Types of fluid serous cavities
Serous exudates
Serous fluid may be observed in streptococcal, staphylococcia, tuberculosis, syphilis and rheumatism. Serous fluid light yellow, clear, It contains about 3 % squirrel. Seroplastic serous exudate is different from the presence of fibrin clots.
To serous fluid streptococcal and staphylococcal origin characterized by the presence of neutrophils in the total absence or presence of single cells and mezoteliotsitov.
When serous tuberculosis pleurisy Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the pleural cavity not penetrate, tuberculoma in the pleura are missing. This exudate contains a different number of lymphocytes, mezoteliotsitov, fiʙrina; Mycobacterium tuberculosis are not detected.
In tuberculous pleurisy with Tuberculomas on the pleura in the exudate revealed their elements (epithelioid and giant cells Pirogov-Langhans on the background of lymphoid elements) or elements cheesy decay, neutrophilic granulocytes, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
When syphilitic or tuberculous pleural effusion lymphocytes predominate in the exudate is not at all periods of the disease. So, in tuberculous pleurisy in the first ten days of illness in the exudate contains 50-60 % neutrophilic granulocytes, 10-20 % lymphocytes and many mezoteliotsitov.
As the disease progresses the number of lymphocytes increases, and neutrophilic granulocytes and mezoteliotsitov - decreases. Long predominance of neutrophils is a poor prognostic sign, it may indicate a transition serous tuberculous pleurisy in TB empyema. In tuberculous pleurisy exudate not neutrophilic granulocytes phagocytose tubercle bacilli, whereas pleurisy, caused by pyogenic flora, phagocytosis of neutrophilic granulocytes is observed frequently.
In tuberculosis exudates appear in degenerative changed neutrophilic granulocytes with wrinkled, fragmented and rounded nuclei. Such cells are difficult to distinguish from true lymphocytes. Besides, tuberculous exudate in nature always contain red blood cells, sometimes there are so many, that the exudate is bloody character.
Tuberculosis characteristic pronounced leykoliz, primarily neutrophilic granulocytes. The predominance of lymphocytes in exudate, perhaps, due to their greater resistance. It is not always a large number of lymphocytes in the exudate coincides with lymphocytosis. In some cases of tuberculosis pronounced increase in the number of eosinophilic granulocytes in the blood and exudate. Perhaps their absence and effusion, and blood.
During a protracted form of tuberculous pleurisy exudate are found in plasma cells. The diverse cellular composition of serous fluid in tuberculosis can be observed only at the beginning of the disease, and during the height of the disease, usually, dominated by lymphocytes.
Eosinophilic exudate
If pleural effusion number of eosinophilic granulocytes in the serous fluid sometimes reaches 97 % cellular composition. Eosinophilic exudate may be observed in tuberculosis and other infections, abscess, injuries, multiple metastases to the lungs, larvae migrate to the lungs and ascarids etc..
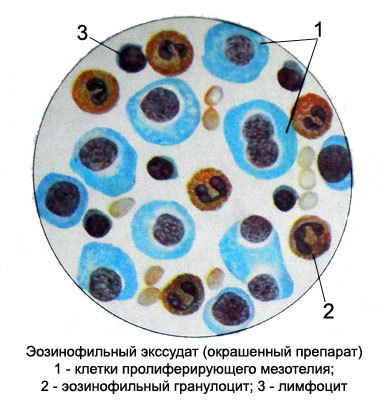
By the nature of eosinophilic exudate is:
- serous;
- hemorrhagic;
- purulent.
Increasing the number of eosinophilic granulocytes in the exudate can be combined with increasing the content of their blood and marrow is observed when either the normal amount of eosinophilic granulocytes in the blood.
Purulent exudate
Purulent exudate in origin and clinical manifestations can be different. Most often purulent exudate develops secondarily (primarily affects the lungs or other organs), but may be primary in inflammatory processes in the serous cavities, caused by a variety of pyogenic microorganisms.
