Pulmonary tuberculosis – status and sputum
Pulmonary tuberculosis is a chronic infectious disease specific.
The causative agent of tuberculosis refers to a large group of mycobacteria, related lower plant organisms,- radiant mushrooms (actinomycetes). Mycobacterium tuberculosis resistant to acids, alkali and alcohol. Their length ranges from 1,5 to 6 m, and thickness - of 0,2 to 0,5 m. They are slightly curved, may have a thickening at one or both ends. Mycobacterium tuberculosis at an angle to each other or in parallel, aggregations or clumps.
Electron microscopy found, that the cytoplasm of their homogeneous, It contains large granules, sometimes vacuoles. Under the influence of various factors Mycobacterium tuberculosis can change their biological and morphological properties and become grainy, The filter, and drug-resistant L-shape.
Mycobacterium granular form (Grain Fly) are acid-fast granules are temporary, prehodyashtim sostoyaniem microorganism. The filter shapes have the ability to penetrate through tissue and bacterial filters.
The appearance of the L-shaped membrane disruption is due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis under the influence of various factors, so that their shape changes and they take the form of grains, Balls, Irregularly, differently refracting light, and t. P. Such transformation of mycobacteria can cause massive antibiotic therapy.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis detected at bacterioscopic study drugs sputum, stained by Ziehl-Nelsenu. However, they are painted in red, and the background of the drug - in blue.
Tuberculosis is characterized by an extraordinary polymorphism of clinical and pathological manifestations and clinical course due to the wave-like alternation of outbreaks and attenuation of inflammation. The combination in each case of the disease alterative, exudative and proliferative processes in tissues leads to a variety of morphological changes.
Alterative - A change in the structure of cells and tissues, which can manifest different kinds of dystrophies until necrosis.
Exudation - A consequence of vascular response in inflammation. It begins with a reflex contraction of the small arteries and capillaries, very quickly replaced by an extension of the entire vasculature of the site. As a result of the expansion and overflow occurs in blood vessels inflammatory hyperemia. Blood flow slows down gradually, reaching complete stasis. Due to the accumulation in the inflammation of biologically active substances in it dramatically increases the permeability of the blood and lymph vessels, which leads to increased protein displacement process fluid from the blood and lymph tissue in the body cavity, and.
Proliferation - the proliferation of tissue elements, helps limit the inflammatory focus, and in some cases considered as a morphological sign of attenuation of the inflammatory process.
TB infection occurs most often by aerogenic, t. it is. if it enters the body through the mycobacteria airways. In place of the introduction of Mycobacterium tuberculosis occurs perifocal inflammation. This focus specific inflammation called primary affect. Around it develops non-specific inflammation (pneumonia), then affects the lymphatic vessels (limfangoit) and regional lymph nodes (lymphadenitis). So there is a formation of primary tuberculosis complex (primary tuberculosis).
Tuberculosis, occurring in the human body, had undergone primary tuberculosis, is called secondary.
An intermediate position between primary and secondary tuberculosis takes hematogenous tuberculosis, characterized by multiple organ damage. The agency, affected tuberculous process, along with fresh and always found the older changes. This diversity is due to the reactivity of the organism, and the structural features of the fabric, in which inflammation develops.
With the predominance of alterative changes in diseased tissue degeneration foci observed until necrosis (alterative, or necrotizing, type of tissue reaction), and in areas of necrosis found a huge number of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Exudative and poliferativnye change while recede into the background. Necrotic foci may be the size of a grain of millet to and slightly larger than a pea.
When predominantly exudative reactions in the tissues of the affected organ marked focal accumulations of fluid protein and cells with a predominance of mononuclear leukocytes on polymorphonuclear. Proliferative changes in this poorly expressed. The exudate detected Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Such lesions in organs and tissues may be small, the size of a millet grain, or very large - eg, Lightweight, they can take the acinus, clove, rarely entire stake. Their color gray or gray-pink, and the development of necrosis - yellow.
In tuberculous inflammation exudate can also accumulate in the cavities. His character in these cases different - serous, seroplastic, less often - purulent (eg, in tuberculous pleurisy, pericarditis, peritonitis).
Describes the types of tissue reaction (alteration and exudation) tuberculosis have no specific morphological features and is very difficult to distinguish from normal inflammation.
Morphological specificity of tuberculosis is clearly manifested in the mostly productive reaction (with a predominance of proliferative changes), resulting in focal sprawl typical of tuberculosis inflammation productive granulation tissue, referred to as TB granuloma, buhorok, tuberculoma. When viewed with the naked eye tubercle is a gray nodule size from barely noticeable to the point of millet grain.
It should be noted, that the concept of "tuberculosis bump" is not quite equivalent to the concept of "tuberculous granuloma". Depending on the reactivity of the body bump with the same macroscopic picture can be exudative, alterative, or productive. Tuberculous granuloma should be called only one bump, It is dominated by the productive tissue reaction. Most often it is the granulation tissue, consisting of a plate-like cells with a pale stained nucleus puzyrkoobraznym. These cells because of the similarity with flat epithelial cells called epithelioid.
