Cytological diagnosis of malignant tumors of the serous membranes
Tumors of serous membranes may be primary malignant (mesothelioma) and secondary, t. it is. metastatic. In most cases, the tumors of the serous membranes appears exudate, in which detected tumor cells.
Mesothelioma and the condition of serous membranes
Mesothelioma - a primary tumor, emanating from the mesothelium. Rarely. It grows to form a single node or a large number of small nodules, with a significant surface of the serous membrane can be bumpy.
When mesothelioma effusions, usually, hemorrhagic, sometimes serous, viscous or viscous consistency, quickly accumulates, that should be considered when making a diagnosis.
In vivo cytological diagnosis of mesothelioma It presents considerable difficulties, since the exudate revealed elements of epithelial and connective tissue growth with varying degrees of atypia.
According to the international classification of WHO, emit predominantly epithelioid, fibrous and mixed forms of malignant mesothelioma. In practice, the most frequent cytological two variants of mesothelioma - an option, resembling adenocarcinoma (zhelezistыy cancer), and a mixed.
Option, resembling adenocarcinoma, not very different from any other glandular cancer localization.
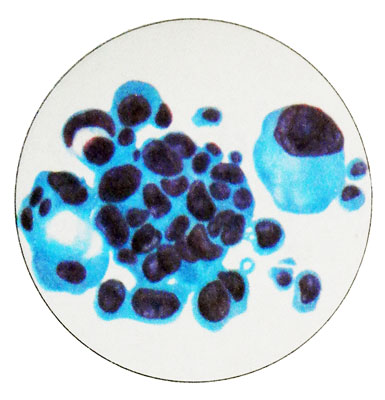
Dominated round, but there are flattened, cubic and prismatic cells. Pronounced nuclear and cellular polymorphism. Perhaps the presence of giant multinucleated cells. The cell nuclei are mainly rounded or oval with different sizes and coarse chromatin pattern melkoglybchatym, sometimes sparse irregular Aufhellung. Hypertrophied nucleoli. Mesothelioma cells are separate and groups in the form of sockets, papillae- prominent formations, rounded complexes and structures zhelezistopodobnyh.
At low tumor differentiation cells are more monomorphic and almost do not form groups, characteristic of adenocarcinoma. Where, when atypia of tumor cells is weak, mezoteliomu differentsiruyut regenerator-proliferativnыmi Processes. In this embodiment, the cytologic tumor cells do not differ from the proliferating cells- present mesothelium, an extensive single-layer clusters of strands and layers. Characterized by mild pronounced signs of atypia cells and significant degenerative changes (vacuolization and so on.).
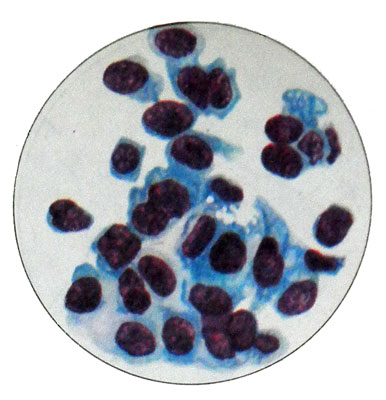
In the mixed form of mesothelioma along with cells, observed during variant, resembling adenocarcinoma, cells detected, similar to fibroblasts and fibrocytes. They are of small size, fusiform and elongated, processes often have different lengths. The cell nuclei and the larger the average value, round or oval, many of them hyperchromic, with uneven contours and uneven or blurred pattern of chromatin. Pale cytoplasm, basophilic, granular or tyazhistaya. Cells are arranged separately and clusters in the form of beams, cords. Epithelial cells and connective tissue intermingled, They form a tight cluster.
The cytologic diagnosis of any variant of mesothelioma It can be put only in the simultaneous detection of epithelial and connective tissue cells, in the absence of a combination of clinically diagnosed only.
