The structure and function of the mammary gland
The adult, normally developed female mammary gland consists of 15-25 shares, each of which is based on the type of the complex alveolar glands. Ducts shares opened at the top of the nipple milk cancer and to expand the mouth of the nipple, forming lactiferous sinuses, are reservoirs for milk.
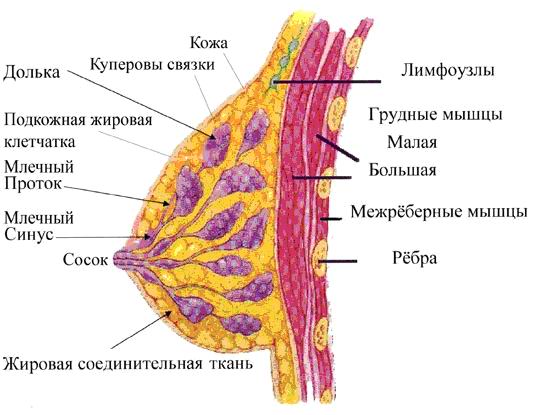
Meanwhile shares of the breast deposited layer of loose connective tissue and adipose. In the connective tissue interlayers meet fibroblasts, macrophages, lymphocytes, plasma cells, sometimes - eosinophilic granulocytes.
The alveoli cancer and collective galactophore are lined with cuboidal epithelium, Milky Strait (fine, medium and large) - Cylindrical, lactiferous sinuses - multilane prismatic, areola region - stratified squamous epithelium. Full development of the mammary gland during pregnancy reaches.
Secretory alveolar process starts in the second half of pregnancy, Shortly before the birth of the breast stands colostrum. The secretion of the mammary gland is accomplished by type of apokrinovomu otshnurovyvaniya top of the cytoplasm laktotsitov. The milk from the alveoli into the Milky moves reduction of process occurs when the myoepithelial cells - zvezdchatыh mioэpiteliotsitov. After a period of lactation the mammary gland undergoes involution, but part of the alveoli, formed during pregnancy, preserved.
Growth and development of the mammary glands in girls during puberty stimulated by estrogen. During the menstrual cycle mammary secretory activity increases during ovulation and decreases during menstruation. With the onset of menopause or after castration the mammary gland undergoes involution.
