Gestational age and toxic effects of drugs
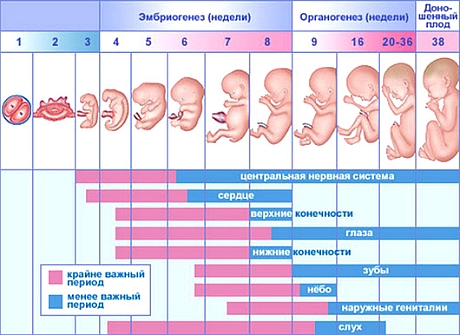
There are so-called critical periods of embryogenesis, when the most dangerous effects of adverse factors - microorganisms, drugs or metabolic products of excessive concentration.
In the first week of pregnancy damaging factors cause the death of the embryo and abortion or, conversely, do not leave the consequences (All or nothing) due to the high regenerative capacity of the embryo. At the end of this period begins on cell differentiation, increases metabolism of the embryo and reduces the regenerative ability. At this time, enhanced sensitivity to drugs (I critical period). After implantation, begins the period of organogenesis, completed by 3-4 month of intrauterine life. During this period, the most sensitive are the first phase 3-8 weeks (II critical period), when most evident teratogenic and embryotoxic effects of drugs, respectively, resulting in the formation of defects and fetal death. Affects those organs, which at this point in the process of differentiation. Malformations depend on the direct action of the drug in the fetal organs and tissues. There is some specificity of teratogenic drugs.
After completion of the fetal organogenesis begins, or fetal development period, continuing to 40 weeks. During this period, there are virtually no embryotoxic and teratogenic lesions, with the exception of genital malformations in female fetuses, arising under the influence of drugs androgenic effect. On 18- 22-weeks of age (III critical period) place the most significant changes in the bioelectric activity of the brain, gemopoéza, hormone production.
Currently, I accumulated a lot of data on the undesirable action of drugs on the fetus.
Unwanted influence of drugs, used during childbirth
| ||
| Drug substance | Effect of fruit | Action rozhenitsu |
| Narcotic analgesics | ||
| Trimeperidine | Respiratory depression fetus during pregnancy pathology, prematurity | In the commonly used doses it has no pronounced side effects |
| Pyrytramyd | Respiratory depression, increasing, when combined with phenothiazine and benzodiazepine | - «« - |
| Pentazocin | Respiratory depression and adaptation of the cardiovascular system to the intrauterine life. The use in obstetrics inappropriate | - «« - |
| Fentanyl | Respiratory depression fetus and mother | - «« - |
Local anesthetics | ||
| Trimecaine Lidocaine hydrochloride | Fetal hypoxia, acidosis due to lower utero-placental blood flow, hemodynamic instability in the fetus (negative inotropic effect, decrease in atrioventricular conduction, bradycardia), secondary fetal hypoxia | Allergic reactions, decrease in blood pressure up to collapse |
Neingalyatsionnyh and inhaled general anesthetics | ||
| Halothane | CNS depression | Increased sensitivity of the heart to catecholamines. Gepatotoksichnostь, increased bleeding, decrease in muscle tone of the uterus |
| Nitrous oxide | The decrease in Apgar, gipoksiya, Acidosis | No effects |
| Ketamine hydrochloride | It is safe for the fetus at a dose 1 mg / kg body weight of pregnant woman. At a dose of 3 mg / kg and above - CNS depression. Rarely used | When administered intravenously 7-100 mg increases the intensity 2-3 subsequent uterine contractions |
| Metoksifluran | CNS depression fetus, not recommended for use in preterm labor | Increasing the sensitivity of the myocardium to catecholamines |
| Sodium hydroxybutyrate | The decrease in Apgar, CNS depression muscle relaxation | With rapid intravenous maternity - excitement, vomiting, tonic convulsions, respiratory arrest |
| Predion | At doses 10-20 mg / kg body weight not affected mothers to the fetus | Local thrombophlebitis |
| Propanidid | Gipoksiya, acidosis due to violation of fetoplacental blood flow | Lowering blood pressure |
| Thiopental sodium | CNS depression | CNS depression |
| Trichloroethylene | CNS depression | Increased blood pressure. Do not use a cat-- xolaminami, premature labor. In case of overdose - respiratory depression and heart rhythm disturbances |
Means for premedication | ||
| Droperidol | At doses, used in obstetrics (0,1-0,15 mg / kg body weight of pregnant woman), It has no effect on the fetus. Used in combination with other analgesics and anesthetics | - |
Anticonvulsants | ||
| Diazepam | Odnokratnaya dose (10-20 mg) dlya harmless fruit. At high doses and repeated administration - CNS depression (It can last for several days), respiratory depression, apnea, risk aspirations, hypomyotonia, gipotermiя, strengthening of jaundice due to inhibition of conjugation of bilirubin | - |
| Promethazine | When used during delivery does not affect the fetus | Dry mouth, reduction of blood pressure when administered intravenously, infiltrates after intramuscular administration |
| Phenobarbital | Hemorrhagic Syndrome | - |
A schematic diagram of the periods of fetal development is shown in Figure
According to the degree of teratogenicity drugs classified:
- Category A - drugs with undiagnosed teratogenic or clinic, any experiment; eliminate the risk of teratogenicity studies do not allow any;
- Category B - drugs, which was absent in the experiment teratogenicity, However, no clinical data;
- Category C - drugs, have an adverse effect on the fetus in the experiment, but there is no adequate clinical monitoring;
- Category D - drugs, teratogenic, but the need for their use outweighs the potential risk of the fetus; These drugs are prescribed for health reasons. Women should be advised of the possible consequences for the fetus;
- Category X drugs with proven teratogenic in experimental and clinical. Contraindicated in pregnancy.
It is also used for the distribution of drugs in the teratogenicity 4 groups: particularly dangerous, dangerous (correspond to the category X), conditionally dangerous (correspond to the categories D and C), virtually no dangerous (correspond to categories A and B).
| Classification of drugs for teratogenicity | |||
| Particularly dangerous | Dangerous | Relatively dangerous | Almost safe |
|
|
|
|
