and the appearance of menses cause an increase in demand for iron. Often this join such factors, as a loss of appetite and poor diet, sometimes associated with a desire to lose weight. All that matters, most likely, and hormonal factors. So, proven, that androgens contribute to greater and more active erythropoiesis iron absorption, whereas estrogens do not have similar effects. The role of a congenital deficiency of iron in the pathogenesis of iron deficiency anemia in adolescents remains controversial.
ESSENTIAL, or idiopathic, iron deficiency anemia previously associated mainly with iron malabsorption due to reduced secretory activity of the stomach, Now, however, it proved, that the vast majority of patients with iron absorption is not reduced, and increased. Currently, there is a tendency to integrate into the group of essential iron-deficiency anemia All forms of the disease, in which you can not find it obvious cause.
The diagnosis of essential iron-deficiency anemia as it allows the physician to neglect the need for further examination of the patient. However, in patients of this group can often unrecognized bleeding from the stomach and intestines, sometimes associated with tumor.
On the other hand, under the guise of essential iron-deficiency anemia often occur more, much more rare forms of iron deficiency anemia:
- Isolated pulmonary siderosis;
- angioneuroma;
- violation of the iron reutilization.
Sometimes diagnosis of essential iron-deficiency anemia It puts patients with anemia if hypochromia erythrocytes with a high iron content (Thalassemia, violation of the synthesis of porphyrins, saturnism).
Clinical manifestations of iron deficiency anemia
Clinical manifestations of iron deficiency varied and dependent on a number of factors. With a lack of iron in the body is not immediately anemia. It is preceded by a long period of latent iron deficiency, when there is clear evidence of an impairment of its reserves in the body.
With a significant decrease in hemoglobin levels to the fore symptoms, caused by insufficient oxygen to tissues: weakness, dizziness, heartbeat, breathlessness, swoon. The frequency of these symptoms varies. Often patients complain of headache, most often appear in a poorly ventilated room. These symptoms are not unique to iron deficiency anemia, but in varying degrees,, with varying frequency and other forms of anemia.
For iron deficiency characterized by sideropenic symptoms:
- xerosis;
- cracked skin of hands and feet;
- bridou, or Zayed.
The cracks in the corners of the mouth observed in iron deficiency 10-15 % adults. Often marked a dramatic thinning of the nails, They expressed their fragility. In the most severe forms of iron deficiency anemia bulge nails replaced their flattening and even concave. As a symptom of iron deficiency is often described koilonychia (spoon-shaped nails).
Quite often there glossitis, manifested by pain and redness language, atrophy of his buds. Sometimes there dysphagia, which wrongly regarded as a tumor of the esophagus.
A characteristic feature of iron deficiency - muscular weakness. This symptom occurs in the vast majority of patients with iron deficiency anemia. Now it is proved, that muscle weakness - is a consequence not only of anemia, but the activity of α-deficit glitserofosfatoksidazy, which includes iron.
Probably, muscle weakness associated with voiding, observed in iron-deficiency anemia. These include the urgent need to urinate, bed-wetting, often observed in girls, and the inability to hold urine when you laugh, cough. The absence of cramps during urination, changes in urine. For iron deficiency characterized by the fact, that patients are often unable to stop the beginning of urination "
There is also a rapid accumulation of urine after injury, taking blood from a vein, painful injections, what, probably, due to the decrease in the number of ferritin, having antidiuretic effect.
The defeat of the stomach and intestines during iron-deficiency anemia manifest violation of gastric secretion, sometimes the development gistaminoupornoy ahilii. Almost half of the patients revealed atrophic gastritis. Children showing signs of violation of the intestinal absorption of fat, ksilozы, gland.
As for adults, and adolescents characterized dysgeusia, which is called Cock chlorotica. Thus patients often eat inedible substances (chalk, dentifrice, coal, clay, sand, raw cereals, dough, raw minced). Typically desire to eat ice (palofalija), addicted to the smell of kerosene, oil, gasoline, acetone, Gutalin, Exhaust trucks, galoshes, and even the smell of urine.
The cause of such symptoms is not completely clear. It is only to note a clear dependence of these unusual tastes of iron deficiency, since they are completely while taking iron supplements and often recur in the case of re-aggravation of iron deficiency anemia.
