The structure of the male genital organs – Spermatogenesis
By the male genitals are testicles, epididymis, semyavыnosyaschye Strait, seminal vesicles, prostate and penis.
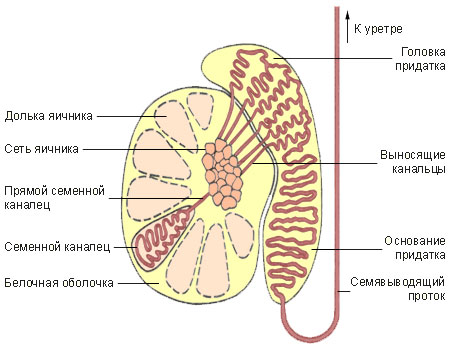
Testicular parenchyma is divided by thin connective barriers according of 100-250 Dolek, which consist of convoluted seminiferous tubules length of approximately 0.7 0,8 m each.
Between the tubules are the connective tissue and interstitial endocrinocytes (Leydig cells), which produce the hormone.
Spermatogenesis It occurs in the seminiferous tubules. At the border membrane in the seminiferous tubules are supporting cells (Sertoli cells), that, interconnected processes, form loops, filled epithelium, in different stages of spermatogenesis.
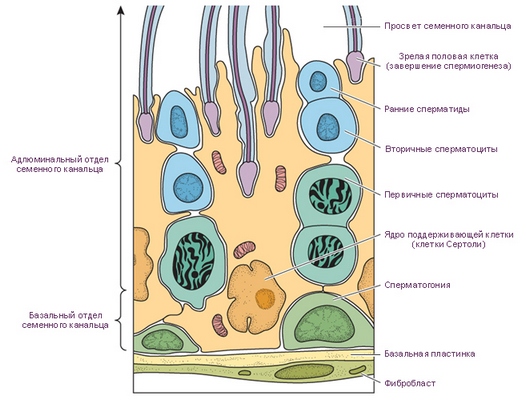
Supporting large-sized cells, outstretched, pear-shaped or fusiform, length from 20 to 40 m, with light, angular nucleus. The cytoplasm of these cells are multiple trophic inclusion (droplets of fat and lipids, protein crystals, and others.). Spermatydы, maturing in sperm, normally tightly adjoin the supporting cells, implementing and trophic, apparently, hormonal function.
On the border between the membrane of the seminiferous tubules supporting cells are located spermatogonia - progenitor cells of spermatogenesis. Part of spermatogonia, pushing off in the division by limiting membrane, stop dividing and growing strongly, turning into spermatocytes I order (primary). RSB spermatocytes divide (meiosis), resulting in a pairing chromosomes (konayugatsiya) and reducing their numbers by half. So, before dividing spermatocytes, like all somatic cells, have at 46 chromosome, and after meiosis they become 23, which is characteristic of gametes (spermatotsitov, spermatids and spermatozoa).
Spermatocyte I order is divided into two spermatocytes II of the order (secondary), are again divided, turning into spermatids.
Spermatydы, in turn, turn into sperm. In the ejaculate, containing a large number of cells of spermatogenesis, You can find giant multi spermatids (2-12 Cores).
Parorchis It includes a head, which is associated with egg, body and tail, rolling in semyavynosya- extending duct. Efferent tubules of the testis and epididymis duct lined with pseudostratified epithelium.
Semyavыnosyaschye Strait have a length of approximately 0,45 m. Coming out of the scrotum, they pass through the inguinal canal into the pelvis to prostate. The vas deferens is lined by columnar epithelium.
The seminal vesicles located at the base of the bladder. The mucous membrane is covered with a single layer of the seminal vesicle prismatic epithelium, preserving the structure of two-row seats. Excretory duct of the seminal vesicle empties into the ejaculatory ducts, which, together with the opening of the prostate utricle opens on seed hill, located on the back wall of the prostate urethra. Semяvыnosящiй flow vыstlan odnosloйnыm prizmaticheskim эpiteliem.
On each side of the urethra in its upper part positioned bulbourethral gland, ducts that open into the urethra. Alveolar end section of these glands are lined with a single layer of flat, and the other departments - cubic or prismatic epithelium.
The mucous membrane of the urethra in the prostate of the transitional epithelium covered, below the confluence of the ducts bulbourethral glands (pereponchatoy parts) - Multilane prismatic, and from the area of the scaphoid fossa (located in the glans penis) - Flat with signs of keratinization.
