Trematodы – Class flukes - Description, morphology and development cycle
Class flukes, or trematodes (Trematode), parasites combines small size (from 1 to 20- 30 mm) with the lancet- or leaf-shaped body, squished, continuous, without segments.
The highest value for the differentiation of individual species has a reproductive system, although most trematodes - hermaphrodites, all flukes - biohelminths, parasites in humans and animals. The bodies are fixing two muscular sucker - oral and abdominal.
Disease, caused by trematodes, referred trematodozov.
The development of parasites It is, usually, double change of hosts. Intermediate hosts for the majority of trematode are various kinds of shellfish, in the body which takes the reproduction of the parasite in the larval stage. When changing the double masters are an additional host fish, crabs or crayfish, the body that are being actively implemented larvae (opisthorchiasis, paragonimoze). The final boss - a man and various animals (dog, cat, fox, sable, Otter and others.).
Opystorhys – Cat fluke
Opystorhys, or cat fluke (Opisthorchis felineus), It is the causative agent of opisthorchiasis.
The length of the parasite 8-13 mm (sometimes up 19 mm), body lanceolate, elongated, for main conc konychesky suzheno. At the tail end are two of four- and five lobes testicles, in the middle part of the body lies uterus, filled eggs, whereby it has a dark brown color, the whole parasite yellowish, almost transparent.

Eggs pale, yellowish or grayish color, very small, Oval, with well-defined shell. On the pole is narrowed cap with a small roll of shell around, at the opposite pole stands a small bump.
In sexually mature parasite opistorhisov in the bile ducts of the liver, gallbladder and pancreas final host. Lots of eggs in the bile gets to the intestine and excreted in the feces into the environment. Further development of the parasite is only possible in reservoirs.
The helminth eggs are formed larvae - miracidia, that come out of them in the body of the intermediate host - a freshwater mollusk (Leachi cottage) and transformed into sporocysts, producing redia, which migrate to the liver clam. From redia formed larvae - цerkarii, leaving the body of the mollusk and use tail freely floating in the water. Further development is possible with the active introduction of cercariae into the body additional host - fish (carp), where they encyst, turning into metacercariae (muscle, subcutaneous tissue).
Man (another definitive host) infected by eating fish, affected metacercaria (slaboprovyalennoy, salted, raw or half-baked). In human colon larvae are released from the skins, and then through the common bile and pancreatic ducts penetrate into liver, gallbladder, pancreas. After 2-4 weeks worms reach sexual maturity and produce eggs. The human body can fluke parasite for many years.
Clinical manifestations opisthorchiasis due to sensitization to the development of allergies, mechanical action parasite, vascular occlusion parasites congestive and subsequent infection, reflex influence on the functions of the alimentary canal, etc..
Diagnosis opistorhoz set upon detection of helminth eggs in the feces and duodenal contents. For opisthorchiasis characterized by rather pronounced changes in the blood - increasing the number of eosinophilic granulocytes (to 80%), normal or slightly reduced the number of leukocytes, prïznakï hypo- or normochromic anemia.
Klonorxis – Chinese fluke
Klonorxis, or Chinese fluke (Clonorchis sinensis),- Pathogen clonorchiasis, similar clinical picture with opisthorchiasis. Body leaf-shaped parasite, reddish, translucent, slightly larger, than Opisthorchis (to 25 mm), the front end is more extended, rear, where the branched testes, rounded. In the middle part of the body is the womb, filled eggs; ymeyutsya RED sucker.
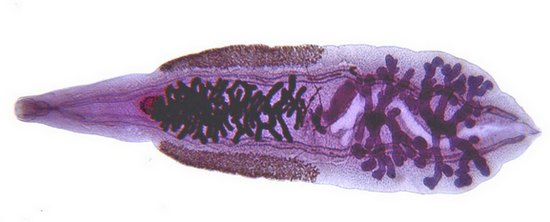
The cycle of the parasite is similar to the cycle of development of the Siberian fluke.