Laboratory tests for iron deficiency anemia
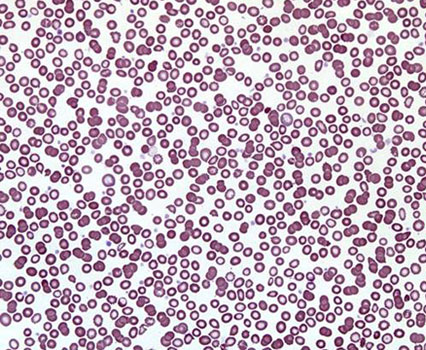
The most characteristic laboratory signs of iron deficiency anemia is gipohromnaya anemia. Although hypochromic anemia observed not only in iron deficiency, but a number of states, accompanied by a high content of iron in the body, most often it is found in iron deficiency anemia. Therefore, the identification of low color index should first get a doctor to suspect iron deficiency anemia.
The content of hemoglobin in iron deficiency anemia It can vary from 20-30 to 110 g / l depending on the severity of iron deficiency. The number of red blood cells may be normal or reduced to 1.5-2.0 T 1 l. Character, but the reduction of the color index or average concentration of hemoglobin.
Often, the laboratory gives the wrong data value of the color index, due to incorrect determination of both the content of hemoglobin, and the number of erythrocytes. So far in many laboratories to count red blood cells used photometric method. However, this method gives a very large error count of red blood cells in the case of reducing the color indicator, since the two erythrocyte hypochromia delay as much light, as normally holds one erythrocyte. Therefore, the application of this method to count red blood cells is not recommended. The second reason is an incorrect definition of the color indicator - the use of the old methods for calculating the hemoglobin content. Most of the error in the determination of hemoglobin gives a visual globinometer (gemometr Sali). Consequently, in practice its use impractical.
Not suitable as methods for the determination of hemoglobin in the ammonia or soda solution. Painting of the solution changes all the time, Optical density is reduced, and the error in the determination of hemoglobin becomes very large.
To determine the hemoglobin, especially in patients with anemia, shall be used gemiglobintsianidny method, and for the determination of the erythrocyte - method of counting in a counting chamber, or on the determination of red blood cell devices, recording the passage through the point count of erythrocyte (tseloskop or similar device), although sometimes small red blood cells slip through this point an ill.
At the wrong determination of hemoglobin or red blood cells in patients with severe iron deficiency anemia often, According to laboratory, color indicator is a mistake to close 1,0. However, when viewing high-quality blood smear revealed hypochromia erythrocytes. This requires the fixation of the smear with methyl alcohol. Laboratory doctors should not give blood for non-compliance and the quantities of color indicator erythrocyte morphology.
Also hypochromia erythrocytes for iron-deficiency anemia is characterized by their Anisocytosis, t. it is. unequal size with a penchant for microcytosis. If iron deficiency is expressed poikilocytosis, the shape of red blood cells is very different.
If iron deficiency is not only to reduce the content of hemoglobin, and erythrocyte. This reduction in the number of red blood cells is explained as a decrease in the rate of proliferation of nuclear erythroid elements compared to the norm, and the presence of significant ineffective erythropoiesis.
Besides, there is evidence of some shortening the lifespan of red blood cells in iron deficiency anemia. Nonetheless, mainly in its development it is still a violation of the formation of hemoglobin and therefore the color index at a low iron deficiency anemia.
The content of reticulocytes in iron deficiency anemia It could be normal (to 2 %), and sometimes somewhat elevated. Increased reticulocyte count in these patients is possible in the case of reticulocytes to study iron supplementation. The increase of reticulocytes may indicate also a significant bleeding in patients.
The contents of leukocytes It tends to decrease, often at the expense of reducing the number of neutrophils.
Platelet count in most cases the iron-deficiency anemia in a normal range, or (less often) increased, especially in the presence of any hemorrhage.
In the bone marrow in iron deficiency anemia significant pathological signs can not be determined. Number of cells, usually, normal. The histological preparation the ratio between red and yellow blood-forming bone marrow is not changed. Occasionally noted moderate hyperplasia. When cytological examination of bone marrow is sometimes found a moderate prevalence of red sprout.
For iron deficiency anemia, as well as for other forms of hypochromic anemia, characteristically violation gemoglobinizatsii erythrokaryocytes. It increased the number of basophilic and polychromatic erythrokaryocytes by reducing the content of forms oxyphilic. The number of megakaryocytes in the normal range or increased (in the event of major bleeding).
When iron deficiency anemia reduces the number of sideroblasts - erythrokaryocytes, iron-containing pellets. Normally, 20-40 % erythrokaryocytes bone marrow contain single pellets. When iron deficiency anemia in the case of color to reveal the blue iron pellets is practically impossible. The study of bone marrow sideroblasts help in conducting the diagnosis in the absence of certainty in the diagnosis.
