Platelets - Types and platelet function – Trombocitopoэz
Megakaryocytes and platelets
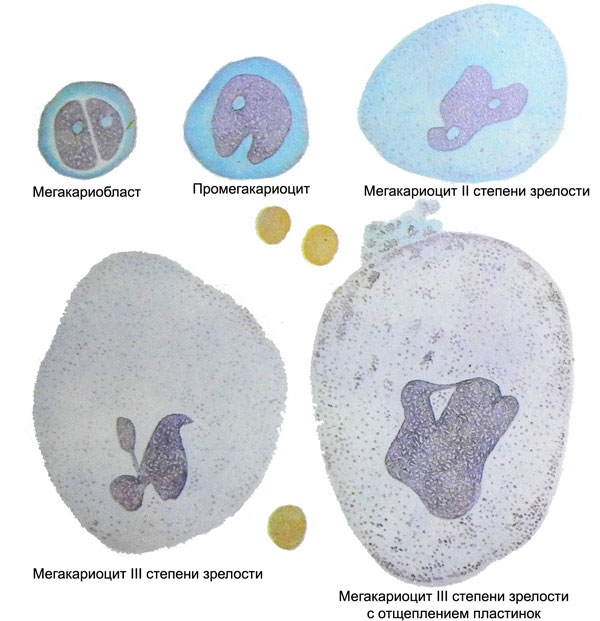
Giant polyploid cells in the bone marrow - megakariocitы - Primordial elements, of which formed platelets - platelets.
They serve as a source of precursor cells myelopoietic, turning in the division and maturation into unipotent, sensitive cells trombotsitopoetinu (UCHTK). Further maturation of cells of this series is as follows: UCHTK > megakarioʙlast > promegakaryocyte (basophilic megakaryocyte I ripeness) > granular megakaryocyte II maturity > Plate-megakaryocyte III maturity.
Under normal conditions, while a number of megakaryocytic maturation varies within 55-94 hours. If the body is not formed trombotsitopoetin, which is typical of a form of inherited thrombocytopenia, the maturation of the cells stop at stage UCHTK.
After the formation of megakaryoblasts practically stops cell division, But the intensity goes endomitosis. As a result of this chromosome set in each cell increases 2 to 4, 8, 16, 32 and even 64. The degree of polyploidy in different megakaryocytes varies, but is dominated by cells 8- and 16x chromosome, whereas cells with a set of at least 8 almost there.
The development of polyploidy accompanied by a sharp increase in cell size, mainly due to the increase in the cytoplasm. As a result, megakaryocytes, II and III reach maturity 60-100 microns in diameter, and sometimes more.
Megakarioʙlast
Megakarioʙlast - Round shape cell, It does not differ in magnitude from other blasts, but with a rough structure of the nucleus. The core or single round, or it consists of two, closely adjacent to each other purplish-brown cloves. It is intensely colored, with mesh or woven into a ball chromatin, It comprises one or several nucleoli. The cytoplasm bazofylna, devoid of grain, It surrounds the nucleus is relatively narrow rim.
With a very strong stimulation thrombocytopoiesis megakaryoblasts can form thin spikes, from which otshnurovyvayutsya primitive blue platelets. However, the main source of such plates are promegakariotsity.
Promegakariocity
Promegakariocity, or basophilic megakaryocytes I maturity - large polyploid cells (30-60 Microns in diameter) intensely stained with the nucleus of coarse structure, which found depressions, banners, lobulation. The large size of the cells is determined mainly by the increase in mass of the cytoplasm, which retains basophilic and almost completely devoid of grain, but sometimes it is possible to see a few azurophilic granules.
When stimulated thrombocytopoiesis (eg, for thrombocytopenia) promegakariotsitov begin to separate from a large number of major grain-blue platelets, sometimes resembling large fragments of the cytoplasm of the mother cell. Considering, promegakariotsity that can cleave platelets, Some authors consider it more correct to call them basophilic megakaryocytes I ripeness.
