The structure and function of the kidney
The kidneys are made up of two layers: outer - and inner cortex - brain. Cortical substance in the form of pillars penetrates the brain. Between the pillars of the pyramid forms the medulla, bases directed to the cortex. The number of pyramids in each kidney ranged from 4 to 16. The tops of the renal pyramids, connecting two – three, end papillae, that, of a cover, surrounded by small renal cups. Small cups, merging, form a large cup, which make up the renal pelvis.
The functional unit of the kidney is the nephron. Their number is about two million.
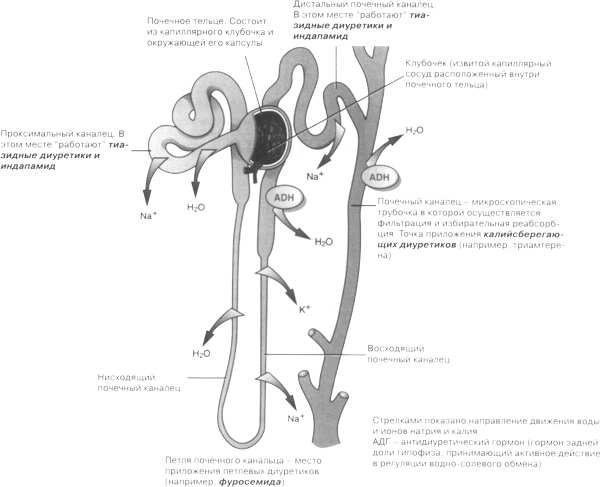
Nephron consists of a renal corpuscle and renal tubule system. The renal corpuscles are distinguished vascular glomerulus (glomerulus renal corpuscles) and envelops its capsule. Glomerular capillaries originate from generating, afferent, arterioles and collected in the outflow, efferent, which subsequently decomposes into the capillary network, supplies blood to tubular segments. In the vascular glomerulus renal corpuscles there are about 50 anastomosing capillary loops together.
Capsule klubochka It comprises two sheets: internal, intimately adjacent to the glomerular capillary network, and outer, rolling in the wall of the tubules of the nephron. A cavity between the sheets, passing into the lumen of the tubules of the nephron.
Tubules in the nephrons It consists of four parts: proximal (the principal), loop of the nephron, distal renal tubules and collecting, which goes into the papillary duct, opening on top of the renal pyramids in the renal cavity cups.
Using electron microscopy, we studied the complex structure of the glomerular capillary wall, consisting of a layer of endothelium, basement membrane and epithelial cell layer.
Endothelial cells flat, with clear cytoplasm, very poor mitochondria. In the cytoplasm of endothelial cells, covered glikokaleksom (layer podocyte sialoprotein), available pore size of 50-100 nm with a special microdiaphragms, through which mainly is filtered. It is believed, that the filtering is also possible without pores, through active pinotsntoza.
The basement membrane glomerular capillaries distinguish subendothelial and subepithelial layers, between which is a layer of dense connective tissue - mesangium with similar cells Process. Mezangij It is consisting of protein filaments kollagenopodobnogo (between which there are about the size of the gap 2 nm - the pores of the basal membrane), Glyco- and lipoproteins. Mesangial both sides covered glikokaleksom podocytes (эpitsitov) and endothelial. The filtration process of the material is lost mesangial. Through the pores of the basal membrane can pass albumin molecule, immunoglobuliny, but their penetration is limited by the presence of glikokaleksa basement membrane and its negative charge.
Mezangiocitы containing plate material, endoplazmeticheskuyu granular network, mitoxondrii, ribosome, and plastic have secretory functions and produce basement membrane material. With mezangnotsitov pathology associated with the development of glomerulosclerosis.
These cells are part of the juxtaglomerular complex and can synthesize renin. Otrostki mezangnotsitov, penetrating through the glomerular capillary endothelium, contact with blood. Besides, mezangiotsity have phagocytic and contractile function.