Exudate can be a transition from serous to purulent. Repeated punctures can watch stages of the process: First exudate becomes seroplastic or seropurulent, and then purulent. He cloudy, thickens, becomes greenish-yellow, sometimes brownish or chocolate color (impurities from the blood).
Enlightenment exudate with repeated punctures and a decrease in the number of cells it indicates a favorable course.
If serous exudate from becoming transparent purulent, cloudy, and the number of neutrophils it increases, this indicates a progression of the process. The collapse of the neutrophils in the early inflammatory process is not, functionally they are full-fledged, actively phagocytose: They can be seen in the cytoplasm of bacteria.
With the rise of degenerative changes appear in the form of neutrophilic granulocytes toksogennoy grain, hypersegmentation cores; the number of pa- lochkoyadernyh neutrophils increases. Typically, a large number of neutrophils in the exudate accompanied by leukocytosis with the emergence of other forms in the peripheral blood.
Later neutrophilic granulocytes disintegrate, while the bacteria are identified in- and extracellularly. With a favorable course of the disease and recovery degenerative changes are mild neutrophilic granulocytes, their number decreases, No decay, found a significant number of histiocytes, mezoteliotsitov, monotsitov, macrophages.
Putrid exudate
Putrid exudate brown or greenish in color, with a sharp putrid odor. Microscopic examination reveals the detritus resulting from the disintegration of leukocytes, Needle fatty acids, Sometimes crystals n- matoidina and cholesterol. In many microorganisms exudate, particularly anaerobes, forming gases.
Hemorrhagic exudate
Hemorrhagic exudate appears with mesothelioma, cancer metastases, hemorrhagic diathesis joined with infection, chest wounds. Izlivshayasya blood diluted with serous fluid and remains liquid.
For sterile hemothorax characterized by a transparent reddish effusion. The protein portion of plasma clots, and fibrin otkladыvaetsya the pleura. In the future, the organization of fibrin leads to the formation of adhesions. In the absence of complications of pleurisy reverse development occurs rapidly.
When slabovirulentnoy infection pleural fluid from hemorrhagic can go into serous-hemorrhagic or serous.
Complication pyogenic infection serosanguineous exudate becomes purulent and hemorrhagic. The admixture of pus in the exudate detected with Sample Petrova, is as follows. Hemorrhagic exudate (1 ml) in vitro diluted five or six times with distilled water. If the exudate has only admixture of blood, hemolyzing the erythrocytes with water and becomes transparent; in the presence of exudation of pus it remains cloudy.
Microscopic examination of exudate pay attention to the red blood cells. If the bleeding has stopped, it is possible to identify only the old forms of red blood cells with various signs of death (microforms, "Mulberries", erythrocyte ghosts, poikilocytes, shizocitы, vacuolated and others.). The emergence of fresh, unchanged on the background of old red blood cells form suggests rebleeding. Prolonged bleeding into the pleural cavity exudate observed changes and unmodified erythrocytes. Thus, eritrotsitogramma to determine the nature of the bleeding (fresh or old, repeated or continued).
When noncommunicable hemothorax can reveal exudate in unmodified segmented neutrophil and eosinophil granulocytes. The distinctive features of them in the period of suppuration are pronounced signs of degeneration and decay. Intensity of these changes depends on the timing and extent of bleeding suppuration.
In the first days after the bleeding and marked karyorrhexis kariolizis, whereby neutrophilic granulocytes become limfotsitopodobnymi and can be taken for them.
Lymphocytes and monocytes more resistant and almost no change in the exudate. In the period of resorption found in the pleural fluid macrophages, mezoteliotsity and plasma cells. In the period of absorption of fluid in it appear eosinophilic granulocytes (from 20 to 80 %). This allergic reaction is a sign of a favorable outcome of the disease.
Upon accession pyogenic infections cytogram exudate is characterized by an increase in the number of neutrophils with the increase in them signs of degeneration and decay.
