Sporovyky – Morphology and development cycle of pathogenic protozoa
This class includes parasitic forms of protozoa, living cells, cavities and tissues of animals and humans. For Sporozoa organelles characterized by the absence of movement in the adult form and appearance flagella at certain stages of development. The life cycle of the parasite complex, many runs with the change of the two hosts.
As a result of sexual reproduction spores are formed (they are absent from haemosporida), hence the name of the class - Sporozoa.
Of greatest interest Sporozoa haemosporida, which include various types of Plasmodium falciparum. In humans, malaria causes four types Sporozoa: Plasmodium vivax - Pathogen vivax; Plasmodium malariae - A four-day malaria pathogen; Plasmodium falciparum - The causative agent of malaria tropica; Plasmodium ovale - Malaria parasite Oval (a three-day type).
The life cycle of malaria parasites of man consists of:
- sexual development in the body type of female mosquitoes Anopheles (sporogony);
- asexual development in human liver cells (tissue schizogony), in erythrocytes (erythrocytic schizogony) and the formation of red blood cells in the sexual forms (gametocytes or gamont).
Sporogony
When tastes komarom genus Anopheles patient or malaria parasite in his stomach with blood gets gametocytes. After restructuring the nuclear apparatus makrogametotsit (female gametocyte) It turns into macrogamete, and from microgametocyte (male gametocyte) formed four - eight microgametes. In the stomach of the mosquito comes close merger- and microgamete, whereby a mobile zygote, as well as the maturation - ookineta.
Last penetrates through the wall of the stomach and under the outer shell turns into oocysts. When ambient temperature 25 ° C. This process continues for about two days (at a temperature below 16 ° C parasites die at earlier stages of development). With the maturation of oocytes in the nucleus it repeatedly divided, forming a plurality of sporozotov - elongated spindle-shaped cells of 11-15 m in length and 1 1,5 m width. Matured oocyst bursts, sporozoites are released and are carried with hemolymph throughout the body of a mosquito, concentrating in the salivary glands, after which the mosquito becomes infectious. Sporozoites in the salivary glands of the mosquito preserved until 1,5 of the month, One mosquito can infect more people.
Şizogonija
When an infected mosquito bites a human body fall sporozoites, which are carried by the blood and lymph flow in various organs and tissues. In human blood sporozoites may be no more 1 no. During this time they get into liver cells (gepatocitы), where the fabric, ectoglobular, the development cycle of the plasmodium.
Once inside the hepatocyte, circumsporozoite rounded, increases, the core of its shares - formed trophozoite, and then schizont. For 6-12 th day schizont fills the hepatocyte, pushing its core to the periphery. Such a large (to 60 m) schizont fabric by dividing a large number of splits (to several tens of thousands) small mononuclear merozoites.
Merozoites P. sickles penetrate into erythrocytes and they develop only (pre-erythrocytic cycle lasts for five to six days). Other types of malaria (P. vivax) pre-erythrocytic schizogony slower, ending in 7-8 days after infection, merozoites formed several times smaller and they are of two types: one embedded in the red blood cells and give rise erythrocyte schizogony, others - in hepatocytes, whereby tissue (paraэritrocitarnaя) schizogony is repeated.
Erythrocytic schizogony. Fabric merozoites penetrate the red blood cell, and most of them are converted in the asexual stage - trophozoites, and then schizonts, by dividing that produce erythrocytic merozoites. Red blood cells are destroyed, released merozoites penetrate into new red blood cells, and erythrocytic schizogony is repeated.
The erythrocytic cycle of malaria parasites are distinguished stage merozoites, koltsevydnoho trofozoyta (rings), amebovydnoho trofozoyta, schizont and morula.
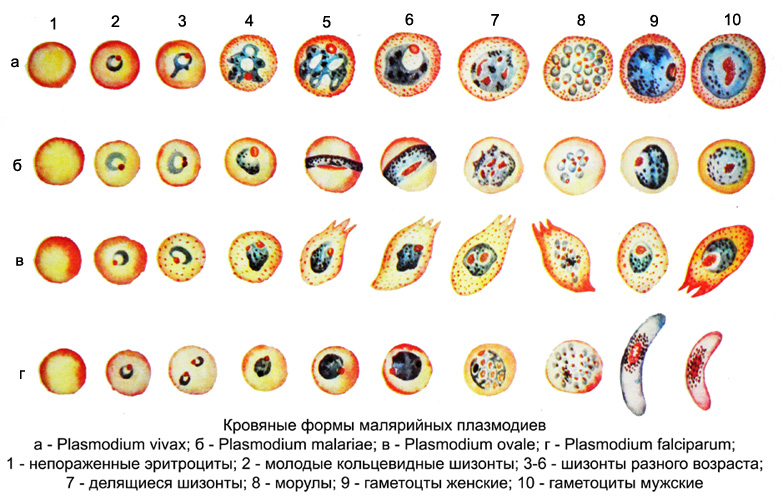
Young merozoite It is an oval clump of cytoplasm with one core, He rounded in the erythrocyte. As the conversion and merozoites in trophozoite it appears vacuole, surrounded by the cytoplasm in the form of the rim. The parasite takes the form of rings (duodenal). In stained preparations are visible narrow, sharply defined rim of the cytoplasm of the parasite, enveloping the vacuole, small and dense ruby red nucleus, cytoplasm is homogeneous, unpigmented.