The cells of the epithelial layer (podocitы) They are part of the inner layer of the glomerular capsule. They have cytoplasmic processes - legs. Large legs start perinuclear zone podocytes and cover the surface of the capillary. Small feet, or pedikuly, depart perpendicularly from large. intertwined, and are also located on the surface of the capillary. The system of small legs forming a so-called lattice slit diaphragm, pore diameter which is 5-12 named. Slot diaphragm glikokaleksom covered and bordered to the basement membrane of the capillary. In the cytoplasm of podocytes are filaments and microtubules, which together with the slit diaphragm filtration process is carried out on the principle of micro-pumps: the filtrate is pumped into the cavity of the capsule glomerulus.
The outer part of the glomerular capsule It consists of the basement membrane, rich reticular and collagen fibers, and epithelial cells cubical, containing actomyosin (whereby they are called myoepithelial). Mioepitely, cutting, It changes the volume of the capsule, participating in the process of filtration.
Proximal (home) tubule of the nephron It consists of crimped (clotted) and direct parts. Direct part goes into a loop of the nephron. Cages, lining of the proximal convoluted tubules of the nephron, cube-shaped, height 8 m, the most complex structure in comparison with other parts of the tubule epithelium. In the cytoplasm of these cells has a rod-shaped striation - brush border microvilli, facing the lumen of the tubule. This striation is composed of many outgrowths of the cytoplasm (to 6500 in the same cell), which increases the suction surface. Brush border contains a number of enzymes (fosfatazu, ATF canine, 5-Nucleotidase, aminopeptidazu, carbonic anhydrase, and others.), and covering her cell membrane includes metabolic-sodium-transport system. Glikokaleks, covering the microvilli brush border, only allows macromolecules. Invagination of the basement membrane and membranes of adjacent cells in the cell cytoplasm tubules of the nephron increases in intracellular membranes, that create a diffuse space reabsorption. The basal part of the cell, between intracellular membranes, contains numerous mitochondria, where the energy is produced, necessary for the absorption and secretion of. The secretion of urine is carried out with the participation of the developed granular endoplasmic ethical networks and plate set.
Cages, lining the descending part of the loop of the nephron, flat stellate. In this section there is a diffusion of water and substances dissolved in it.
The distal tubule of the nephron It consists of a straight (rising) and twisted parts. Lining of epithelium cubic, I do not have a brush border, It contains mitochondria, intracellular membranes, canalicular apparatus, enzymes. These cells carry optional reabsorption, which is governed mostly posterior pituitary hormones, adrenal and renal juxtaglomerular complex.
In the area, where convoluted tubule distal part of the nephron approaching glomerulus renal corpuscles, epithelial cells becomes high (cylindrical), and the core of their hyperchromic. This part of the complex called the juxtaglomerular tight spot. The cells of this region are arranged in a stockade on the basal membrane, in which there are gaps. Due to the close contact of the cells with dense spots juxtaglomerular kidney complex effect of the composition performed on urine haemocirculation glomerular renal corpuscles.
The epithelium of the distal nephron çastï tubules easily damaged by lack of oxygen as a result of renal hemodynamics. Here epitheliocytes exposed to toxic products urine, that can lead to necrosis.
Collective renal tubules cells consist of two types - a transparent and dense. In distal renal tubules, which transports urine, transparent cells predominate, permeable to water molecules. Dense cells predominantly located in the proximal renal tubules collecting. These cells contain many mitochondria, possess the expressed enzymatic activity. Particularly high activity karboamgidrazy. Dense cells secrete hydrogen ions.
Most of the loop of the nephron renal tubule and collecting form renal medulla.
The element structure of the kidneys is juxtaglomerular complex, which plays an important role in the production of renin, Erythropoietin and the regulation of blood pressure. Inter- interstitial cells of the kidney medulla produce prostaglandins, which have antihypertensive and antndiureticheskoe action at the level of the microvasculature.
The kidneys are formed vitamin D3 and kallikrein, which splits off from kininogen kinin. Kidney kinins have a marked vasodilatory effect on cortical (large), and the juxtaglomerular (small) bloodstream.
