Thalassemia – Anemia, related to violation of the synthesis of globin
Etiology and pathogenesis of thalassemias
Thalassemia - A group of diseases, in which there is an inherited disorder of the synthesis of one globin chains. As a result, patients show marked or a slight hypochromic anemia. The iron content of blood serum normal or raised.
Thalassemia, in which the synthesis of β-disturbed globin chain, It called b-талассемией. This type of thalassemia occurs most frequently. At d-талассемии It violates the synthesis of α-chain. Cases have also been described y-, d- и bd-талассемии, under which disrupted the synthesis of globin chains of the same name.
In the pathogenesis of clinical manifestations of thalassemia major importance is given to the detection of excessive amounts of globin chains. So, when β-thalassemia due to violation of the synthesis of β-chain is a large amount of free α-chain. In that case, when the redundant circuit is not part of the fetal hemoglobin and hemoglobin A2, they are unstable in solution and aggregates. Excessive synthesis of α-chain is a major cause of ineffective erythropoiesis in the β-thalassemia. As a result of the death of erythrokaryocytes in the bone marrow is disrupted relationship between germ sharply irritated red bone marrow and a small increase in the level of reticulocytes. Death erythrokaryocytes bone marrow and to a lesser degree of reticulocytes and red blood cells of peripheral blood in the spleen leads to the development of severe anemia homozygous. In the spleen, liver foci found red blood formation. Yellow (adipose) no bone marrow. Excess hematopoiesis in bone leads to their deformation, and severe hypoxia - a violation of the child's development.
When α thalassemia in the complete absence of synthesis of α -chains and therefore the total absence of hemoglobin A, A2 and F comes fetal hydrops, associated with severe anoxia, which causes fetal death. Excess β-chain in thalassemia can form hemoglobin, consisting of four β - chains - hemoglobin H. Cages, containing hemoglobin H, very easy to remove from circulation the spleen. Anemia of hemoglobinopathies H is due to both the peripheral red blood cell hemolysis, and insufficient hemoglobin synthesis.
Genogeography thalassemias
Since homozygous thalassemia leads to early death, population-based study of its distribution may be based only on the detection of heterozygous carriers of disease.
The most common b-талассемия. It is found in Italy, Greece, Spain, Portugal, as well as in Southeast Asia and Africa. Also described cases of β-thalassemia in the Caucasus and Central Asia.
a-Талассемия found among residents of Nigeria, Italy, Greece, Thailand. Hemoglobinopathies H - A form of α-thalassemia, meets residents of Italy, India, Chinese. Registered sporadic cases of hemoglobinopathies H or other variants α-thalassemia among the peoples of Dagestan, in Azerbaijan and a number of regions of the European part of Russia.
Гомозиготная b-талассемия
In homozygous β-thalassemia clinical manifestations of disease are observed at the end of the first or at least on the second year of life. During the first months of life the child is quite satisfactory, found moderate anemia, but it is not always possible to resolve the issue, whether the child has inherited the disease from one or both parents.
For this form of β-thalassemia is characterized by a significant increase in the size of the spleen, yellowness and grayish skin and mucous membranes, marked pallor. Sharp hematopoietic hyperplasia (red) bone marrow leads to violations of the skeleton: almost quadrangular shape of the skull, flattened nose, prominent cheekbones, narrowing of the eye slits.
Radiological findings revealed thickening of the cancellous bone of the cranial vault, transverse striations on the outer plate of the frontal and parietal bones. Children lag behind in physical development, reduced resistance to infections, violation of sexual development.
The hemoglobin content is reduced to 1,86-3,1 mg / l (30-50 G / l). Detected expressed hypochromia erythrocytes. Color indicator - 0,5 and lower. The content of reticulocytes increased, However, the degree of stimulation of red germ hematopoiesis is much higher than generally corresponding to the degree of irritation reticulocytosis (ineffective erythropoiesis). So, often with a ratio of 0.1 leykoeritroidnom 0,2/1,0 of reticulocytes increased to 2.5-4 %. Serum iron levels often increased, but may be at the upper limit of normal. The number of bone marrow sideroblasts increased. Morphologically hypochromic erythrocytes, pronounced anisocytosis, often identified mishenevidnost erythrocytes, basophilic punktatsiya. Osmotic resistance of erythrocytes is usually raised.
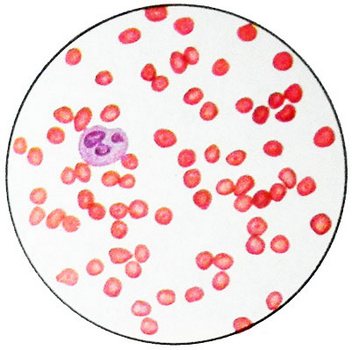
For homozygous β-thalassemia is characterized by increased levels of bilirubin due to indirect its fractions. Via 51Cr revealed shortening of life span of red blood cells. Desferalovy test can detect elevated levels of iron reserves. Excess iron deposition leads to the development of liver cirrhosis, Diabetes, underdevelopment of secondary sexual characteristics, kardiosklerozu.