Eggs klonorhisa so similar to the eggs Opisthorchis, it is almost impossible to differentiate them. According to recent data, a detailed microscopic examination of a large increase in egg klonorhisa can note a protruding shell caps on the edges in the form of "coat hanger". Shell rough, thick, rough, particularly on the, opposite lid, which is separated from the egg precise winding line. Lid higher, than eggs Opisthorchis. Eggs klonorhisa light golden color.
A presumptive diagnosis klomorhoza is placed upon detection of helminth eggs in the feces or duodenal contents, final - after studying the treatment of parasites precipitated.
Liver fluke – Giant fluke
Liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica) and giant fluke (Fasciola gigantika) - Pathogens, called fascioliasis. The man is rare, mainly parasitize various farm animals, especially ruminants.
Liver fluke leaf-shaped, size 20-30 mm, and the size of the giant may reach 70 mm. The internal structure and the development cycle of these helminths similar. The head end of the body issued a coracoid lip, which are located next to two suction cups. In the middle third of the body are difficult branched testes, and in front of them and the left - branching staghorn ovary. Directly behind the abdominal sucker, in front of the body, located rosette uterus.
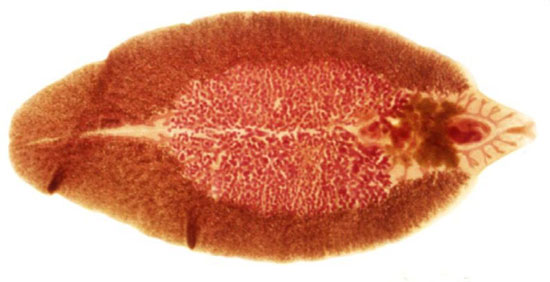
Eggs fasciolae very large, Oval, tan, with well-defined dual-shell, have a cap and bump the poles. Inside seen numerous yolk cells.
Fasciola parasites in the bile ducts of the liver of the final owners - large and small cattle, horses, sheep, pigs, rodents, Sometimes a person. There are cases of localization of worms in the blood vessels in humans, in the eyeball, beneath the skin. The life of these helminths in humans of up to three - five years. The intermediate host is the freshwater clam.
Eggs fasciolae come with bile into the digestive tract, excreted with feces and fall into the water or on moist soil, where they develop larvae - miracidia, that, coming out of the eggs, floating in water with the aid of cilia.
Further development of the parasite occurs in the body of the mollusk-pond, as well as in Opisthorchis. Infection of animals and humans It occurs in the use of water from contaminated ponds, eating aquatic vegetation. From gut larvae of Fasciola - adolescariae penetrate the bloodstream or through the peritoneum of the liver, where, after three or four months, reach sexual maturity and begin to excrete the eggs.
The clinical course of fascioliasis distinguish migration (acute) phase of the disease, and chronic, with the development of symptoms of liver disease and bile ducts, manifestations of sensitization, Sometimes symptoms of pancreatitis, Appendicitis, abscesses, eye disease, light, throat, due to localization in these organs fasciolae.
The diagnosis of fascioliasis are adjusted based on detection of helminth eggs in the feces and in duodenal contents. However, it should take into account the possibility of a "transit" of eggs, caught in the digestive tract as a result of eating the liver of animals infested. In such cases,, temporarily excluded from the food liver, conduct follow-up study after 5-7-10 days.
Dykrotselyy – Lancet fluke
Dykrotselyy, or lanceolate fluke (Dlcrocoelium lanceatum) infests the bile ducts farm animals (cattle, sheep); in humans is rare. Parasite whitish, His body is elongated, tapering toward the tip. The front end of the body pointed, the back is rounded. Ymeyutsya RED sucker, paired testes oval, okruglennый яichnik and trubchataя petleobraznaя uterus. The length of the parasite 5-15 mm.
Eggs rather small, Asymmetric, Oval, with a small cap at one pole, brown and thick shell (immature eggs - yellowish). The mature egg is the larva with two large oval vacuoles. The intermediate host is a land snail.
