Description of the liver, structure and functions of the liver in the human body
Liver - The largest iron man, its mass reaches 1.5-2 kg. Its main function is protective, consisting in the removal of infectious and toxic agents. So, detoxified in the liver nitrogenous substances, that result from the metabolism of proteins and with the blood to the liver. Here synthesized urea, which is excreted from the body by the kidneys. Besides, liver glycogen is converted into monosaccharides, coming back with blood. By reducing the concentration of glucose in the blood, it is formed from hepatic glycogen.
The liver synthesizes the most important plasma proteins (albumin, Some fraction of globulins, fibrinogen, prothrombin, Factor VII, or proconvertin and others.), lipids, and bile, that, acting in the gut, It helps emulsify fats and absorption of their degradation products in the blood and lymph. The liver is involved in the metabolism of cholesterol and vitamins, and in the embryonic period the function of blood forming organs.
The liver is covered with serous membrane, under which there are podseroznaya basis and fibrous sheath, that on the lower surface of the liver with portal vein and hepatic artery immersed inside body. Inside the liver connective tissue stroma forms a body, dividing the liver parenchyma into small slices, the number of which reaches the human liver 500000. This structural and functional units of the liver. The classic form of representation they have a hexagonal prisms. Interlobular connective tissue, which are blood vessels and bile groove, underdeveloped, As a result, the liver slices badly demarcated from each other. More pronounced growth of connective tissue in the liver leads to the development of severe disease - cirrhosis.
Slices of liver formed hepatic plates (beams) and intralobular sinusoids vessels. Hepatic plates are cords of hepatocytes (liver cells), arranged radially.
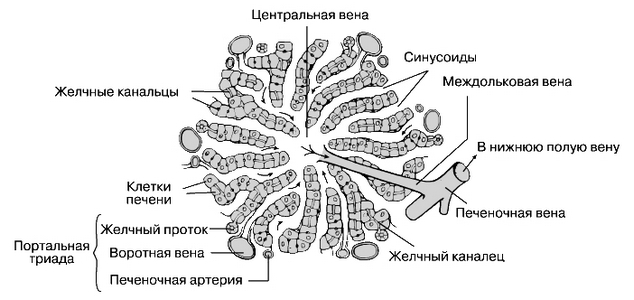
Between the hepatic plates in the same direction from the periphery to the center tested sinusoidal capillaries. Their walls are lined with endothelium, between cells that are dispersed stellate retikuloendoteliotsity (Kupffer cells), do not form a continuous layer. This liver macrophages, originating from bone marrow monocytes. With the exception of the peripheral and central parts of sinusoidal vessels over a large area does not have a basement membrane. In the liver hepatocytes plates are arranged on the narrow slit width 0,5 to 1 um - bile capillaries, do not have their own wall.
Gepatocitы, involved in the formation of bile capillaries, have on their contact surfaces are small depressions in the form of grooves. The points of contact of two hepatocytes groove of one of them coincides with the other groove, so that between them is formed a small gap. Bile capillaries begin blindly and become the interlobular bile ducts. The direct connection between blood and bile capillaries missing, as between them are hepatocytes. Only in diseases, accompanied by damage and loss of hepatocytes, the bile of bile can directly enter the blood capillaries (jaundice).
Stellate retikuloendoteliotsity elongated, elongated at the poles form, size from 15 to 40 m, They have a fairly large nucleus with nucleoli and basophilic cytoplasm light.
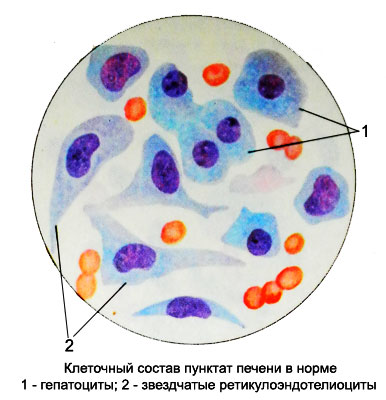
Stellate retikuloendoteliotsity may also have a rounded shape. These cells can absorb from the blood circulating in her substance, resulting in their cytoplasm are found fragments of red blood cells, hemosiderin, fat droplets, etc..
Hepatocytes in punctate irregular polygonal shape, diameter 20-25 mm. The nuclei of these cells are rounded, size of 6-8 microns, It contains one or two small nucleolar.
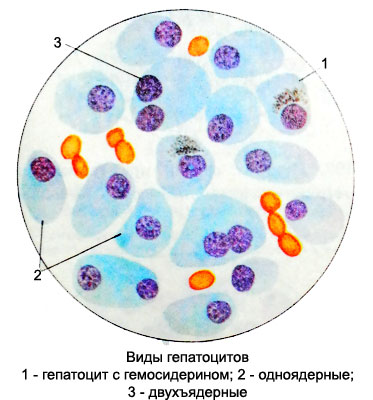
Normally, in the 20% cell there are two nuclei, that should be seen as a manifestation of regenerative processes in the liver. In various diseases of the liver hepatocytes increases the number of dual-core.
Cytoplasm gepatocitov depending on the functional state or degree of dystrophic changes in them it is colored in blue, in the light or light purple- purple tones. It contains many mitochondria, uniformly distributed in the cytoplasm, and RNA, which is revealed in the form of basophilic granules. The amount of such pellets depends on the conditions of protein nutrition organism. Besides, It can be detected in the cytoplasm of the fat droplets, glycogen, hemosiderin and clumps of bilirubin.
In various pathological processes degenerative changes observed in the nucleus, and in the cytoplasm of hepatocytes. Nuclear chromatin becomes more rough, there are sites parahromatina, nucleus and nucleoli increased. When changes in the nuclei pyknotic chromatin structure becomes indistinguishable, They are painted in darker tones. Degenerative changes in the cell cytoplasm is usually associated with an increase in vacuolization, fatty degeneration and other changes.
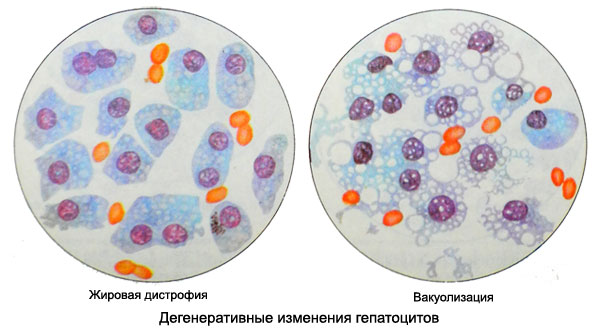
Normally, in the liver punctate found mainly hepatocytes and blood cells, stellate retikuloendoteliotsity rare. Count of 500-800 cells and determined the percentage of different types of hepatocytes.
Gepatogramma OK, %.
- Mononuclear hepatocytes - 80-92,4
- Dual hepatocytes - 8,5-21,4
- Multinucleated hepatocytes - 0.2-0.4
- Degenerativnыe gepatocitы (with deposition of lipid and t. d.) - 0.4-0.5