Cholesterol exudate
Cholesterol exudate is a long-existing (sometimes for several years) encysted effusion in serous cavities. Under certain conditions (reabsorption of serous cavities of the water and some mineral components of exudate, and in the absence of fluid influx into the closed cavity) exudate of any etiology may acquire the character of cholesterol. This exudate enzymes, destroying cholesterol, absent or is contained in a small amount.
Cholesterol exudate - thick liquid yellowish or brownish color with a pearlescent shade. The admixture of broken red cells may give a chocolate hue effusion. On the walls of the tubes, moistened with exudate, macroscopically visible impressions of cholesterol crystals in the form of tiny sparkles. Besides cholesterol cholesterol crystals reveal exudate fatty degenerated cells, products of cellular decay and drop fat.
Chylous, hilusopodobny and psevdohilezny (milky) exudate
Common to these types of fluid is similar in appearance to diluted milk.
Chylous exudate It is due to hit in the serous cavities of the damaged lymph vessels or lymph large thoracic duct. Lymphatic vessels can be damaged by trauma, tumor invasion, abscess or other reasons.
Milky kind of liquid caused by the presence in it of fat droplets, which is stained with Sudan III red and osmic acid - black. When standing in the exudate formed creamy layer, pop-up, and deposited on the bottom of the tube cell elements (erythrocytes, leukocytes, including many lymphocytes, mezoteliotsity, and in the presence of tumors - Tumor cells). If we add to exudate one or two drops of caustic with ether and shake tube, the liquid is clarified.
Hilusopodobny exudate It is a result of the disintegration of cells with abundant fatty degeneration. In these cases, a history information purulent pleurisy, and puncture revealed gross thickening of the walls of the pleural cavity. Hilusopodobny exudate found in atrophic cirrhosis, malignancies, etc.. Microscopic examination revealed an abundance of fatty degenerated cells, fat debris and fat droplets of different sizes. Microflora otsutstvuet.
Psevdohilezny exudate macroscopically also recalls milk, but suspended therein particles, probably, They are not fat, since they do not stain with Sudan III and osmic acid and do not dissolve during the heating. Microscopic examination revealed mezoteliotsity occasionally and drop fat. Psevdohilezny exudate observed in lipoid and lipoid-amyloid degeneration of the kidneys.
Content cysts
Cysts can occur in various organs and tissues (yaychnykah, kidney, brain and others.). The nature of the contents of the cyst even one organ, such as the ovary, It may be different (serous, purulent, hemorrhagic etc.. d.) and, in turn, defines its transparency and color (Colorless, zheltovataya, bloody, etc.. d.).
Microscopic examination of blood cells are usually found (erythrocytes, leukocytes), epithelial, vыstilajuщego Verily (often in a state of fatty degeneration). Cholesterol crystals may occur, gematoidina, fatty acids. The colloid cyst found colloid, in dermoid - flat epithelial cells, hair, fatty acid crystals, cholesterol, gematoidina.
Hydatid cyst (bubble) It contains a clear liquid with a low relative density (1,006- 1,015), wherein there glucose, sodium chloride, succinic acid and salts thereof. The protein is detected only with the development of the inflammatory process in the cyst. For the detection of succinic acid echinococcus bubble liquid evaporated in a porcelain dish to the consistency of syrup, acidified with hydrochloric acid and extracted with ether, evenly mixed with alcohol. The ether extract is poured into another cup. Ether was removed by heating in a water bath. At the same succinic acid crystallizes in the form of hexagonal prisms or tables. The resulting crystals were examined under a microscope. If the fluid contains protein, then it is removed by boiling, adding 1-2 drops of hydrochloric acid. Reaction to succinic acid is carried out with a clear filtrate.
Cytological diagnosis of echinococcosis It is possible only at the stage of an open cysts during spontaneous outpouring of its contents to the authorities, communicating with the external environment (often the breakout echinococcus bubble in the bronchus). In this case, microscopic examination of sputum from the bronchi revealed typical tapeworm hooks and slices parallel striated chitin shell of the bubble. You can discover and scolex - head with two beaters and four suckers hooks. Besides, in the material can be identified fatty degenerated cells and cholesterol crystals.