Development Cycle dikrotseliya mainly proceeds in the same manner, that of other flukes, but it has some features. So, miracidium mollusk in the liver turns into sporocysts I order, inside which is formed a lot of debate about the cysts II, and then cercariae. Coming out of the sporocysts, cercariae actively penetrate into the capillaries of the lung mollusc, where encyst, glued several pieces, forming teams of cysts. If respiratory movements mollusc teams cysts are released into the environment and, together with mucus remain on the surface of plants, which crawls clam.
Animals, eating grass, swallow with her teams cysts, of which are located in the duodenum young worms, subsequently migrate into liver. To a man prefabricated cysts can get off the grass (habit of keeping a blade of grass in his mouth).
Diagnosis diskrotselioza is placed upon detection of helminth eggs in the feces (should be aware of the possibility of revealing the transit of eggs, In this case, the study should be repeated).
The lung fluke
The lung fluke (Paragonimus westermani) - Pathogen Paragonimiasis. This parasite egg-shaped, russet, 7- 13 mm length, It has a shell with spines. Typically the presence of helminth twisted intestine, extending to the rear end of the body. Paired branched testes are located in the posterior third of the body, on the left side - branched ovary. Testes and ovaries are lobed structure. Uterus underdeveloped, It has the form of a coil.
Eggs lung fluke Oval, big, golden-yellow or brown, filled with large yolk cells, They have a distinct cap, which is formed around the protrusion (cap as it is pushed into the egg).
The cycle of development of lung fluke It comes to the change of the three owners. The final boss - a man, dog, cat, pig, wild pig, leopard, tiger, Ounce, wild cat. The main intermediate host - a freshwater clam, optional - Cancer.
Invasive lung fluke larvae (metaцerkarii) It enters the body by eating poorly-cooked crayfish. The intestines of the final host larvae are released from the shell, penetrate the gut wall into the abdominal cavity, and then through the aperture and into the lung pleura, where intsistiruyuteya in small bronchi. Besides, adult worms can invade the lymph nodes, brain, pancreas and other organs.
Lung fluke eggs are found in the sputum, and due to possible ingestion it can be detected in the faeces of the patient.
Metagonimus
Metagonimus (Metagonimus an gawai) - Pathogen metagonimoza. This small parasite length 1-1.25 mm, whose body was covered with spines.
Eggs megatonimusa limonoobraznoy form, symmetric, a thin smooth skin. The flat cap is separated from the rest of the egg flat thin line, at the opposite pole there is a bump. The development of the parasite takes place with the participation of the final (man, dog, cat, pig, mouse, fox, pesets), intermediate (gastropod) and further (Many freshwater fish) owner. In the body of the fish larvae are scales, gills, PLAVNIK, muscle. A person infected by eating insufficiently cooked fish. Adult worms are parasites in the small intestine, causing inflammation and severe, Thrust diarrhea.
Diagnosis metagonimoza It is made by detection of eggs in feces.
Nanofiet
Nanofiet (Nanophyetus schi drive the iowi) - Pathogen nanofietoza. Very fine fluke length 0.5 1 mm, pear, nearly round shape, yellow-gray, ymeet RED sucker.
Eggs nanofieta big, Oval, gray or yellowish, contain large yolk cells, have a cap, shell (similar to the broad tapeworm eggs).
Nanofiet parazitiruet Human small intestine, dogs, cats. The eggs are excreted in the feces of the definitive host. The larval stage of development nanofieta It takes place in the body of gastropods (intermediate host) and freshwater fish (additional host). A person infected by eating insufficiently cooked fish.
Diagnosis made on the basis of detection of helminth eggs in the feces.
Shystosomы – Blood flukes
Shystosomы, or blood flukes (Schistosoma),- Dioecious fluke size 4-20 mm. Deferred females formed eggs contain a larva - miracidiй. Schistosoma are the causative agents schistosomiasis - Diseases, widespread in countries with a hot climate.
The cycle of schistosomes proceeds with the change of intermediate host, which are mollusks. Цerkarii (larvae) enter the body of the final host, actively penetrating the skin, mucosa, penetrating light clothing. Young parasites migrate to the host's body and reach the abdominal veins, which develop into adult worms.
