Holding or stopping breathing, apnea: what is this, causes, symptoms, diagnostics, treatment, prevention
Breathing – slowed or stopped; Respiration slowed or stopped; Not breathing; Respiratory arrest; Apnea
If breathing stops for any reason, it's called apnea. Slow breathing is called bradypnea. Difficulty or heavy breathing is known as shortness of breath.
When breathing slows or stops, it could be a sign of a serious illness.
Apnea is defined as a pause in breathing from a few seconds to several minutes., during which the level of oxygen in the blood decreases. This is the result of insufficient supply of oxygen to the body., which can lead to a wide range of health problems. Apnea can be divided into two main categories: central sleep apnea (CSA) and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
Central sleep apnea is caused by the brain's inability to properly signal the breathing muscles., while obstructive sleep apnea is caused by a physical blockage of the airways. It is important to understand, that apnea can occur regardless of whether, are you awake or sleeping.
Prolonged sleep apnea means, that the person stopped breathing. If the heart is still active, this condition is known as respiratory arrest. This is a life-threatening event, which requires immediate medical attention and first aid.
Causes of holding or stopping breathing
Difficulty breathing can occur for many reasons.. In most cases, the most common causes of sleep apnea in infants and young children are different from the most common causes in adults..
Common causes of difficulty breathing in infants and young children include:
- Asthma
- Bronchiolitis (inflammation and narrowing of small respiratory structures in the lungs)
- Breathlessness
- Encephalitis (brain inflammation and infection, which affects the vital functions of the brain)
- Hastroэzofahealnыy reflux (heartburn)
- Holding your breath
- Meningitis (tissue inflammation and infection, lining the brain and spinal cord)
- Pneumonia
- Miscarriage
- Convulsions
Common causes of difficulty breathing (shortness of breath) in adults are:
- Allergic reaction, swelling of the tongue, throat or other airways.
- Asthma or other lung diseases
- Cardiac arrest
- Breathlessness
- Drug overdose, especially because of alcohol, narcotic painkillers, ʙarʙituratov, anesthetics and other depressants
- The liquid in the lung
- Obstructive sleep apnea
Other causes of sleep apnea include:
- Head injury or neck injury, mouth and larynx (voice box)
- Acute cardiovascular disease
- Arrhythmia
- Metabolic (chemical, mineral and acid-base) body disorders
- Drowning
- Stroke and other diseases of the brain and nervous system (neurological)
- Chest wall injury, heart or lungs
When to call a healthcare professional if you hold or stop breathing
Seek immediate medical attention or call the emergency number, if the person is experiencing any of the following problems:
- Stumbles or has trouble keeping his feet
- There is a seizure or convulsions
- Loses consciousness
- Stays sleepy
- turns blue
If a person stops breathing, call an ambulance and perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation (if you know, how to do it). Being in a public place, look for an automated external defibrillator (AED) and follow the instructions.
What to Expect When Visiting a Doctor If You Have Breathing Problems
CPR or other emergency measures will be performed in the emergency room, doctor or paramedic.
As soon as the person's condition stabilizes, the doctor will conduct a medical examination, which includes listening to heart sounds and breath sounds.
Questions will be asked about the person's medical history and symptoms, including:
Have you experienced similar symptoms before?
- Has this ever happened before?
- How long did the attack last?
- Has the person had recurring short episodes of apnea?
- Episode ended with sudden deep breathing?
- The episode occurred while awake or while sleeping?
Disease history
- Has the person had a recent accident or injury?
- Has the person been sick recently?
- Whether there was any difficulty in breathing before the cessation of breathing?
- What other symptoms have you noticed?
- What medication is the person taking??
- Whether the person uses street or recreational drugs?
Diagnostic tests and treatments, which can be fulfilled, include:
- Airway Support, including oxygen, breathing tube through the mouth (Intubation) and breathing apparatus (fan)
- Blood and urine tests
- endotracheal tube
- Chest X-ray
- CT scan
- Defibrillation (electrical activation of the heart)
- ECG (electrocardiogram or cardiogram)
- Fluids through a vein (intravenously or intravenously)
- Medications to treat symptoms, including antidotes to eliminate the effects of poisoning or overdose.
Apnea treatment
Treatment for sleep apnea often focuses on addressing underlying medical causes. If the apnea is caused by an underlying medical condition, treatment may include medication, lifestyle changes or surgery. Some lifestyle changes include quitting smoking, weight loss and limiting alcohol consumption.
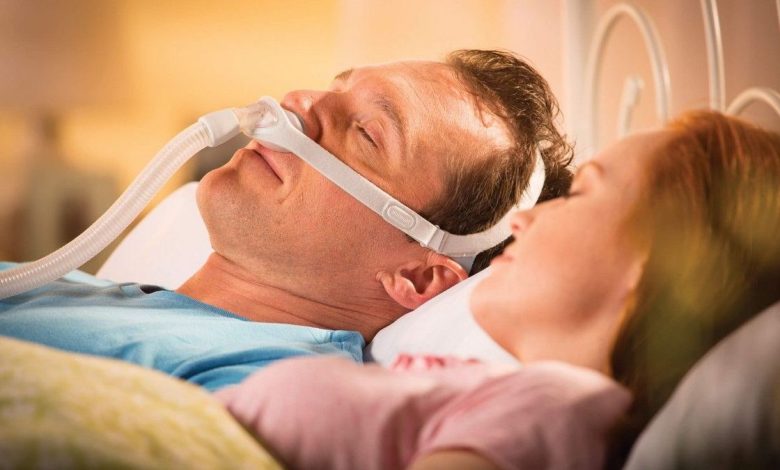
Surgery may be used to treat underlying physical problems, causing apnea. In some cases, your doctor may suggest using a continuous positive airway pressure machine. (CPAP). This machine helps to pressurize the airways and keep them open while you sleep..
In addition to the above treatments, there are other treatments, which can help relieve sleep apnea symptoms. These treatments include neck exercises, language stabilization, posture and diet modifications, supplemental oxygen and mouth appliances.
Sleep apnea prevention
Apnea can be prevented, addressing any underlying medical causes and making certain lifestyle changes. Lifestyle modifications to prevent sleep apnea include smoking cessation, maintaining a healthy weight, giving up caffeine, alcohol and sedatives, as well as stress management. Besides, people can buy a CPAP machine, to improve the quality of your sleep.
In conclusion, sleep apnea is a potentially serious condition, which can cause difficulty breathing, fatiguability, decreased concentration and other serious symptoms. It can be caused by a variety of underlying health and lifestyle issues., and it is important to identify and treat the underlying cause of sleep apnea, to prevent serious health consequences. Fortunately, there are medicines, treatments and lifestyle changes, that can help manage and prevent sleep apnea.
Sources and literature
Hartman ME, Cheifetz IM. Pediatric emergencies and resuscitation. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Bloom NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 81.
Short MC, Neumar RW. Adult resuscitation. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen’s Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 8.
Roosevelt GE. Pediatric respiratory emergencies: diseases of the lungs. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen’s Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 169.