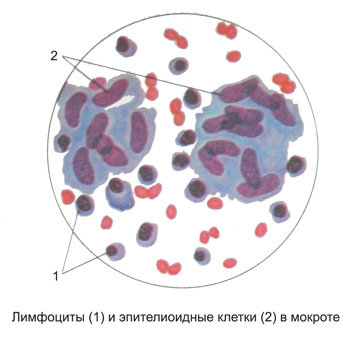
Among the epithelioid cells, which develop from the local connective tissue cells, reticular cells and vascular endothelial, usually visible argyrophilic delicate filaments or granular mass of coagulated protein exudate. Besides, can meet the individual cells of the lymphoid type, macrophages and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Many of these cells on the periphery of tubercles, and they are often arranged in a palisade, t. it is. for- tial for relations center for buhorka.
For tubercles characterized by the presence among the elements described above giant cells with multiple nuclei, which are usually arranged in a ring around the periphery of the cell.
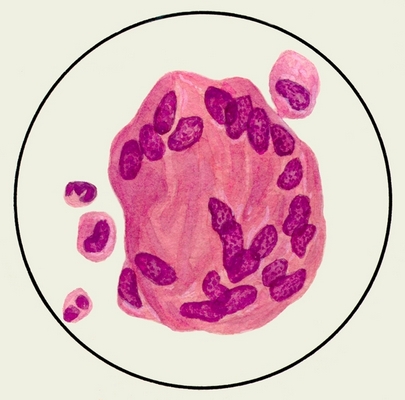
These cells are named to describe their authors called polynuclear giant cells Pirogov-Langhans. They are formed of epithelioid cells, and their feature is, that the nucleus of the cell divides, while her body is not involved in the division, and only growing. There is evidence the formation of giant cells from capillary endothelium (abortifacient budding capillaries). In the early development of hillocks giant cells are closer to the center, and at the center of caseation appear on the periphery.
The bumps described structure, t. it is. consisting of granulation tissue type epitelloidnogo, They called epithelioid. They correspond to the proliferative phase of tubercles and show mostly productive form of tuberculosis. Granulation tissue, forming epithelioid tubercles, typically comprises a few blood vessels. It speaks, capillaries, formed in the granulation tissue tubercle, in the future, as it were "consumed" as a result of their participation in the construction of the endothelium of the tubercle. The epithelioid tubercles Mycobacterium tuberculosis usually slightly, They are located between the cells, in their cytoplasm, including giant cell cytoplasm. Sometimes the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis presents considerable difficulties.
In other cases, tubercles have said structure epithelioid, and are focal accumulations of lymphoid cells such as macrophages and with a mixture of neutrophils among protein mass exudate. Such bumps are called lymphoid. They can be considered as exudative phase of tubercles, manifestation of exudative tissue reaction. Specific features they have, and to identify the etiology of inflammation can be achieved only by the color of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Sometimes the tubercles are under the microscope focal necrosis of organ tissue. These necrotic bumps can be attributed to the significant prevalence of alterative changes. They correspond to the first, alteratyvnoy, phase of tuberculosis. The bumps of this type can be seen in individuals in a state of cachexia, and in the elderly. Probably, they are an expression of negative anergy, and establish a specific etiology only when stained material from the foci of necrosis in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
One of the most important features of tuberculous inflammation is the development of curd (caseous) necrosis at the focus of inflammation to tissue death, in which it develops. Caseation is a kind of dry (coagulation) and necrosis under microscopic examination appears as a cloudy swelling, and then the fatty degeneration of the cytoplasm of cells, followed kariolizis, karyorrhexis and complete disintegration of cells, constitute the focus of inflammation, and cells of the organ, where the focus is located. In the interstitial tissue of the organ at the same time, swelling the fibrous structures, their fibrinoid transformation and decay. Pockets of cheesy necrosis can be different sizes depending on the size of the focus of tuberculous inflammation. They look like yellowish dry weight, resembling cottage cheese (casein), hence the name - caseation.
Caseation may occur in the initial, alteratyvnoy, tuberculous inflammation phase, but this is rare and special conditions. Caseate like exudative, and productive tubercles. Using a special coloring preparations, determine the properties of collagen and elastic fibers. All this allows in each case to establish the nature of tuberculosis inflammation and trace its phase.
Caseation granuloma develops only when the reactivity of the organism, but it is the result of direct action of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, or insufficient blood supply. Evidence of this is the possibility of a different outcome epntelnoidnyh tubercles, namely their fibrous transformation. In these cases, epithelioid cell transformed fibroblasts tubercle, producing fiber, whereby in place or around the tubercle develops fibrous connective tissue. Fibrotic granulomas conversion can occur prior to the development caseation. In this case, the granuloma is entirely transformed into a fibrous knot hyalinized. Fibrotic transformation of the periphery of the tubercle can occur while, when the center has already begun caseation: In this case, necrotic curdled mass surrounding sheath of connective tissue (encapsulated). When encapsulation cheesy tubercles connective tissue is formed by elements of the tubercle, and also due to the reactive overgrowth of connective tissue surrounding.
