Interaction of drugs at the stage of formation of metabolites
The interaction of a number of drugs in the course of their distribution in the body can be considered as one of the important stages of the pharmacokinetic, which characterizes their biotransformation, leading to most cases, the formation of metabolites.
Metabolism (biotransformation) - The process of chemical modification of drugs into the body.
Metabolic reactions are divided into nonsynthetic (when drugs undergo chemical conversion, subjected to oxidation, recovery and hydrolytic cleavage or more of these transformations) - I phase of metabolism and Synthetic (conjugation reaction and others.) - Phase II. Typically, non-synthetic reactions are only the initial stage of biotransformation, and the resulting products can participate in synthetic reactions and then eliminated.
Products of non-synthetic reactions may possess pharmacological activity. If the active substance itself has not, introduced into the organism, and any metabolite, it is called prodrug.
Some drugs, products of metabolism which have an important therapeutically active | |
Drug substance | The active metabolite |
| Allopurinol | Alloksantin |
| Amitriptyline | Nortryptylyn |
| Acetylsalicylic acid * | Salicylic acid |
| Acetogeksamid | Gidroksigeksamid |
| Glutetimid | 4-gidroksiglyutetimid |
| Diazelam | Dezmetïldïazepam |
| Digitoxine | Digoxin |
| Imipramine | Desipramine |
| Codeine | Morphine |
| Kortizon | Gidrokortizon |
| Lidokain | Dezetillidokain |
| Methyldopa | Metilnoradrenalin |
| * Prednisone | Prednisolone |
| Propranolol | 4-gidroksiprolranolol |
| Spironolactone | Canrenone |
| Trimeperidine | Normeperidine |
| Phenacetin * | Acetaminophen |
| Phenylbutazone | Oksifenʙutazon |
| Flurazepam | Dezétilflurazepam |
| Khloralgidrat * | Tryhlorэtanol |
| Xlordiazepoksid | Dezmetilhlordiazepoksid |
| * prodrug, therapeutic effect is mainly products of their metabolism. | |
Non-synthetic metabolic reactions catalyzed by drugs microsomal enzyme systems of the endoplasmic reticulum of the liver enzyme systems or nemikrosomalnyh. These substances include: amphetamine, warfarin, imipramine, meprobamate, prokaynamyd, phenacetin, phenytoin, phenobarbital, quinidine.
In the synthetic reactions (conjugation reactions) drug or metabolite - a product of non-synthetic reactions, connecting with the endogenous substrate (glukuronova, sulfuric acid, glycine, Glutamine), form conjugates. They, usually, do not have biological activity and, It is highly polar compounds, a good filter, but poorly reabsorbed in the kidneys, which contributes to their rapid excretion from the body.
The most common reactions are conjugation: acetylation (the main pathway sulfonamides, and hydralazine, isoniazid and procainamide); sulfation (the reaction between the phenolic substances or alcohol groups and the inorganic sulfate. The source of the latter may be sulfur-containing acid, for example cysteine); methylation (Some inactivated catecholamines, niacinamide, thiouracil). Examples of different types of reactions of metabolites of drugs are listed in Table.
Types of reactions of metabolism of drugs | |
Type of reaction | Drug substance |
I. Nonsynthetic REACTION (catalyzed by enzymes of the endoplasmic reticulum, or enzymes nemikrosomalnymi) | |
| Oxidation | |
| Aliphatic hydroxylation, or oxidation of the side chains of the molecule | Tiolental, metogeksital, pentazocin |
| Aromatic hydroxylation, or hydroxylation of the aromatic ring | Amphetamine, lidokain, salicylic acid, phenacetin, phenylbutazone, chlorpromazine |
| O-Dezeling | Phenacetin, codeine |
| N-delating | Morphine, codeine, atropyn, imipramine, Isoprenaline, ketamine, Fentanyl |
| S-delating | Barbituric acid derivatives |
| N-oxidation | Aminazin, imipramine, morphine |
| S-oxidation | Aminazin |
| Desamidization | Fenamin, gisgamin |
| Desulfurization | Tioʙarʙituratы, tioridazin |
| Degalogenizatsiya | Halothane, metoksifluran, enfluran |
| Recovery | |
| Restoration of the azo group | Sulfanilamide |
| Reducing the nitro group | Nitrazepam, chloramphenicol |
| Recovery of carboxylic acids | Prednisolone |
| Recovery, catalyzed by alcohol dehydrogenase | Ethanol, khloralgidrat |
| The ether hydrolysis | Acetylsalicylic acid, norzpinefrin, cocaine, prokaynamyd |
| The amide hydrolysis | Lidokain, pilocarpine, isoniazid novokainamid fentanyl |
II. SYNTHETIC REACTION | |
| Conjugation with glucuronic acid | Salicylic acid, morphine, paracetamol, nalorfin, sulfonamides |
| The conjugation with sulphate | Isoprenaline, morphine, paracetamol, salicylamide |
| The conjugation with amino acids: | |
| Salicylic acid, a nicotinic acid |
| Isonicotinic acid |
| Paracetamol |
| Acetylation | Novokainamid, sulfonamides |
| Methylation | Noradrenaline, histamine, thiouracil, a nicotinic acid |
The conversion of some drugs, taken orally, essentially depend on the activity of enzymes, produced by the intestinal microflora, which hydrolyze unstable cardiac glycosides, which significantly reduces the effect of cardiac. Enzymes, produced by resistant microorganisms, catalyze hydrolysis and acetylation reactions, due to which the antimicrobial agents lose their activity.