A person infected with schistosomiasis while swimming or working in the infected pond, as well as water consumption of a. Eggs, deferred females in blood vessels, moving bloodstream, penetrate the vessel walls and enter the lumen of the intestines or bladder and genitalia. During the promotion of eggs exposed to prolonged mechanical tissue damage and the action of proteolytic enzymes of the parasite, which creates prerequisites for the development of benign and malignant neoplasms.
In humans, three kinds of parasitic schistosomes:
- Shystosoma krovyanaya (Schistosoma haematobium);
- Şistosoma Mansona (Schistosome mansoni);
- Schistosoma Japanese (Schistosoma japonicum).
Blood fluke – Shystosoma krovyanaya
Blood fluke (Schistosoma haematobium), parasitizing the blood vessels of the urinary bladder, It is the causative agent of urinary schistosomiasis. Male parasite length 12 14 mm, female - up 20 mm. Uterus parasite contains 20-30 large eggs colorless fusiform, without caps, with a spike on one end.
The clinical picture of the disease It is characterized by allergic symptoms in the initial and latent periods, gematurieй, sores, hemorrhage, papillomatoznyh growths on the mucous membrane of the bladder. Cystoscopy revealed shistozomatidnye bumps (clusters of eggs) and "sand" spots (calcified eggs). Blockage of the ureter may cause hydronephrosis. Women formed polypous growths on the mucous membrane of the vagina, cervix, fistula urethra and perineum, bladder stones.
Diagnosis It is made by detection in urine of eggs and data cystoscopy; used serological tests - test with cercariae, indirect agglutination reaction with an antigen from cercariae, eggs, liver affected shellfish.
Intestinal schistosomiasis – Hookworm Mansona
Pathogen intestinal schistosomiasis (şistosomoza Mansona) - Schistosome mansoni. Male parasite size 10 12 mm, female, 12-16 mm. The uterus is usually a few eggs, sometimes one.
Eggs big, without caps, are a thorn in the side of a hook. The adult parasites live in the blood vessels of the liver and colon. Females lay eggs, who then go out into the lumen of the intestines and faeces fall out. Often the eggs entered the bloodstream to the liver, lungs, kidneys and other organs. In the bowels of schistosomes cause damage, resembling a severe form of dysentery, and sometimes leading to death. Intermediate host - Clam.
Diagnosis It is made by detection of eggs in the feces by the method of deposition, used as a study biopsies mucosa rectum and sigmoid colons, immunological reactions.
Japanese schistosomiasis – Katayama disease
Pathogen Japanese schistosomiasis (Katayama disease) - Schistosoma japonicum. Male parasite length 9-20, samka- 15-20 mm. It uterus is 50-300 eggs of pale yellow, oval, without caps, with a barely noticeable hooked thorn near one of the poles. Intermediate host - Clam.
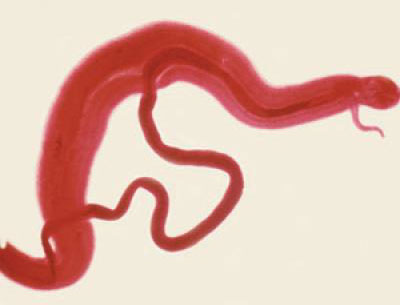
Цerkarii They enter the body, and other definitive hosts (cattle and small ruminants, dogs, cats and others.) through the skin and mucous membranes. Adult worms parasitize in the portal and mesenteric veins. Eggs, deferred fertilized female, pass through the wall of the intestine and excreted in the feces.
The clinic Japanese schistosomiasis are three stages: primary, intestinal (resembling dysentery) and late, with the development of liver cirrhosis, sores, fistul, papillomatosis intestines. If you get the eggs from the bloodstream into the brain in patients develop epilepsy, marked tumor syndrome with paralysis and blindness.
Diagnosis Japanese schistosomiasis It is made by the detection of eggs in the feces and the results of serological.
It should be taken into account, that the differentiation of different species of schistosomes by a serological impossible.
