Cystitis – state and urinalysis
Cystitis - bladder infection. Observed in individuals of any age, mostly women. The frequency of the disease is due to an intermediate position between the upper bladder urinary ways and urethra, close anatomical relationship with his sexual organs and lower intestines department, which promotes the penetration of infection from these bodies in the bladder. Activators of cystitis are Escherichia coli, staphylococcus, streptokokk, diplokokk, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, etc..
Of great importance in causing cystitis and other factors are: introducing the bladder tools in the study, the use of some drugs (geksametilentetramina), Local circulatory disorders, supercooling, constipation; women - pregnancy, delivery, climacteric and involution periods. The infection can penetrate into the bladder by ascending from the urethra, downward - from the upper urinary tract (that there is a relatively rare) and by hematogenous.
Depending on the nature of cystitis (purulent, catarrhal), its prevalence (cervical, tryhonyt, common) and the inflammatory process bladder mucosa may be in varying degrees of hyperemia, edematous, infiltrated, places with ulceration and areas of necrosis, encrusted salts, etc.. d. The number and color of urine in this disease are normal.
Depending on the availability of blood in the urine and pus may cause turbidity. When purulent cystitis purulent sediment or saniopurulent, and the alkaline - Mucopurulent viscous or muco-saniopurulent stringy.
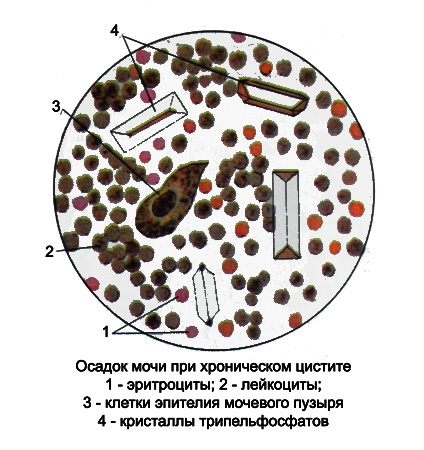
The acid reaction of urine observed with cystitis, caused by E. coli or Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and Alkaline - With the disease, caused by other pathogens. It should be taken into account, that any infection, causing inflammation of the bladder, easy to join and other microorganisms, decomposing urea to ammonia release, whereby the reaction of the urine becomes alkaline with a characteristic smell of ammonia. Thus precipitates tripelfosfaty phosphates and amorphous.
Relative density of urine in normal urine output is normal.
Albuminuria (lozhnaya proteinuria) It occurs due to the presence in it of inflammatory exudate. The amount of protein is dependent upon the nature of the inflammation and the blood impurities. When purulent inflammation significantly more protein, than in catarrhal.
Smears of urine sediment in cystitis depends patomor- fologicheskih changes in the mucous membrane of the bladder and urinary reaction.
If acute cystitis inflammatory process extends to the whole of the bladder mucosa and the nature of purulent inflammation, the white blood cells cover the entire field of view of the microscope, RBCs often appear unchanged. Epithelial cells of the bladder, in this case it is difficult to detect, since the surface layer of the mucous membrane is covered with pus. If some areas struck mucosa (tryhonyt, cystauchenitis), the transitional epithelial cells of the bladder can be detected in the urine in varying amounts, often in the form of layers of different sizes. Number of leukocytes and erythrocytes in this case may vary considerably.
In chronic cystitis with rezkoschelochnoy reaction urine white blood cell count may vary, they swell, increasing, partially or fully destroyed, forming a slimy, stringy precipitate, where there is little remaining leukocytes. This cystitis the urine is necessary to investigate as soon as possible after receipt of. A microscopic examination of the sediment in addition to the remaining white blood cells against a background of mucus show a small amount of unchanged erythrocytes and epithelial cells isolated. Almost always detected in the form of phosphate salts and amorphous tripelfosfaty.
Detecting in cystitis with acidic urine short, rather wide rods and the presence of fecal odor of urine indicate, that is the causative agent of cystitis, By-see- momu, B. coli. Such sludge should be Gram-staining. Gram-negative E. coli.
Membranous cystitis accompanied by necrotic changes of the bladder epithelium (like surface, and its deeper layers). Epithelial cells in the urine can Detect- alive in the form of clusters and layers. Sometimes revealed small grayish film, Inlaid phosphates and containing puckered, necrotizing bladder epithelium.
Desquamative cystitis characterized by the presence in urinary sediment a significant number of epithelial cells and transient protein traces. Leukocytes usually slightly (3-10 In the field of view). Desquamative cystitis is observed after administration of hexamine (as a result of the chemical action of formaldehyde on the mucosa of the bladder), and some other substances, and a number of infectious diseases (eg, in typhoid).
Leukoplakia of the bladder It comes as a result of metaplasia of the epithelium of the mucous membrane in his flat keratinizing. Thus epithelium growing, Stratum and exfoliating- It is in substantial numbers. In the urine there is a blood. Diagnosis is based on detection in urine of small membranous structures, representing the horny layers of the squamous epithelium and unchanged erythrocytes. If you suspect that you need to take a leukoplakia urine catheter.
When calculous cystitis there are sand or pebbles, formed in the kidneys and go down the ureters into the bladder, and stones, formed in the bladder. Salts, dropping of urine due metabolic disorders or other reasons, often have mechanical origin (eg, Due to the delay in the flow of urine from the bladder prostatic hypertrophy, narrowing the urethra, etc.. d.), settle on epithelial cells, Blood clots or muco-purulent scraps, gradually forming sand or stones.
Stones irritate the bladder, causing dermatitis, which is manifested typical symptoms, increased frequency of urination day. Urine thus comprises elements, typical cystitis (protein, leukocytes, epithelial). As a result, the mechanical integrity violations mucosa occurs close- or microhematuria, and in urine sediment may be present fibrin and crystals gematoidina. Changes in the bladder mucosa, associated with permanent injuries to her, create conditions for the development of micro-organisms got there and the emergence, thus, Secondary alkaline cystitis. Bladder stones on the composition of the same, as well as kidney stones: uric acid, oksalatov, Phosphates, at least - of xanthine, cystine, cholesterol, proteins, often mixed.