There are examples of, When the enzymatic activity of microflora contributes to the formation of drugs, which exert their activity. So, ftalazol (ftalilsulьfatiazol) organism is practically not exhibit antimicrobial activity, but under the influence of enzymes of intestinal microflora is hydrolyzed to form norsulfazola and phthalic acid, providing antimicrobial effect. With the participation of enzymes of the intestinal mucosa are hydrolyzed reserpine and acetylsalicylic acid.
However, the main body, Where are the biotransformation of drugs, It is the liver. After absorption in the intestine, they fall through the portal vein to the liver, where and undergo chemical transformations.
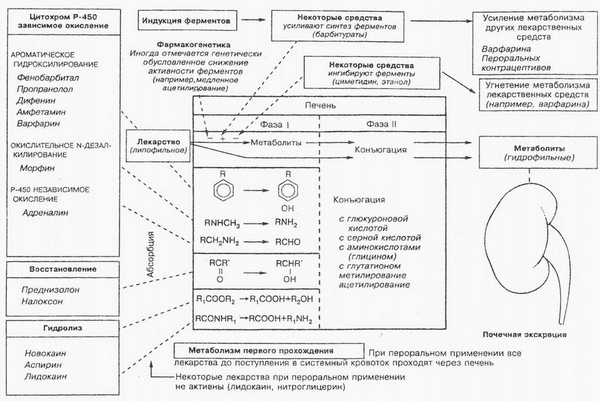
Through the hepatic vein drugs and metabolites thereof enters the systemic circulation. The combination of these processes is called "first pass effect", or elimination presistemna, as a result of which the quantity and effectiveness of substance, entering the bloodstream, may vary.
The drugs, having a "first pass effect" through the liver | ||
| Alprenolol | Kortizon | Oxprenolol |
| Aldosterone | Labetalol | Organic nitrates |
| Acetylsalicylic acid | Lidokain | Pentazocin |
| Verapamil | Metoprolol | Prolranolol |
| Gidralazin | Moracizin | Reserpine |
| Isoprenaline | Morphine | Phenacetin |
| Imipramine | Metoklopamid | Ftoruracil |
| Isoprenaline | Methyltestosterone | |
It will be appreciated, that the medication they peroralnom biodostupnost individually for each patient and varies for each drug. Substances, undergoing significant metabolic transformations in the first passage in the liver, may not have pharmacological effect, such as lidocaine, nitroglycerin. Besides, first pass metabolism can be carried out not only in the liver, but in other viscera. For Example, chlorpromazine more metabolized in the gut, than the liver.
On presistemna for elimination of one substance often influenced by other drugs. For Example, chlorpromazine reduces the "first pass effect" of propranolol, as a result of the concentration of β-blockers in the blood.
The absorption and first-pass elimination and determine the bioavailability, largely, the effectiveness of drugs.
The leading role in the biotransformation of drugs played enzymes of the endoplasmic reticulum of the liver cells, often referred to as microsomal enzymes. There are more than 300 drugs, capable of altering the activity of microsomal enzymes. Substances, increase their activity, We got the name inductors.
Inducers of liver enzymes are: hypnotics (barbiturates, khloralgidrat), trankvilizatorы (diazepam, xlordiazepoksid, meprobamate), neuroleptics (chlorpromazine, trifluoperazine), anticonvulsants (phenytoin), anti-inflammatory (phenylbutazone), certain antibiotics (rifampicin), Diuretic (spironolactone) and etc.
The active inducers of liver enzyme systems are also considered dietary supplements, Small amounts of alcohol, coffee, chlorinated insecticides (dikhlordifyeniltrikhloretan (DDT), geksaxloran). Small doses of certain drugs, such as phenobarbital, phenylbutazone, nitrates, can stimulate its own metabolism (autoindukciâ).
