Delayed or no tooth formation: what is this, causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
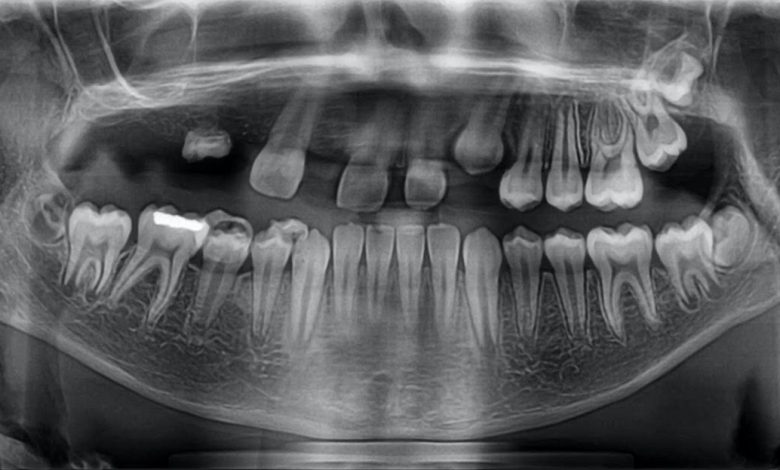
Tooth formation – delayed or absent; Delayed or absent tooth formation; Teeth – delayed or absent formation; Oligodontia; Anodontia; Hypodontia; Delayed dental development; Delayed tooth eruption; Late tooth eruption; Delayed dental eruption; Congenitally missing tooth
Tooth formation is a process, in which teeth develop into the jaw. Delayed or absent tooth formation can occur for a variety of reasons and can have a significant impact on a person's oral health..
What it is?
Delay or lack of tooth formation occurs, when one or more teeth do not develop at the expected time or do not develop at all. This can happen both with dairy (dairy), and permanent teeth. Delayed tooth formation is also called hypodontia., while the lack of tooth formation is called anodontia.
Causes of Delayed or Lack of Teeth Formation
There are several potential causes for delayed or non-forming teeth.. This includes:
- Genetics: some genetic disorders, such as clavicular dysplasia, can affect tooth development.
- Environmental Factors: exposure to certain chemicals or medications during pregnancy can affect tooth development.
- Nutritional deficiencies: lack of certain vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin D and calcium, may affect tooth development.
- Trauma: Trauma to the jaw or face can affect tooth development.
Symptoms of delayed or absent tooth formation
Symptoms of delayed or absent tooth formation depend on the number and location of affected teeth.. Common symptoms include:
- Cracks in the teeth
- Crowding of teeth
- Difficulty biting or chewing
- Speech difficulties
- Facial asymmetry
Diagnosis of delayed or absent tooth formation
The diagnosis of delayed or absent tooth formation is usually made during a dental exam.. The dentist will examine the teeth and jaw and may take x-rays or other imaging studies, to determine the extent of the problem.
Treatment of delayed or absent tooth formation
Treatment for delayed or absent tooth formation depends on the underlying cause, as well as the number and location of the affected teeth. Possible treatment options include:
- Orthodontic treatment: braces or other orthodontic appliances may be used to straighten teeth and eliminate crowding.
- Dental implants: missing permanent teeth can be replaced with dental implants.
- Prosthetics: the dentist can design and install artificial teeth, such as dentures or bridges, to replace missing teeth.
Prevention of delayed or absent tooth formation
It is not always possible to prevent delayed or absent tooth formation, since the causes are often genetic or environmental in nature. Nonetheless, maintaining good oral health and avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals or medications during pregnancy can help reduce the risk of dental problems. Besides, make sure, that you and your child are getting enough vitamins and minerals, especially vitamin D and calcium, which can promote healthy tooth development.
In conclusion; delayed or absent tooth formation can occur for a variety of reasons and can have a significant impact on a person's oral health. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent further complications and ensure optimal oral function and aesthetics.. Regular check-ups at the dentist and maintaining good oral hygiene are key to preventing dental problems..
Used literature and sources
Dhar V. Development and developmental anomalies of the teeth. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Bloom NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 333.
Dineen L, Slovis TL. The mandible. In: Coley BD, ed. Caffey’s Pediatric Diagnostic Imaging. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 22.
Turner EG, Dean JA. Eruption of the teeth: local, systemic, and congenital factors that influence the process. In: Dean JA, ed. McDonald and Avery’s Dentistry for the Child and Adolescent. 11th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 20.