Malignant mesothelioma is sometimes metastasizes to the lung, while it is almost impossible to differentiate the primary tumor with metastases.
Lymphosarcoma and condition of serous membranes
When lymphosarcoma effusion serous exudate, in the sediment can be detected only lymphocytes, like tuberculosis. Therefore differential diagnosis of small cell (highly differentiated) variant of the tumor is extremely difficult, but no clinical data is simply impossible.
In contrast to the serous tuberculous pleurisy, for lymphosarcoma characterized by an abundance of cells, whose structure is different from lymphocytic. Even with the small cell variant of lymphosarcoma cells are more loose structure of chromatin network, a shrunken form lymphocytes, inherent in the normal pleurisy, in no exudate.
When large- (poorly differentiated) form of lymphosarcoma revealed numerous large cells with large nuclei loose, which should be differentiated from low-grade fibrosarcoma cells.
When mediastinal lymphosarcoma is very important to study the pleural exudate. In the absence of sprouting tumor cells in serous cavities effusion in lymphosarcoma not detected.
Multiple myeloma and condition of serous membranes
With multiple myeloma in a punctate of serous cavities dominated immature plasma cells with severe atypia cells and nuclei, frequent multinucleated cells. Characterized by a high mitotic index.
Multiple myeloma must be distinguished from reactive proliferation of plasma cells, whereby mature plasma cells predominate.
Sarkoma Juinga
Ewing's sarcoma can metastasize in serous cavities. The morphological characteristics of this tumor are described in Chapter. 19 "Cytological diagnosis of inflammatory processes and tumors of bone and cartilage tissue".
Hodgkin's disease and the condition of serous membranes
Cytological diagnosis of tumors by examining punctate serous cavities presents considerable difficulties. The tumor diagnosis is valid only in the identification of giant cells in the exudate Berezovskogo- Sternberg. However, even if on the serous membrane of specific granules these cells are rarely found in punctate of serous cavities.
Leukemia and condition of serous membranes
Leukemia, complicated by pleurisy or ascites, characterized in effusion cells the same, and that in the blood of the patient.
So, in chronic myelosis in the exudate can reveal a lot of immature granulocytes, in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells are found varying degrees of maturity, etc.. d.
Pseudomyxoma peritoneum and the condition of serous membranes
When pseudomyxoma peritoneum It accumulates in the peritoneal cavity mucus, gotten into her at break of ovarian cysts, bowel diverticula. Together with mucus in the peritoneal cavity enter epithelial cells, that, implantiruyasy of bryushine, continue to secrete mucus. Microscopic examination reveal exudate mucus, mezoteliotsity, gistiocitы, lymphocytes, neutrophil and eosinophil granulocytes, plasma cells.
Mezoteliotsity arranged separately and clusters in the form of layers and cords. Significantly pronounced signs of degeneration and proliferation of the mesothelium. Epithelial cells are cubic or prismatic contain the apical part of the secret, are located separately, clusters and small groups, are found in small amounts in exudate. A break in malignant ovarian cysts exudate revealed cancer cells.
Metastasis of cancer and the condition of serous membranes
Metastasis of cancer in the peritoneal cavity most commonly observed in tumors of the stomach, intestines and ovaries, and in the pleural cavity - in lung cancer and breast cancer. The tumors metastasize to other sites in the serous membrane considerably less.
When cancer metastases in the serous membranes exudate is found in a large number of tumor cells of different sizes, often very large, with large nuclei and phenomena steatosis, vacuolization and pronounced polymorphism; also revealed signet ring cells.