The joint appointment of two drugs, one of which induces hepatic enzymes, and the second is metabolized in the liver, dose of the latter should be increased, and the abolition of the inductor - lower. A classic example of such cooperation - a combination of indirect anticoagulants, and phenobarbital. Special studies have shown, what in 14% of cases the cause of bleeding in the treatment of anticoagulants is the abolition of drugs, inducing hepatic microsomal enzymes.
Very large inducing activity of microsomal liver enzymes has antibiotic rifampicin, somewhat less - phenytoin and meprobamate.
Phenobarbital and other inducers of liver enzymes is not recommended for use in combination with acetaminophen and other drugs, biotransformation products are toxic starting compounds. Sometimes liver enzyme inducers used for accelerating biotransformation of compounds (metabolites), alien to the body. Tak phenobarbital, which promotes the formation of glucuronides, It can be used for treatment of jaundice with impaired bilirubin conjugation with glucuronic acid.
Induction of microsomal enzymes often have to be regarded as undesirable, as accelerating biotransformation of drugs leads to inactive or less active compounds and to reduce therapeutic effects. For Example, Rifampicin can reduce the effectiveness of treatment with glucocorticosteroids, which leads to higher doses of hormonal preparation.
Much less frequently as a result of biotransformation of the drug substance are formed over the active compounds, In particular, in the treatment of furazolidone for 4-5 days in the body accumulates dvuoksietilgidrazin, which blocks monoamine oxidase (MAO) and aldehyde dehydrogenase, catalyzes the oxidation of aldehydes to acids. Therefore, patients, taking furazolidone, do not drink alcohol, since the concentration of blood acetaldehyde, formed from ethyl alcohol, may reach a level, in which there is a pronounced toxic effect of this metabolite (acetaldehyde syndrome).
The drugs, reduces or blocks the activity of liver enzymes, We received the name of inhibitors.
Medicinal substances, inhibits the activity of liver enzymes, include narcotic analgesics, certain antibiotics (actinomycin), antidepressants, cimetidine, etc.. As a result of the combination of drugs, one of which inhibit liver enzymes, It slows down the rate of metabolism of the other drug substance, increases its concentration in blood and the risk of side effects. So, H antagonist gistaminovыh2-repeptorov cimetidine dose-dependently inhibits the activity of liver enzymes and slows the metabolism of indirect anticoagulants, which increases the likelihood of bleeding, and β-blockers, that lead to bradycardia and hypotension. Perhaps inhibition of metabolism of indirect anticoagulants quinidine. Developing cooperation with such side effects can be severe course. Chloramphenicol inhibits the exchange of tolbutamide, diphenylhydantoin and neodikumarina (ethyl bïskwmacetata). It describes the development of hypoglycemic coma in combination therapy with chloramphenicol and tolbutamide. Known fatal cases while appointing patients azathioprine or mercaptopurine and allopurinol, inhibiting xanthine oxidase and slows the metabolism of immunosuppressive drugs.
The ability of some agents to violate the metabolism of other sometimes deliberately use in medical practice. For Example, Disulfiram is used in the treatment of alcoholism. This drug blocks the metabolism of ethanol in step acetaldehyde, the accumulation of which causes discomfort. Similarly, there are also metronidazole and antidiabetic agents from the group of sulfonylureas.
A kind of blockade of the activity of the enzyme is used in cases of poisoning with methyl alcohol, Toxicity is determined formaldehyde formed in the body under the influence of the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase. It also catalyzes the conversion of ethanol to acetaldehyde, and the affinity of the enzyme to the above ethyl alcohol, than methyl. Therefore, if you are among the two alcohol, the enzyme catalyzes the biotransformation mainly ethanol, and formaldehyde, having significantly higher toxicity, chyem uksusnyi aldehydes, formed in fewer. Thus, Ethyl alcohol can be used as an antidote (antidota) in case of poisoning with methyl alcohol.
Ethanol alters biotransformation of many medicinal substances. Single use it blocks inactivation and various drugs may enhance their effect. In the initial stage of alcoholism activity of microsomal liver enzymes may increase, which leads to a weakening of the action of drugs due to the acceleration of biotransformation. Opposite, in the later stages of alcoholism, when many of the liver violated, should be considered, that the action of drugs, biotransformation are in the liver is broken, can significantly worsen.
Drug interactions at the level of metabolism can be realized through the change in hepatic blood flow. Known, that the factors limiting the metabolism of drugs with a pronounced effect primary elimination (propranolol, verapamil, and the like.) - Is the amount of hepatic blood flow and to a lesser extent the activity of hepatocytes. In this regard, any drugs, reducing a regional hepatic blood flow, reducing metabolic rate of the groups of drugs and increase their content in the blood plasma.
