mumps disease, эpidemicheskiy mumps: What's it, treatment, symptoms, diagnostics, mumps prevention
Mumps (Epidemic Parotitis)
What is mumps?
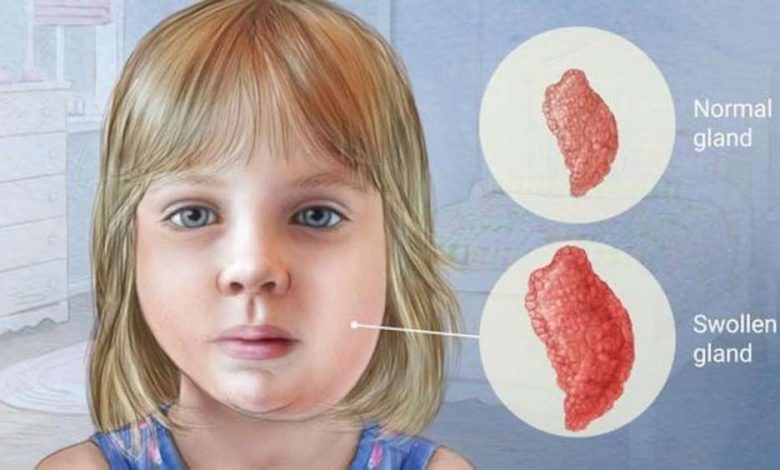
Mumps is a viral infection. It causes fever and swelling of the parotid gland, next to the ear. Once the pig was a fairly common disease, but now it is uncommon, due to the widespread use of vaccines against mumps.
Causes of mumps
The mumps virus is usually spread through contact with the saliva of an infected person. It is also easily spread through close contact with a sick pig.
Risk factors for mumps
Factors, that may increase the risk of infection include mumps:
- Lack of vaccination against mumps and contact with patients;
- Born after 1956 year and never bolevshie mumps or been vaccinated against mumps;
- Age: 10-19 years;
- Season: winter;
- Weakened immune system, Even after vaccination.
Symptoms of mumps
About a third of mumps cases do not cause symptoms. Symptoms usually occur through 2-3 weeks after infection.
With the development of the disease Mumps can cause the following symptoms:
- Painful swelling of the parotid gland;
- Fever;
- Discomfort;
- Anorexia;
- Sore throat;
- Headache;
- Kryvosheya;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Drowsiness.
Other symptoms of mumps:
- Swelling and pain under the tongue, in front of the jaw or chest;
- Men: painful inflammation of the testicles;
- Women: ovaritis, resulting in pain or abdominal pain.
Diagnosis of mumps
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical examination. Diagnosis is based on the identified symptoms of mumps.
Treatment of pigs
Mumps is caused by a virus, so it can not be cured with antibiotics. The focus is on relieving symptoms.
Basically mumps will last about 10-12 days. To remove the discomfort:
- Apply hot or cold compress on the swollen area;
- Gargle with warm salt water, to reduce pain;
- To treat fever, take acetaminophen or ibuprofen;
- Note: Children and teens with a current or recent viral infection should not take aspirin, because of the risk of Reye's syndrome. Ask the doctor, What other medicines are safe for your child.
- Drink plenty of fluids. Avoid tart or acidic drinks, such as, orange juice or lemonade;
- Eat soft, light meal.
Complications of mumps
Most healthy children are rare complications. But, If complications occur, they include:
- Temporary deafness;
- Swelling or infection of the brain, pancreas, heart or other organs;
- Orchitis;
- Problems with male fertility.
Prevention of mumps
Vaccination is the best way to prevent mumps. Mumps vaccine contains live viruses, which can not cause disease. It is usually administered in combination with other vaccines:
- The vaccine against measles and rubella (MMR);
- Measles, rubella, and varicella (MMRV).
Vaccination is aged 12-15 months of age and again in 4-6 years. If you or your child has never been vaccinated against mumps, Consult a physician.
Although the majority of children and adolescents should be vaccinated according to the schedule, certain groups must not be vaccinated:
- Person, who had severe allergic reactions to the vaccine or the vaccine components;
- You can not be vaccinated against mumps during pregnancy. It should also be avoided during pregnancy 1-3 months after vaccination;
- Persons with weakened immune systems;
- Persons with a high fever or severe upper respiratory tract infection.
If you are not vaccinated, avoid contact with sick pig.