Method for determination of serum iron
Among the biochemical methods of diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia is most commonly used method for determination of serum iron. For this purpose, the method is widely used Henry, and modifications thereof
Using previously used for the determination of iron reagents (orgofenantrolin, a-, a1-dipiridil) undesirable, as they give a very unstable complexes (rodanity), or painting the complex is very weak and virtually almost no difference between normal and abnormal.
In determining serum iron should be used only twice with distilled water, distilled in a glass distiller, wash all laboratory glassware, necessary for research, only in double distilled water, not to use it for drying a drying cabinet.
It is necessary to mention two very important circumstances. At first, Blood should be collected in a special tube, sterilized over steam or carefully washed twice with distilled water, wherein the second distillation of water must be carried out through the glass equipment. Ordinary distilled water, distilled through a metal distiller, It contains traces of metal, that during heating in an acidic medium can pass in the ionized form and inflate the findings. Usually, Sisters receive treatment from special biochemical laboratory test tubes for blood to determine serum iron. Secondly, sick, who has studied the iron content of blood serum, It should not take iron supplements at least five days.
Average iron content of blood serum - 12,5-30,4 mmol / l. In severe iron deficiency anemia is reduced to a level of 1,8-5,4 mmol / l, vыrazhennoy- with mild to 7,2-10,8 mmol / l.
Serum iron binding capacity
In addition the study determined serum iron serum iron binding capacity. Normally, approximately 1/3 transferrin is saturated with iron, and 2/3 Its free, I can attach a considerable amount of iron. Under the zhelezosvjazyvajushhej ability of blood serum is not the absolute amount of transferrin, a number of iron (in mikromoljah), that can mess with the trasferrinom (in 1 l serum). Normal total iron-binding capacity ranges from blood serum 50 to 85 mmol / l.
To determine unsaturated, or latent, zhelezosvjazyvajushhej ability subtract the amount of serum iron from General zhelezosvjazyvajushhej ability. Another indicator is the saturation ratio derived is the percentage ratio of serum iron and its General zhelezosvjazyvajushhej ability. Normally it ranges from 20 to 50 %.
For iron deficiency anemia is characterized by increase the total capacity of zhelezosvjazyvajushhej serum, significant an increase in latent zhelezosvjazyvajushhej ability and a sharp decline in the percent transferrin saturation. It should be noted, what, Although, on average, the majority of patients has increased total capacity zhelezosvjazyvajushhej, in some cases, it may remain normal. It is believed, that the definition of a common zhelezosvjazyvajushhej ability to some extent enables to estimate iron stores in the body. However, study the content of serum iron and zhelezosvjazyvajushhej ability of blood serum does not always reflect the iron stores in the body. So, eg, with anemia, associated with infection and inflammation, dropping the iron content in the serum with normal stocks it in the body.
Desferalovyj test
For evaluation of reserves of iron can also be used desferalovyj test. Desferal (desferoksamin) -chelating agent, selectively outputs of ions of iron- Is a product of the metabolism of Actinomyces Streptomyces pilisus; 100 weight parts of desferala are able to associate 8,5 part of the trivalent iron.
It is now known, that source of iron, included in complex with desferalom, There can be no haemoglobin, Neither transferrin. There is a certain parallelism between the iron content in the holdings in the form of ferritin and hemosiderin and amount of iron, excreted in the urine after the introduction of the desferala.
To determine the reserves of iron enters the patient 500 mg Desferal, after which is determined by the iron content in daily urine. Normal per day excreted 0.8-1.3 mg iron. In patients with iron deficiency anemia the iron content in the urine after the introduction of the desferala significantly less, than normal. In some patients it is reduced to 0,2 mg per day and more.
An exact match between the reserves of iron and its content in the urine after the introduction of the desferala cannot be. When conducting the test should take into account desferalovogo, that iron excretion with urine reflects not only his reserves in the body, but the degree of intensity of erythropoiesis and the breakdown of red blood cells.
Method for determination of serum ferritin
One of the currently used methods of valuation of stocks of iron in the body is method for determination of serum ferritin.
Although ferritin is a protein, contained in the tissues, previously thought, that he appears in serum in liver necrosis. In recent years, with the development of radioimmunnologicheskih methods of determining ferritin has been proven, that it is a certain amount of serum for all healthy people. When determining the serum ferritin, those methods are used labeled antibodies to ferritin or tagged ferritin. According to the literature, ferritin normal ranges often within 12-300 µg/l (ng / ml); in healthy women it averages about 34 ug / l, While for men is about 94 ug / l.