In some cases, tuberculosis center has steadily increased, always discovering a tendency to caseation and decay. Before reaching any surface (cloth, Authority), a hotbed of tuberculosis opened, curdled mass is removed and emptied in a lumen - in the organ formed extensive defects, called cavities. Such cavities may arise as a result of pulmonary tuberculosis foci tyromatosis and the allocation of curd through the bronchi, renal tuberculosis outbreak at the opening of the renal pelvis, etc.. d.
In advanced cases of tuberculosis with the development of fibrosis in the lung cavities around the fibrous tissue grows to form a dense fibrous capsule. Fibro-cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis is the most dangerous in the epidemiological form of the disease, since it in most cases the patients recovered Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
In other cases, from the very beginning of the process or in a certain period, it reveals a tendency to fibrotic conversion of tubercular granulation, reactive development of connective tissue, encapsulation cheesy foci. These phenomena affect the tubercular process, and often lead to a complete cessation of its. In the curd is deposited lime, causing tuberculosis foci transformed into stony growths or chalk-like powder weight, surrounded by connective tissue scar, wherein the bone can be formed.
The character of sputum tuberculosis depends on the course of the process. In patients with open pulmonary tuberculosis can be detected in sputum Mycobacterium tuberculosis and elements decay tubercle (connective tissue fibers).
When productive inflammation in the sputum found items cheesy necrosis of small clusters of shiny grains among structureless mass, often with pieces of elastic fibers, sometimes with giant multinucleated cells Pirogov-Langhans.
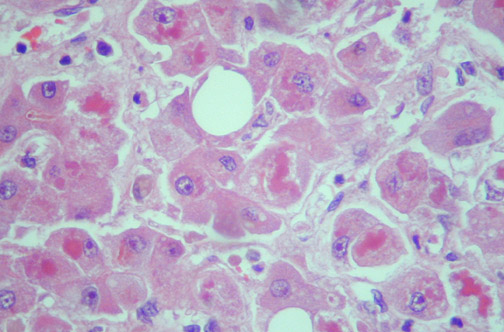
Exudative inflammation with serous exudate, a protein consisting of liquid with a small amount of alveolar cells, epithelial cells of the bronchial tubes and certain white blood cells, recalls serous pneumonia. Exudates may also be catarrhal with a high content of these cell elements (leukocytes little). Detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the serous and catarrhal pneumonia, tuberculosis is very difficult.
Seroplastic and other types of tuberculous pneumonia with a significant number of cells and fibrin exudation give a picture of cheesy necrosis. In sputum while elastic fibers are found, leukocytes (partially able steatosis), alveolar cells, voloknistыy fibrin and mycobacteria tuberkuleza.
Where, when the final result of various forms of pulmonary tuberculosis in the process is the breakdown of lung tissue with the formation of cavities and voids, sputum revealed hydrolysed or staghorn fiber and grain risovidnye.
Sputum can also be found calcified elastic fibers (tetrad elements Ehrlich), are formed in old, fully or not yet fully calcified tubercular foci, It reveals, for various reasons. They are best seen in native preparations of small particles of sputum, especially with careful view them under a microscope.
The next element is the tetrad Ehrlich calcified cheesy decay, which macroscopically in the form of whitish sputum friability tracks, acquiring at a small magnification view tracks, consisting of black point masses. The third element of the tetrad Ehrlich - cholesterol crystals, fourth-mycobacterium tuberculosis, revealed by staining Ziehl-Nelsenu.
Thus, elastic fibers three tuberculosis may occur in groups and clusters of various sizes among purulent particles, and in the small scraps of sputum. Besides, They can be observed in the form of individual fibers and their fragments. The discovery of these fragments and single fibers is of great diagnostic value, as the evidence of active TB.
Often, Mycobacterium tuberculosis can be detected only in formulations, particles prepared from sputum, They have been identified elastic fibers. For this notice in the preparation or place a piece, wherein the fibers have been found, the drug is removed from the scanned cover glass, and the preparation is dried and stained with Ziehl-Nelsenu.
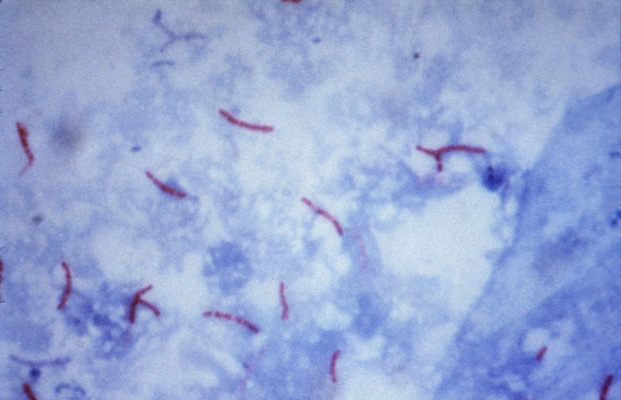
With a low content of M. tuberculosis in sputum is very important to carefully and correct processing of the material. Detection of sputum specimens in native elements, characteristic of tuberculosis process, followed by coloring them Ziehl-Nelsenu helps clarify the diagnosis. You can also use the method of flotation, in which Mycobacterium tuberculosis are found, and cheesy decay and elastic fibers are not detected.