Depending on the content of hemoglobin A in a patient homozygous β-thalassemia isolated β0- и b -талассемию. In cases β0-thalassemia hemoglobin A generally not formed, whereas β thalassemia occurs only a sharp decline in the synthesis of β-chain.
The diagnosis of homozygous β-thalassemia can be easily confirmed by the content of the study of fetal hemoglobin in red blood cells. In most cases, it is raised to 20-90 %, hemoglobin A2 often increased, However, the combination of β-thalassemia with δ-thalassemia is a violation of not only the synthesis of β-, and δ-chain, part of the hemoglobin A2, whereby hemoglobin A2 It may be normal or even sharply reduced.
Гетерозиготная b-талассемия
Heterozygous β-thalassemia - the result of inheritance of the disease is only one of the parents. This thalassemia often occurs with mild clinical illness, with less severe clinical symptoms. Perhaps asymptomatic disease. Complaints of patients with heterozygous thalassemia reduced to fatigue, weakness, reduced efficiency, especially in cases, when the patient is engaged in physical labor. On examination, the patient sometimes drew the attention of a small pale, occasionally slight ikterichnost skin and sclera.
Characteristic symptomatic heterozygous β-thalassemia is a slight increase in spleen.
Hematologic parameters in the heterozygous thalassemia may vary considerably. Hemoglobin normal or close to normal. The so-called thalassemia minima occurs with hemoglobin levels 6,83-7,45 mmol / l (110-120 G / l), often show a decrease in hemoglobin to 5,59-6,21 mmol / l (90100 g / l) — thalassemia minor. Very rarely is a reduction in hemoglobin levels to 4,34 mmol / l (70 g / l). Anemia is, usually, hypochromic character. The color indicator can be reduced to 0.5-0.6, more often it is 0.7-0.8. In addition to red blood cells are often detected hypochromia aniso- and poikilocytosis, as well as erythrocytes mishenevidnost varying degrees. The presence of this feature is not required for heterozygous thalassemia, as it is often found in iron deficiency anemia, lead poisoning, and in individuals, underwent a plenektomiyu.
A characteristic feature is the presence of thalassemia basophilic erythrocyte punktatsii.
The content of reticulocytes usually rises to 2-5 %, found significant irritation of red bone marrow germ, 2-3 times higher than the, that corresponds to the level of reticulocytes. It reduced the number of mature erythrokaryocytes, containing hemoglobin. The content of iron granules is increased in the bone marrow or less normal. Sideroblasts iron granules, ring around the core, They found relatively rare.
Serum iron content in patients with heterozygous thalassemia normal or increased. Stocks of iron, defined by a dough desferalovogo, also increased.
A characteristic feature of heterozygous β-thalassemia is to increase the osmotic resistance of red blood cells. Not infrequently 100 % hemolysis in thalassemia occurs only in distilled water. Sometimes used method of determining the osmotic resistance to low concentrations of sodium chloride as a qualifying test at the population-based study. However, this test is not specific, it may be positive in other kinds hypochromic anemia. Nearly 3/4 patients with heterozygous β-thalassemia detected increase in indirect bilirubin.
The diagnosis of heterozygous β-thalassemia is made by increasing the content of fractions of hemoglobin A2 to 4,2-8,9 % (the total amount of hemoglobin). For the quantitative determination of hemoglobin A2 method is used on cellulose acetate electrophoresis. Approximately half of the patients detected increase in fetal hemoglobin to 2.5-7 %.
An important diagnostic feature is the presence of this disease in any of the family members.
a-Талассемия
Synthesis of α-globin chain synthesis in contrast to the β-chain is controlled by two pairs, most likely, neravnoznachnыh Genov. So many different options possible α-thalassemia.
In the complete absence of α-chain, In homozygous dysfunction of all four alleles in the fetus can not be fetal hemoglobin, that leads to the development of hydrocephalus (hydrocephalus), and then to the fetal death. With the defeat of one or two genes occurs anemia, often expressed mild. Clinical manifestations of α-thalassemia with the defeat of the two genes, probably, depend on, which genes are amazed.
The clinical picture of the disease almost completely corresponds to the clinic heterozygous β-thalassemia. Often found enlargement of the spleen, rarely liver. Determined moderate hypochromic anemia with the presence of red blood cells and red blood cells mishenevidnyh with basophilic punktatsiey, a slight increase in reticulocytes and red sprout a sharp irritation of the bone marrow, small hyperbilirubinemia, increase in serum iron and osmotic resistance of red blood cells. Characterized by the presence in the family of blood relatives, suffer from the same deficiency anemia. But, Unlike β-thalassemia, when α-thalassemia not increase the amount of fetal hemoglobin and hemoglobin A2 due to, what they, as well as hemoglobin A, contain α-chain. Hence, Unlike β-thalassemia, relations between factions in the α-thalassemia are not changed. To suggest the presence of α-thalassemia can be in cases, when the clinical picture resembles β-thalassemia, but there is no increase in hemoglobin A2 and F. Diagnosis and thalassemia should be based in these cases only the study of the biosynthesis of globin chains in vitro.
