The structure and function of the ovaries
Yaychnyk - Paired organ. It is covered with a layer of germinal epithelium, the remnant of the embryonic reproductive platen. In newborns covered with a single layer of the ovary or cubic columnar epithelium, adult women - Flat. By this, the surface epithelium (mesothelium) located albuginea - a dense connective tissue capsule.
The ovary distinguish the cortex and medulla.
IN cortex germ cells are formed and produced hormones. The medulla of ovaries formed by connective tissue, which are blood vessels and nerves. In the ovarian cortex under the capsule are numerous primary follicles, consisting of germinal egg (oogonia). Between primary ovarian follicles found growing follicles of varying degrees of maturity, as well as atretic (atrophy) follicles. Besides, in the cortex of the ovary yellow body located.
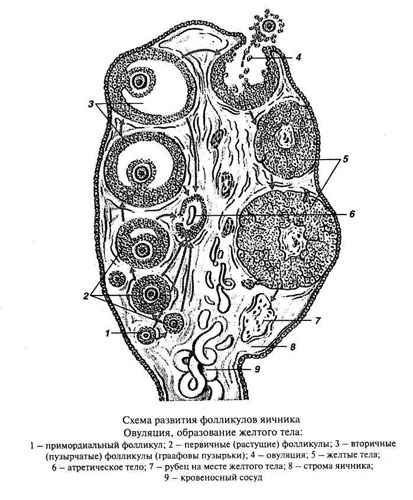
During oogenesis primary ovarian follicle becomes secondary (bubbly). At the beginning of the growth of epithelial cells proliferate heavily follicles, which becomes a multilayered granular layer and forms.
As the size of the follicle form the theca (shell) follikula. The cells of the granular layer secrete follicular fluid, whereby in its thickness appears cavity, filled with liquid, and pushed to the oocyte follicle TEKAMA. These follicles, reaching their maximum growth, and are called secondary. The plot of the granular layer, which is oocyte, referred to oviparous mound. A further increase in the secondary follicle, overflowing liquid, It leads to its stretchability, and then to break with the release of the oocyte 1st order (ovulation).
Content ruptured ovarian follicle is poured into the cavity of the peritoneum, from whence oocyte 1st order It falls on the fringe of the funnel and into the lumen of the fallopian tube. Here, by dividing the oocyte maturation and the 1st order turns into oocyte 2nd order and, finally, a mature egg, ability to fertilize.
The wall of the bursting of the secondary ovarian follicle, from which after ovulation retained its granular layer and connective tissue sheath, It is going to fold, caused a blood clot quickly organized, being replaced by connective tissue scar, resulting in the center of the future of the corpus luteum appears connective tissue scar.
Further yellow body It goes through four stages of development. Stage proliferation and vascularization replaces glandular stage of metamorphosis. At this stage, the epithelial cells of the granular layer former follicles hypertrophy and they accumulate yellow pigment (Lutein), belonging to the group lipochromes (Such cells are called lutein). As a result, the volume of the newly-formed transformations of the corpus luteum increases rapidly, and it starts to produce progesterone. Such yellow body called menstrual, period of its development lasts 12-14 days. When pregnancy occurs the safety of the corpus luteum is longer, it reaches its maximum development.
The difference between the corpus luteum during pregnancy and during menstruation is the length of the existence and size. The corpus luteum of pregnancy reaches 50 mm and more, whereas menstrual - 150-200 mm. After the cessation of operation of the corpus luteum, as catamenial, and pregnancy, undergoes involution (stage reverse development). As a result, the former site of the corpus luteum remains connective scar, called off-white body, which is stored in the ovary several years and resolves.
In some cases, an excess of the pituitary luteinizing hormone luteinization (t. it is. the transformation of cells of the granular layer of follicles in the luteal) comes back in nelopnuvshih follicles, Consequently, no ovulation. Education of anovulatory lutea is pathological, accompanied by disturbances of the menstrual cycle and may cause infertility (temporary or permanent).
A significant number of follicles, before reaching the stage of secondary (at the beginning or in the middle of its development), undergoes a kind of restructuring destructive (atreziyu). As a result of this restructuring is formed atretic body, somewhat reminiscent of the corpus luteum, from which it differs by the presence in the center of wrinkled shiny shell (in the corpus luteum in this place is connective tissue scar). Over time, the body and the remains of atretic oocyte gradually replaced by scar tissue.
Established, what in composition of follicular fluid growing and mature follicles in addition includes a protein hormone estrogen gonadokrinin. This hormone, as estrogens, produced by cells (grainy) follicular epithelium. Suggest, gonadokrinin that inhibits the growth and maturation of oocytes in the neighboring, less developed follicles, promoting their atresia. Atreziyu, thus, It should be viewed as a physiological mechanism, preventing superovulation, t. it is. excessive formation of eggs. Influenced gonadokrinina atresia and is subject to liquidation and mature follicles, Ovulation is for one reason or another does not occur.
Fluid, accumulating in the cavity of the growing primary follicles and secondary follicles contained, rich эstrogenami. The development of estrogen participate cells of the granular layer. The growth of the uterus and the establishment of the sexual cycle begins after puberty. Climacteric termination of the ovaries is accompanied by menstrual irregularities, and cessation of menstruation and senile atrophy of the uterus.
Ovarian function is activated follitropin and lutropin - Anterior pituitary hormones, action begins after, both in growing primary follicles segregated cavity. For further development of these follicles need to influence follitropin. To the growing follicles produce estrogen, We need additional effect of small amounts of lutropin. Since lutropin specifically activates the interstitial cells, latest, apparently, They are also involved in the formation of estrogens. Hence, estrogens are involved in the development of epithelium growing follicles and interstitial cells.
Increasing the concentration of lutropin It triggers ovulation and the formation of the corpus luteum. The functioning of the corpus luteum, t. it is. production and secretion of progesterone them, It enhances the effect of prolactin. The greatest of his yellow body reaches during pregnancy. The destruction of his in the first half of pregnancy leads to abortion, the use of progesterone often prevent miscarriage. Under the influence of progesterone the uterine glands secrete mucus, mucosa swells, and its vessels are filled with blood. At the same time, progesterone inhibits the growth of follicles in the ovary. Therefore, while the corpus luteum is under flowering, the growth of follicles in the ovary is absent.
The functioning ovary along with specific ovarian hormones (estrogen and progesterone) produced (in a small amount) male sex hormones - androgens, which are produced by special cells, located in the gate area of the ovary. An important role in the regulation of ovarian function plays the nervous system.
Ovarian Function It reflected on the state of endometrium and vaginal mucosa, epithelium which cyclically varies during the menstrual cycle. Property vaginal epithelium change under the influence of hormones underlies the hormone cytological diagnosis.