Granular megakaryocytes II maturity
Granular megakaryocytes II maturity, as is evident from their names, characterized, that the cytoplasm of the cell is filled with abundant azurophilic granulation, losing the basophil, and painted in a reddish-purple color. Cell size is further enhanced (to 60 100 m or more) with further changes in the nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio in favor of cytoplasm. Amplified distortion and fragmentation of nuclei, takes the form of baskets, chain, antlers, etc.. P.
Laminar megakaryocytes III maturity
In laminar megakaryocytes III maturity found in the cytoplasm not only abundant ase- rofilnaya grain, but also a clear close-meshed network of lipid-protein membranes, which divides the cytoplasm into a plurality of cells, each of which is the future of platelet. The separation membrane derived from the shell megakaryocyte, grow into the cell cytoplasm, branches and merge with each other.
According to specified data, Each mature megakaryocyte forms around 3000-4000 platelets, and otshnurovka these cells does not occur gradually, As volleys and bы. Therefore, in the bone marrow smears revealed megakaryocytes, surrounded by hundreds of newly precipitated platelets (in the manufacture of stroke are often "smeared" behind a sliding megakaryocytes, like a train or tail of a comet). With the increased needs of the organism in the past are easily separated platelets and megakaryocytes from grainy and even basophilic megakaryocytes (promegakariotsitov). It may be noted a very fast elution of platelets from the bone marrow into the blood stream, in this connection in myelogram, along with normal or even elevated total content megakaryocytic cell number, reduced the number of cells, III reaching maturity, and cells, surrounded by just otshnurovavshimisya platelets.
Until recently, such a picture, characteristic of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, and all other types of thrombocytopenia with a short period of existence of platelets, mistakenly interpreted as a sign of slow maturation and lack of productivity (functional disability) megakariotsitov. Currently, however, it proved a complete failure of these views. In particular, lack of maturation (nedozrevanie) megakaryocytes when immune thrombocytopenia associated with premature expenditure reserve of these cells in the production of platelets, as evidenced by an increased amount in the blood of large blue immature platelets, Deprived granulomera, and drastic shortening (to several hours) labeled platelet lifetime in the bloodstream of the patient.
According to the literature, megakaryocytic number of cells in the bone marrow punctate may be different - from 0,01 to 1,8 %, and this figure, as well as other parameters are normal myelogram, It should be considered relative. The clinical significance have only marginal deviations from the norm: amegakariocitoz - An almost complete disappearance of the cells from the bone marrow or gipermegakariocitoz - A significant increase in their number. But in this case, you should find out, how changes are consistent with the observed changes in the platelet count in the blood. So, amegakariotsitoza identify bone marrow constantly normal amount of platelets in the blood, surely, an artifact, and he should not attach any importance. Opposite, Thrombocytopenia can proceed at normal or elevated levels of megakaryocytes in the bone marrow (which is typical for an accelerated loss or increased consumption of platelets in the body), and at amegakariotsitoze, due to which decreases production of platelets.
A certain diagnostic value has counted In bone marrow cells of various megakaryocytic series. Normally 2-6 % these cells constitute megakaryoblasts, 5-20 % -promegakariocity (basophilic megakaryocytes), 60- 70 % - Grainy and laminar megakaryocytes and about 20 % - Metamegakariotsity and naked nuclei.
Platelets – Zimmermann's corpuscle
Platelets, or platelets - Devoid of the cell nucleus, formed from the cytoplasm and membranes of megakaryocytes. They flattened, They have the form of lenticular lens round or oval. Upon contact with a surface under investigation, when damaged blood vessels, and also under the influence of a number of biologically active substances (ADF, adrenaline and others.) they quickly swell, acquire saccular shape, many filamentous form and tree shoots, pseudopodia. Especially easy to undergo this major young platelets, therefore the electronic Microphotograms they often have an irregular polygonal shape.
Dimensions of normal platelets ranging from 1,5 to 3,5 m, and, the younger the cell, so they are larger and heavier. Therefore trombotsitometriya (like the definition eritrotsitometricheskoy Price-Jones curve), as well as their separation by density gradient weight, It has important diagnostic value. Normally, about 30 40 % platelets are young populations; they have a diameter greater than 2,5 m.