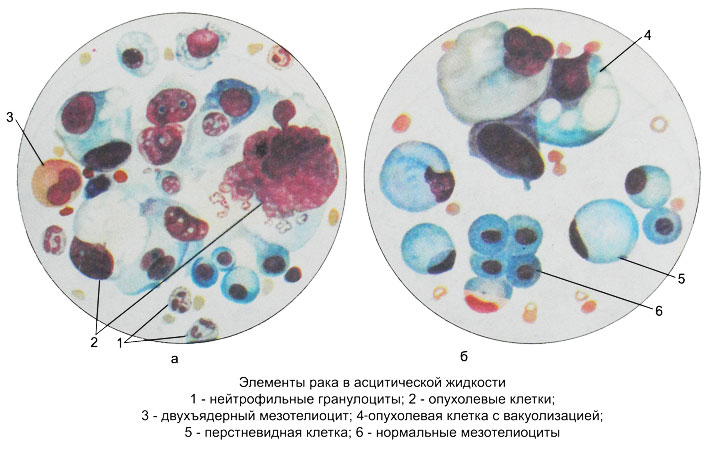
Important diagnostic value has the character of groups of tumor cells, depending on the histological structure of the tumor. There are sharply limited group of cells rounded zhelezistopodobnogo, alveolar and papillary structure, occasionally in the form of rods, cords and bulbs.
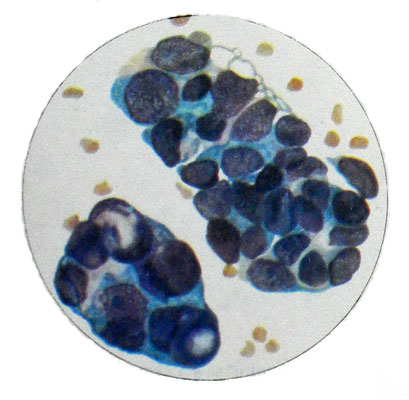
Sarcoma and condition of serous membranes
The serous membranes can metastasize and sarcoma.
The study should begin with a study of native preparations, and then painted them in Pappenheim. In stained preparations more clearly identified polymorphism cells, multicore, the presence of large nucleoli and other characteristic features. The cores of various shapes, often located eccentrically.
The cytoplasm of the cell has the form of a wide rim with differently pronounced basophilic, often vacuolated, with the presence of steatosis. The cells are arranged close, chaotic conglomeration of groups or entities as zhelezistopodobnyh. The presence of exudate in individual cells, sometimes with significant structural changes, It does not allow to conclude that they belong to the malignant neoplasms, because their appearance may be due to cell proliferation and desquamation nonneoplastic nature.
The fluid from serous cavities can be detected elements, to easily identify the primary site of cancer.
Mainly in ascites rarely pleural, liquids (especially in native preparations) groups on the surface of the atypical epithelial cells are found layered limestone formation - acervulus, first described by Ehrlich. They are concentrically layered egg-shaped formation in the form of lumps and balls, sometimes very small, refracting light, crystals.
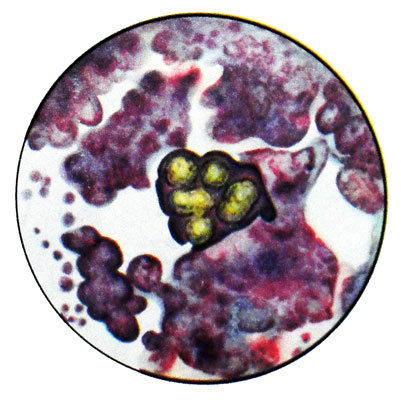
Acervulus made up of protein-lipid substance interspersed with calcium salts. Most often they occur in epithelial ovarian tumors. Finding psammous ovary cells is indicating a possible metastasis of ovarian cancer.
Brain sand tumor It may also occur in cancer of the meninges, lung and stomach. In the case of a woman in the peritoneal cavity exudate and sputum psammous primary cancer cells most likely localized in the ovary, and metastases - in the lungs and abdomen.
If you find zhelezistopodobnyh groups of tumor cells, which is contained in the cytoplasm pink (when stained by Pappenheim) Colloidal, it should be assumed metastasis of thyroid cancer.
Detection of malignant cells in the pigment melanin indicates metastasis in serous cavities melanoblastoma.