Sometimes the diagnosis of α-thalassemia can be put in newborns. In the study of blood hemoglobin electrophoresis revealed Bart, devoid of α-chain and consisting of four γ-chains.
Hemoglobinopathies H
Hemoglobinopathies H - a variant of α-thalassemia. It is characterized by a mild course of a relatively, a significant increase in spleen, liver, slight jaundice due to increased indirect bilirubin, anemia of varying severity, but often the content of hemoglobin below 4,34- 5,59 mmol / l (70-90 G / l).
A marked hypochromia erythrocytes, mišenevidnostʹ, basophilic punktatsiya. Just as with other forms of thalassemia, when hemoglobinopathies H shows signs of ineffective erythropoiesis - a sharp irritation red sprout bone marrow slight increase in reticulocytes.
A feature, hemoglobinopathies H distinguishes from other forms of thalassemia, Multiple small inclusions are all erythrocytes, that appear in the cells after incubation with the dye bright cresyl.
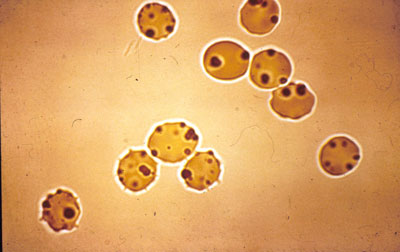
They are caused by precipitation under the influence of the dye-oxidant unstable hemoglobin H, composed of four β-chains. This hemoglobin is unstable in solution haemolysate. It is precipitated at 55 ° C for 1 no, as well as in the medium, containing isopropyl alcohol.
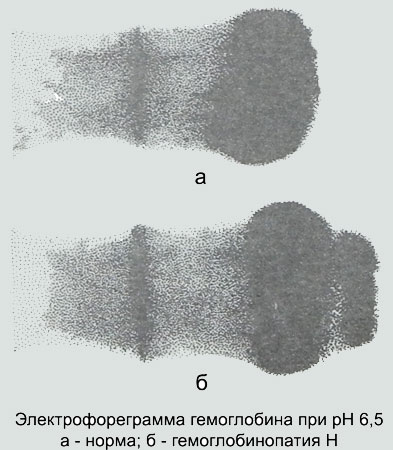
Electrophoresis at pH 8,6 Hemoglobin H moves ahead of normal hemoglobin A.

At pH 6,5 Hemoglobin H moves towards the anode, and hemoglobin A - the cathode.
bd-Талассемия
For βδ-thalassemia is characterized as a violation of the synthesis of β-, and δ-globin chains.
Clinically heterozygous βδ-thalassemia is different from heterozygous β-thalassemia. Usually heterozygous β-thalassemia, an increase in hemoglobin A2. However, hemoglobin A2 It contains δ-chain, and, Consequently, the combination of β-thalassemia with δ-thalassemia is not the most typical laboratory signs of β-thalassemia - an increase in hemoglobin A2.
Often when this is found an increase in hemoglobin F under normal or reduced hemoglobin A2 (so-called HbF-thalassemia).
При гомозиготной b-талассемии, сочетающейся с d-талассемией, almost all of the child's hemoglobin is hemoglobin F. hemoglobin A2 wherein either reduced, or he is absent. There is evidence of a less severe homozygous thalassemia at 100 % Content of fetal hemoglobin. The disease occurs as thalassemia intermedia.
Diagnosis of homozygous β-thalassemia is no difficulty. It is more difficult when there is no increase in the content of fetal hemoglobin. In these cases, the diagnosis can be made only in the study of the biosynthesis of globin chains.
Hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin
This term means a heterogeneous group of states, characterized by a significant increase in fetal hemoglobin synthesis without the expressed clinical and hematological disorders. First, these states have been described in 1955 g.
The majority of homozygous carriers of this disease has been a slight decrease in hemoglobin urovlya to 6,52- 6,83 mmol / l (105-110 G / l), sometimes its normal content with a normal level of red blood cells n a slight decrease color index. Some patients unable to palpate a spleen. Number of reticulocytes within a norm, bilirubin level is not elevated.
When heterozygous carriers of the clinical manifestations are absent. Characterized by a significant increase in the level of fetal hemoglobin. In homozygous carriers of fetal hemoglobin content may be 100 %, geterozigotnom- at 10-25%. In contrast, thalassemia, in hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin content of the red blood cells it all the same.
The main feature of hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin - is the lack of an imbalance between the synthesis of α-chain and the chain of, with which it should communicate. Because the γ-chain synthesis in this disease is significant, after birth no free α-chain, that in thalassemia aggregate and disrupt viability erythrokaryocytes. No signs of ineffective erythropoiesis, almost completely absent anemia. In connection with minor symptomatic treatment of thalassemia requires.