In idiopaticheskoy trombotsitopenicheskoy purple (ITP) and other thrombocytopenia, proceeding with reproduction power of platelets in the bone marrow, It increases blood levels of 4-5 microns in diameter makrotrombotsitov, including many grain-free blue blood platelets, otshnurovavshihsya of nedozrevshih bazofilynыh megakariotsitov.
When congenital defects of platelet quality can be a giant (megatrombotsitы) - Up to 6-10 microns in diameter, characterized that, in particular, for trombotsitodistrofii (Bernard-Soulier disease) and anomalies Meah-Hegglina, or very small - less than 1,5 m (with the syndrome Wiskott-Aldrich).
When determining the size and mass of platelets is of great diagnostic value, it is found in the analysis trombotsitogrammy extreme variability in the distribution of different forms platelets, therefore the display fails to normal trombotsitogrammu. Therefore, in modern textbooks on the physiology and pathology of platelets links to trombotsitogrammu, usually, no, underscoring the futility of this time-consuming full count.
In conventional light microscopy are found in platelets central part of the grain - granulomer and peripheral vitreous grain-free zone - gialomer. However, in many cells of the distinction, due to contact with a foreign surface of platelets, can not be found, and grain is in them evenly.
These electron microscopy show, platelets, Like other cells, covered with three-layer lipid-protein membrane, composed sialoglikoproteiny, contractile protein - actomyosin (trombostenin), adenylcyclase, Ryad glycosyltransferase, fosfolypydnыe mykromembranы, activating blood clotting (factor 3 Platelet, or blood thromboplastin). Deficiency of these substances, hereditary characteristic number thrombocytopathy, It underlies the pathology and platelet dysfunction.
When Glanzmann thrombasthenia (Glanzmann's disease) platelet membranes in no macromolecular glycoproteins, when one of hereditary trombotsitopaty they do not, and so on adenylcyclase. d.
The outer shell of platelets covered with a protein layer thickness of 10 20 nm, wherein a substantial amount of some plasma proteins are concentrated, including blood coagulation factors (I, VIII, XI, XIII et al.), von Willebrand factor, Some immunoglobulins and other proteins. For some of these substances on the membranes of platelets has special receptors. This cytoplasmic "atmosphere" of platelets, who are deprived of other blood cells, It is of great importance in the implementation of local haemostatic reactions.
Shell platelet It forms a large number of deep folds and channels, penetrating into the interior of the cell and penetrating it in different directions. This gives the sponge-like structure of platelets, It provides a good contact with the deeper layers of cells surrounding its shell layer and the plasma protein, facilitates the separation of the environment of various biologically active substances, it is of paramount importance for a complete hemostasis. Selection factors called platelets in the plasma reaction liberation.
Electron microscopy of platelets found in the following structural elements:
- transverse and longitudinal sections of membrane invaginations and channels;
- a large number of dense granules or cells, It is a place of accumulation and storage of ATP, ADF, Serotonin, calcium, probably, factor a 4 Platelet (antigeparinovogo). These granules and the content is released into the environment during the reaction and the release of paramount importance in the implementation of the hemostatic;
- a-гранулы, are analogues of lysosomes, composed of acid hydrolases and cathepsins (Education is about the same magnitude, as dense granules, but with moderate or low density);
- mitoxondrii, or β-granules, few, having low density and relatively simple in structure;
- glycogen granules - dense, with irregular contours, consisting of individual grains;
- and microtubules micromembrane, adjacent to the cell membrane and containing actomyosin contractile protein - trombostenin, which depend on changes in platelet form, consolidation and compaction of platelet plug in the vessel, retraction of a blood clot;
- structure, which correspond to the ribosomes.
Normal platelets in human blood ranging from 180 to 320 T in 1 l. Their life expectancy is about 7-10 days, and by 1/4 to 1/3 all available platelets deposited in the spleen, where each platelet holds about 1/4 part of his life.
When splenomegaly, due to portal hypertension and a number of other reasons, splenic platelet pool increases and decreases, respectively, the contents of these cells in the blood. A significant part of the platelet absorbs the capillary endothelium and other small vessels. The second main place of their death is the spleen, and portal hypertension - and liver.