Method for determination of serum ferritin is now considered one of the best methods of research of stocks of iron in the body. It should be noted, that serum ferritin do not always reflects iron stores. It also depends on the speed of the liberation of the ferritin from tissues and blood plasma.
When iron deficiency increases the content of erythrocyte protoporphyrin. With a low level of iron in the blood serum of protoporfirinu nothing to communicate and it accumulates in erythrocytes. Besides, when iron deficiency increases the synthesis of protoporphyrin.
Normal erythrocyte protoporphyrin content ranges from 0,26 to 0,88 mmol / l. Enhancing its can be observed in various forms of hemolytic anemia due to the fact, that retikulocitah increases the synthesis of porphyrins. Drastically increased the contents of protoporphyrin in hereditary disease — Erythropoietic protoporfirii.
Differential diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia
Differential diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia should be carried out with other gipohromnymi anemia, those with a high content of iron: Thalassemia and anemia, associated with violation of the synthesis of porphyrins and heme.
After confirming the diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia, there is a need to clarify its genesis.
As it is known, the occurrence of iron-deficiency anaemia in women may be due to physiological blood loss. Evaluate the extent of blood loss during menstruation on difference in hemoglobin before and after it, because, At first, even a large blood loss did not lead immediately to reduce the level of hemoglobin, Secondly, these cases usually goes not about massive bleeding, and in a repeating a small blood loss, exceeded the ability of the iron intake to meet its consumption for many years.
The degree of blood loss from the stomach and intestines can be estimated using radionuclide studies. Erythrocytes patient mark in vitro 51Cr, launder and enter patient, then collect the feces and count its radioactivity. Normal amount of chrome stands out with feces, adequate loss no more 2 ml of blood. Because radioactive chromium practically stands out with the faeces only composed of erythrocytes, the radioactivity of feces can judge about losing blood. Melena only in those cases, When the volume of blood in the stool is greater than 100 ml per day. The reaction of Weber is positive only when you select during the day at least 30 ml of blood, and more sensitive reaction of benzidinovaja often gives nonspecific results (due to the heme, contained in meat food) and identifying blood, exceeding 15 ml per day.
Study of the stomach and intestines all patients should be carried out with outstanding genezom of iron deficiency anaemia. Even with heavy menstruation, continuing up to 6-7 days, a study using 51CR may reveal additional source of bleeding gastric tumor, colon, dyvertykulы, gut ulcers.
Where, When figuring out the clear cause of the iron deficiency cannot, by using radioactive iron to delete violation of intestinal malabsorption of iron in patients with severe forms of chronic enteritis, and in individuals, undergoing resection in the past significant Division of the small intestine.
Most hard to diagnosed iron deficiency anemia, associated with blood loss in a closed cavity (endometriosis, glomusnoj tumor, isolated pulmonary siderosis or Goodpasture's syndrome - a combination of isolated pulmonary siderosis with a severe form of glomerulonephritis), when hemoglobin levels decrease, but this assumption cannot be confirmed.
Isolated pulmonary siderosis — a comparatively rare autoimmune or immunokompleksnoe disease characterized by iron deficiency anemia, associated with hemorrhages into the basement membrane of the alveoli as a result of the presence of antibodies against the basement membrane antigen or deposition of immune complexes. This releases iron, which is not recycled and is deposited in the form of hemosiderin.
In isolated pulmonary siderosis, laboratory data indicate anemia of varying severity, hypochromia is noted, aniso-, poikilo- and microcytosis. Color index - 0.5-0.7. The leukocyte count is normal or elevated. Neutrophilia is noted, sometimes with a shift to metamyelocytes or myelocytes. Some of the patients determined by jeoziiofilija. Characterized by increased numbers of platelets. Iron content decreases serum, increases total iron-binding capacity, there is a sharp increase in ESR. In some patients, there is an increase in the content of γ-globulins in the blood serum, and for some it reaches 40 %. Proteinuria is sometimes detected, mild hematuria.
In addition to isolated pulmonary siderosis without kidney damage and Goodpasture's syndrome with a severe progradient course of kidney damage, there are intermediate forms of the disease, in which the picture of isolated pulmonary siderosis predominates, but there are slight signs of kidney damage (moderate proteinuria, mikrogematuriâ, single hyaline casts with normal relative density of urine, normal levels of creatinine and urea).
The color of the sputum may be normal, it may contain streaks of blood. In macrophages of sputum is determined hemosiderin. If no sputum bronchial washings are investigated for the presence of macrophages, contain hemosiderin.