In the future, the amount of cytoplasm increases, it accumulated pigment (breakdown product of hemoglobin) in the form of fine grains or sticks golden yellow, dark brown or black (depending on the pathogen). The young amoeboid trophozoite number of small grains of pigment, as it grows it increases.
When stopping the growth of trophozoite becomes an oval or circular shape (şizont) and it covers almost the entire erythrocyte. When dividing schizont produces two, four cores or more. After the process of division of the newly formed around each core segregated portion of the cytoplasm, whereby a morula, consisting of merozoites, between which is a compact cluster of pigment. After maturation of erythrocytes destroyed morula, merozoites are released into the blood and go (merulyatsiya). Some merozoites dies in blood plasma, and the rest incorporated into new red blood cells - repeated schizogony. Freed at merulyatsii pigment is absorbed by the macrophages.
In addition to asexual schizonts in the blood of the merozoites are formed from germ cells - gametocitы (gamonts), long time which may circulate in the blood, and if swallowed transporter give rise sporogony. Gametocitы P. sickles curved, crescent-shaped; in other types of parasites it is round or oval. The cytoplasm contains a considerable amount of gametocytes pigment, grains are larger, than schizont. Pigment in gametocytes P. vivax, P. malariae, P. oval is more evenly distributed, than schizonts, and in P. sickles it is concentrated in the central part of the female and in the middle third - in the men's gametoditah.
In the blood of newly diagnosed later identified the gametocytes, than schizonts: at three-four-malaria - the second and third attack, when Tropical - 7-10 days after the discovery of annular trophozoites.
Seizures occur in a patient during the mass division parasites and release them into the blood, so the intervals between attacks determine the duration of the cycle of erythrocytic schizogony: in P. malariae - 72 no (attacks in two days), in P. vivax, P. oval, P. sickles - 48 no (seizures a day). It is also possible misuse pristupov- alternating double, triple attacks, due to the formation of additional generations by lagging or ahead in the development of the main parasites generation.
In different phases of attack in the patient's blood found different age forms of the parasite. So, during the chills and fever decays erythrocyte schizonts (Morulem) and the release of merozoites. At high body temperature merozoites into erythrocytes introduced, turning into a ring-shaped trophozoites.
By reducing the temperature of the body is dominated by amoeboid trophozoites (with the formation of pseudopodia); during apyrexia - subadult and adult schizonts; in hours, preceding chills and fever - dividing schizonts.
In addition to these forms of lead generation at different stages of the parasite found additional generation. As a result, the patient's blood can be detected three or four age parasites and forms a. The exception is tropical malaria, in which there are only annular trophozoites (Further development occurs in internal organs).
Only in severe cases of falciparum malaria in peripheral blood can detect more mature schizonts (up to the morula). In P. vivax, P. oval, P. malariae all asexual development cycle takes place in the red blood cells. Their gametocytes detected in peripheral blood in all stages of development, and in P. sickles - Only mature, characteristic crescent-shaped (less mature gametocytes are located in the internal organs).
When fresh malaria parasites detected in the blood of patients during the first attack, sometimes for a day or two before or after the fever, in the case of relapse - the first time the body temperature rises (in some patients with recurrent increase in the number of parasites may be accompanied by fever).
At high body temperature, due to malaria, in the patient's blood parasites are detected continuously. An exception may be only the first attack of the disease (particularly falciparum malaria), that rarely occurs in such a small quantity of parasites, that during the study they were not detected. The absence of parasites in the blood during the second study during the fever indicates other disease.
Malaria parasites can be found in parasite (the primary carrier and relapses).
The undisputed evidence of malaria It is the detection of Plasmodium falciparum in the blood. The easiest, accessible and informative method of diagnostics - microscopic examination of smears and particularly thick drops of blood, because for the same amount of time with this method it is studied in 30-50 times more blood, than in the smear. However, it should be taken into account, in a thick drop parasites deformed, so they are harder to detect, than in the smear.
