Uveitis – Irit – Iridocyclitis
Description uveitis
Uveitis – inflammation of the uvea. Choroid – the middle layer of the eye (iris and surrounding tissue). It is between the retina and the white of the eye. Uveitis can be chronic (long) or acute (It occurs suddenly). This is a potentially dangerous disease. When it appears, you should immediately seek medical advice, to prevent loss of vision.
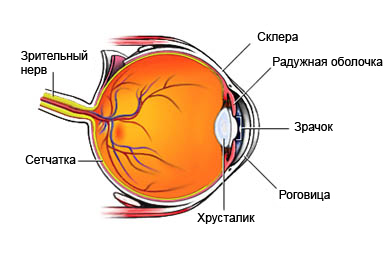
Causes of uveitis
Uveitis can be caused by eye injury. It can also be caused by an infection, such as:
- Syphilis;
- Tuberculosis;
- Toxoplasmosis;
- Herpes virus;
- West Nile Virus;
- Mumps.
The main causes of, usually, unknown.
Risk factors
Uveitis may occur in people with other health problems and diseases of the immune system, such as:
- Rheumatoid arthritis;
- Sarkoidoz;
- HIV;
- Ankylosing spondylitis;
- Inflammatory bowel disease.
Uveitis can occur in children and adults. People, who develop uveitis and ankylosing spondylitis often have specific gene, HLA-B27.
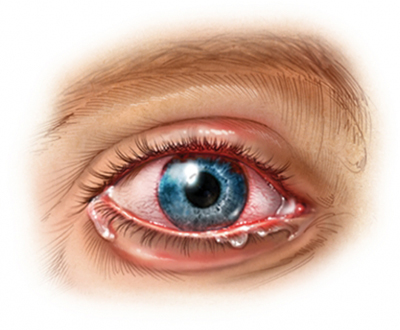
Symptoms of uveitis
These symptoms can also be caused by other diseases. You must inform your doctor, if they came any.
- Red, bloodshot, and watery eyes;
- Blurred vision;
- Sensitivity to light;
- Narrowed, volatile form pupil.
Diagnosis of uveitis
The doctor asks about the symptoms and medical history, and performs a physical exam. Tests may include the following:
- Blood tests, to search for other illnesses and diseases, which may be associated with uveitis;
- Procedures for removing fluid from the eye and further diagnose.
Treatment of uveitis
Treatment will depend on the age, reasons, severity, and other factors. It includes the following:
Medication
Drugs used to reduce inflammation and prevent damage. Medications may be in the form of eye drops, tablets or injections per eye, such as:
- Preparations, that help reduce sensitivity to light and other complications treated;
- Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, such as prednisolone acetate, fluorometholone acetate, Dexamethasone, fluorometolon, prednisolone sodium phosphate, rimeksolon (Veksol), or loteprednol (Lotemaks);
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), to reduce inflammation;
- Antibiotics to treat bacterial infections;
- Antiviral drugs to treat viral infections;
- Preparations for the enlargement of the pupils (tsykloplehyky), to reduce pain and discomfort.
Procedures
In some cases, surgical intervention may be required or installing special eye implants.
It is important to pass the repeated examination for signs of relapse.
Prevention of uveitis
Since the causes of uveitis is often unknown, it is impossible to prevent its occurrence. To reduce the risk of complications or the appearance of recurrence of uveitis, you must take the following steps:
- Refer to an eye doctor immediately after the onset of symptoms of uveitis;
- Follow all the doctor's instructions;
- Regularly wash your hands, to prevent infection in the eye;
- To avoid infection, you need to practice safe sex.
