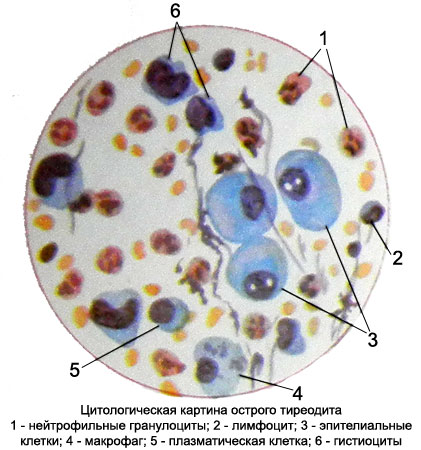
Tireoidit – characteristic punctate thyroid
Inflammation of the thyroid gland can be acute or chronic. The diagnostic puncture is performed, if necessary, to differentiate chronic inflammation with other diseases of the thyroid gland, similar of clinic.
Acute thyroiditis
Diagnosis is based on the sudden onset of the disease, severe pain in the thyroid gland, radiate to the ears, high body temperature, leukocytosis, accelerated ESR.
Functional state of the thyroid gland is not broken. Upon detection of fluctuations in the glands produce its aspiration puncture. Punctate exposed cytological and bacteriological studies. In preparations, prepared for cytology, found pus, t. it is. preserved and dilapidated leukocytes, detritus, erythrocytes, or fibrin, a small number of macrophages.
Dominated by neutrophilic granulocytes and macrophages.
Subacute thyroiditis (de Quervain's thyroiditis, granulomatous thyroiditis, pseudotuberculosis thyroiditis)
The thyroid gland is observed increasing infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells. To further develop a productive inflammation with giant cell reaction.
The punctate revealed chronic inflammation elements (macrophages, gistiocitы, fibrocytes, fibroblasts, neutrophil and eosinophil granulocytes), follicle cells are able degeneration, bands acellular oxyphilic substance, Colloidal, scraps of capillaries. Many gigantic multi-core cell types of cells of foreign bodies, often similar to those of giant multinucleated cells Pirogov-Langhans.
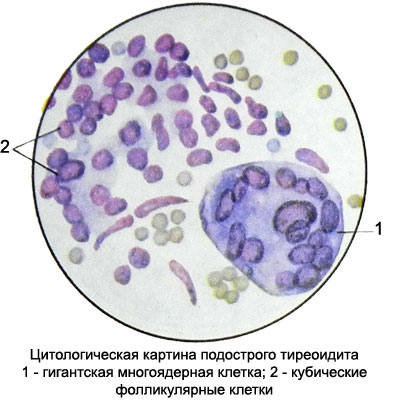
The cytoplasm of the cells intensely stained, basophilic, Homogeneous; kernel oval and round with gruboglybchatoy chromatin structure, hyperchromatic. They are located on the periphery of the cell, stratifying each other and form a broad multi-core ring. Mostly found B-cells.
Chronic thyroiditis
Chronic thyroiditis are lymphomatoid (autoimmune), or Hashimoto's disease, fibro-invasive (goiter Ridelya) and specific (tuberculosis, sifilise, actinomycosisIt is etc.).
For chronic thyroiditis, compared to acute, characterized by a decrease in the number of neutrophils preparations, an increase in macrophages, the appearance of lymphocytes, eozinofnlnyh granulocytes, polynuclear giant cells of foreign bodies, gistiocitov, and fibroblasts and fibrocytes.
Zob Khasimoto (lymphomatoid, or autoimmune, tireoidit) - A rare disease of the thyroid gland, developed mainly in women aged 40-50 years. In peripheral blood marked lymphocytosis. The disease is autoimmune in nature. Thyroid tissue in this disease is exposed to diffuse lymphoid infiltration.
The punctate of thyroid cells predominate, among which can be found even prolymphocytes lymphoblasts and many plasma cells.
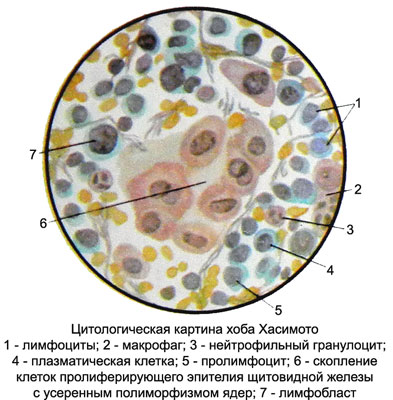
There have neutrophilic and eosinophilic granulocytes in a small amount, and the histiocytes and macrophages with different inclusions. Perhaps the presence of fibrin and bits of broken cells or nuclei. Among the clusters of lymphoid cells are observed some A-cubic cells, sometimes layers or structures zhelezistopodobnye, proliferating epithelia and separate clusters, and B-cells. Detection of at least A-flattened single cells indicates, punctate that is derived from the thyroid gland (instead of lymph node), and the presence of B cells, and diffuse lymphoid infiltration allows the correct diagnosis.
Struma Ridelya (invasive fibrous thyroiditis, Riedel's thyroiditis, Stone goiter) characterized by increasing the density of woody and thyroid. Cause ill unclear.
There is an opinion, that Hashimoto and Riedel Struma - the various stages of the process, but it is not universally accepted by researchers. There aged 40 and older, mostly women. Histologically, the parenchyma of the thyroid gland is almost completely replaced by fibrous tissue.
The elements are detected punctate chronic nonspecific inflammation and proliferative epithelium of the thyroid gland.
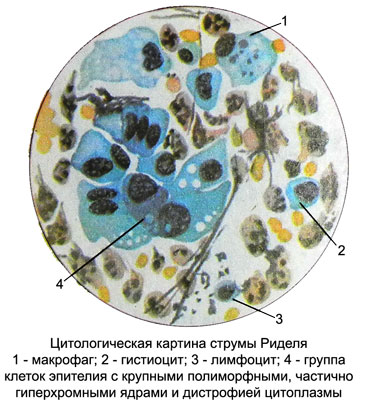
May prevail neutrophilic granulocytes, plasma cells are found, macrophages, fibroblasts and fibrocytes, and lymphocytes in a small amount (perhaps, blood), scattered on the drug, polynuclear giant cells of foreign bodies, fibrin fragments and the remains of destroyed cells. Because follicular thyroid cells are found preserved cubic and flattened, as well as large proliferating epithelial cells with basophilic cytoplasm and expressed polymorphic, hyperchromatic, often pycnotic cores, which are often enlarged and sometimes have nucleoli. Proliferating cells form clusters or cords, that can resemble a picture of thyroid cancer with inflammatory infiltration, what it is always necessary to remember. B cells in a punctate absent.